Abstract
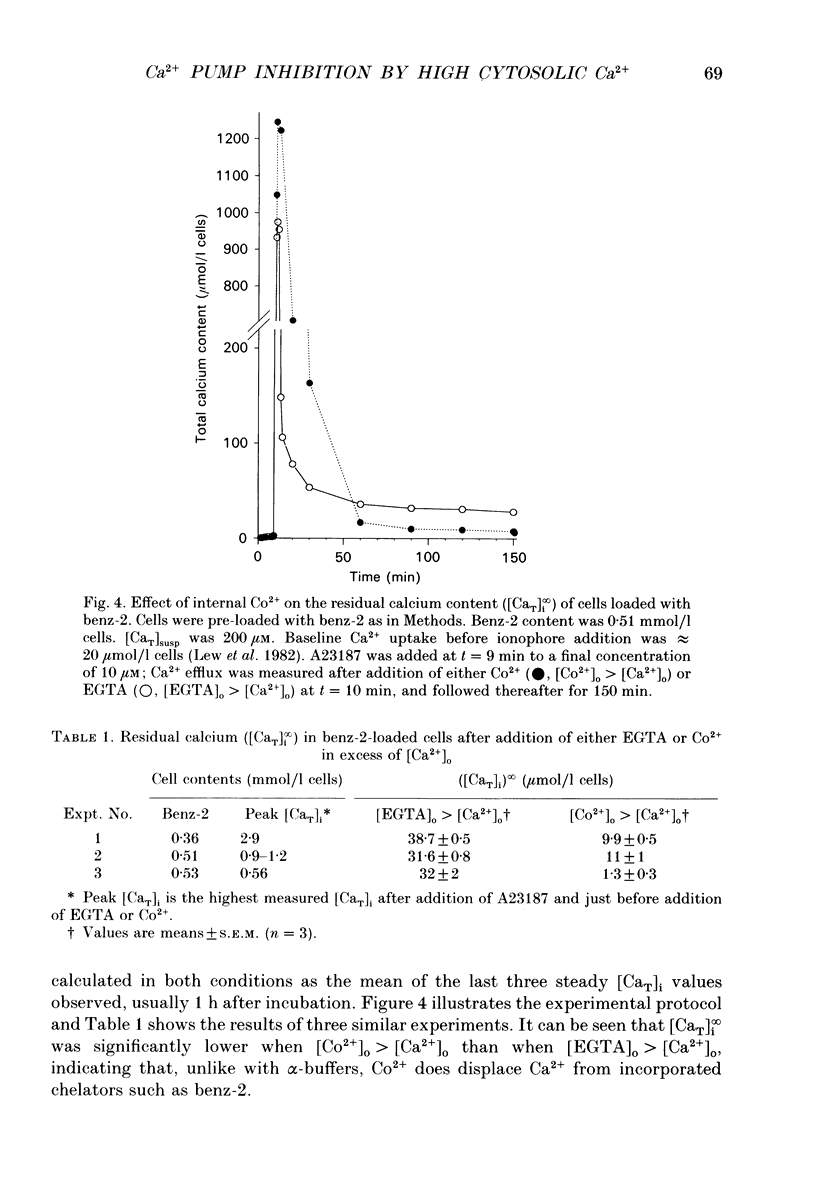
1. The inhibitory effect of high intracellular calcium on the saturated Ca2+ efflux through the Ca2+ pump (Vmax) was investigated in intact human red cells. Cells were loaded with Ca2+ by exposure to the calcium ionophore A23187, at different external Ca2+ concentrations ([Ca2+]o). Ca2+ extrusion by the pump was followed after either ionophore removal or Co2+ addition. 2. fifty per cent inhibition of Vmax was obtained with total intracellular calcium ([CaT]i) of approximately 3 mmol/l cells. For any given initial Ca2+ load, Vmax showed no tendency to increase as [CaT]i was progressively reduced during Ca2+ efflux. This suggests that the pump Vmax was determined by the magnitude of the initial [Ca2+]i. 3. To estimate [Ca2+]i from [CaT]i in Co(2+)-loaded cells, the possible competition between Co2+ and Ca2+ for the known cytoplasmic Ca2+ buffers (alpha-buffers) was investigated first. Comparison between Ca2+ efflux after either Co2+ exposure or ionophore wash-out showed that the efflux patterns were essentially identical, down to the lowest measurable [CaT]i. This indicates that Co2+ does not compete with Ca2+ for the alpha-buffers. Hence, since [Ca2+]i = alpha [CaT]i, and alpha approximately 0.15-0.35, the initial [Ca2+]i load for 50% Vmax inhibition was between 0.4 and 1.1 mM. 4. Ancillary new findings demonstrated that, unlike the situation with alpha-buffers, Co2+ displaced Ca2+ from the cell-incorporated calcium chelator benz-2, and that benz-2 incorporation had no effect on Co(2+)-exposed Ca2+ pump desaturation. This validates the use of benz-2 to study Ca2+ pump kinetics in intact cells.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dagher G., Amar M., Khefif A. Red blood cells Ca2+ pump is not altered in essential hypertension of humans and Kyoto rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 18;903(1):218–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagher G., Lew V. L. Maximal calcium extrusion capacity and stoichiometry of the human red cell calcium pump. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:569–586. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira H. G., Lew V. L. Use of ionophore A23187 to measure cytoplasmic Ca buffering and activation of the Ca pump by internal Ca. Nature. 1976 Jan 1;259(5538):47–49. doi: 10.1038/259047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P. W., Lew V. L. Magnesium buffering in intact human red blood cells measured using the ionophore A23187. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:13–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P., Lew V. L. Use of ionophore A23187 to measure and to control free and bound cytoplasmic Mg in intact red cells. Nature. 1977 May 26;267(5609):360–362. doi: 10.1038/267360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sancho J., Lew V. L. Detection and separation of human red cells with different calcium contents following uniform calcium permeabilization. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:505–522. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sancho J., Lew V. L. Properties of the residual calcium pools in human red cells exposed to transient calcium loads. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:541–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sancho J. Pyruvate prevents the ATP depletion caused by formaldehyde or calcium-chelator esters in the human red cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 28;813(1):148–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassner B., Luterbacher S., Schatzmann H. J., Wüthrich A. Dependence of the red blood cell calcium pump on the membrane potential. Cell Calcium. 