Abstract
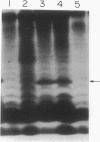
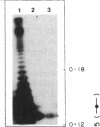
Phosphorylation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from a psychrotrophic bacterium, Pseudomonas syringae, from Antarctica was studied by using sucrose gradient-separated membrane fractions. The bacterium was found to possess an LPS kinase which could phosphorylate more LPS postsynthetically at higher temperatures. The phosphorylation was low at a lower temperature and was also found to occur in vivo. After phosphorylation of LPS in vitro, it was found that the major part of the radioactivity (> 85%) was associated with the core oligosaccharide region of the LPS. The phosphate groups of this region are probably involved in the binding of metal ions, which could be removed by EDTA. The cells grown at the lower temperature probably contained fewer divalent cations because of the smaller amount of phosphate and thereby were more sensitive to EDTA. The cells were also more sensitive to cationic antibiotics at the lower temperature. A possible role of this differential phosphorylation of LPS in modulating the function of the outer membrane as a permeability barrier in the psychrotroph is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhagya Lakshmi S. K., Bhat U. R., Wartenberg K., Schlecht S., Mayer H. Temperature-dependent incorporation of 4-amino-L-arabinose in lipid A of distinct gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Aug;51(3):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90417-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Galanos C. Isolation, purification, and chemical analysis of the lipopolysaccharide and lipid A of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus NCTC 10305. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(2):233–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Watkins W. M. Low magnesium and phospholipid content of cell wals of Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant to polymyxin. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1360–1361. doi: 10.1038/2271360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I., Ball P. Transport of antibiotics into bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1982;23:183–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60338-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewry D. T., Lomax J. A., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. Studies of lipid A fractions from the lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas alcaligenes. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):563–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1330563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGON R. G., CARSON K. J. LYSIS OF CELL WALLS AND INTACT CELLS OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA BY ETHYLENEDIAMINE TETRAACETIC ACID AND BY LYSOZYME. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:193–201. doi: 10.1139/m65-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., HsuChen C. C., Sud I. J. Basis for the selectivity of action of the polymyxin antibiotics on cell membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):480–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris F. G., Beveridge T. J. Site specificity of metallic ion binding in Escherichia coli K-12 lipopolysaccharide. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Jan;32(1):52–55. doi: 10.1139/m86-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton R. Y., Raetz C. R. Lipid A 4'-kinase from Escherichia coli: enzyme assay and preparation of 4'-32P-labeled probes of high specific radioactivity. Methods Enzymol. 1992;209:466–475. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)09057-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton D., Riley D. A. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):727–733. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagannadham M. V., Rao V. J., Shivaji S. The major carotenoid pigment of a psychrotrophic Micrococcus roseus strain: purification, structure, and interaction with synthetic membranes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7911–7917. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7911-7917.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Reske K., Jann K. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides. Analysis of polysaccharide chain lengths by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labischinski H., Barnickel G., Bradaczek H., Naumann D., Rietschel E. T., Giesbrecht P. High state of order of isolated bacterial lipopolysaccharide and its possible contribution to the permeation barrier property of the outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):9–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.9-20.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Release of lipopolysaccharide by EDTA treatment of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsby-Baltzer I., Gemski P., Alving C. R. Heterogeneity of lipid A: comparison of lipid A types from different gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):900–904. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.900-904.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClare C. W. An accurate and convenient organic phosphorus assay. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):527–530. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura T., Mizushima S. Separation by density gradient centrifugation of two types of membranes from spheroplast membrane of Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 3;150(1):159–161. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Rick P. D. Size heterogeneity of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides in outer membranes and culture supernatant membrane fragments. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):630–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.630-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. F., Wray V., Lehmann V. A 31P-nuclear-magnetic-resonance study of the phosphate groups in lipopolysaccharide and lipid A from Salmonella. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 15;81(1):193–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. Biosynthesis of Salmonella lipopolysaccharide. The in vitro transfer of phosphate to the heptose moiety of the core. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Alteration of susceptibility to EDTA, polymyxin B and gentamicin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by divalent cation regulation of outer membrane protein H1. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Feb;129(2):509–517. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-2-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Site of synthesis of lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3973–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. T., Kloser A. W., Schnaitman C. A., Stein M. A., Gottesman S., Gibson B. W. Role of the rfaG and rfaP genes in determining the lipopolysaccharide core structure and cell surface properties of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2525–2538. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2525-2538.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray M. K., Devi K. U., Kumar G. S., Shivaji S. Extracellular protease from the antarctic yeast Candida humicola. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1918–1923. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1918-1923.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray M. K., Sitaramamma T., Ghandhi S., Shivaji S. Occurrence and expression of cspA, a cold shock gene, in Antarctic psychrotrophic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994 Feb 1;116(1):55–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb06675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Kirikae T., Schade F. U., Ulmer A. J., Holst O., Brade H., Schmidt G., Mamat U., Grimmecke H. D., Kusumoto S. The chemical structure of bacterial endotoxin in relation to bioactivity. Immunobiology. 1993 Apr;187(3-5):169–190. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Markowitz O., Razin S. Thermal regulation of the fatty acid composition of lipopolysaccharides and phospholipids of Proteus mirabilis. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):445–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seydel U., Labischinski H., Kastowsky M., Brandenburg K. Phase behavior, supramolecular structure, and molecular conformation of lipopolysaccharide. Immunobiology. 1993 Apr;187(3-5):191–211. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80339-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivaji S., Rao N. S., Saisree L., Sheth V., Reddy G. S., Bhargava P. M. Isolation and identification of Pseudomonas spp. from Schirmacher Oasis, Antarctica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):767–770. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.3.767-770.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations sensitize enteric bacteria to antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Alphen L., Lugtenberg B., Rietschel E. T., Mombers C. Architecture of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K12. Phase transitions of the bacteriophage K3 receptor complex. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov;101(2):571–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb19752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G. 31P N.m.r. evidence for the presence of triphosphate residues in lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):833–835. doi: 10.1042/bj1990833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber H. W., Schlecht S., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T. Fatty acid in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella species grown at low temperature. Identification and position. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):167–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Putten J. P. Phase variation of lipopolysaccharide directs interconversion of invasive and immuno-resistant phenotypes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4043–4051. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]