1988 Apr;9(2):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(88)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosk-Kosicka D., Bzdega T. Activation of the erythrocyte Ca2+-ATPase by either self-association or interaction with calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18184–18189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosk-Kosicka D., Bzdega T., Johnson J. D. Fluorescence studies on calmodulin binding to erythrocyte Ca2(+)-ATPase in different oligomerization states. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 20;29(7):1875–1879. doi: 10.1021/bi00459a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosk-Kosicka D., Bzdega T., Wawrzynow A. Fluorescence energy transfer studies of purified erythrocyte Ca2+-ATPase. Ca2+-regulated activation by oligomerization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19495–19499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratje R. B., Garrahan P. J., Rega A. F. Two modes of inhibition of the Ca2+ pump in red cells by Ca2+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 27;816(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., García-Sancho J. Measurement and control of intracellular calcium in intact red cells. Methods Enzymol. 1989;173:100–112. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)73008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Hockaday A., Sepulveda M. I., Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V., Ortiz O. E., Bookchin R. M. Compartmentalization of sickle-cell calcium in endocytic inside-out vesicles. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):586–589. doi: 10.1038/315586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Tsien R. Y., Miner C., Bookchin R. M. Physiological [Ca2+]i level and pump-leak turnover in intact red cells measured using an incorporated Ca chelator. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):478–481. doi: 10.1038/298478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtner R., Wolf H. U. Phosphorylation of the isolated high-affinity (Ca2+ + Mg2+) ATPase of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 6;598(3):472–485. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Karlish S. J. Studies on the mechanism of regulation of the red-cell Ca2+ pump by calmodulin and ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 21;647(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90296-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Adunyah E. S., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Purified (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase of the erythrocyte membrane. Reconstitution and effect of calmodulin and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):395–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards D. E. Occlusion of cobalt ions within the phosphorylated forms of the Na+-K+ pump isolated from dog kidney. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:497–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff O., Foder B. Delayed activation of calcium pump during transient increases in cellular Ca2+ concentration and K+ conductance in hyperpolarizing human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 23;861(3):471–479. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90456-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff O. Kinetics of calmodulin-dependent (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase in plasma membranes and solubilized membranes from erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jun;209(1):72–80. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J., Rossi G. L. (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ )-activated membrane ATPases in human red cells and their possible relations to cation transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen L. O., Gomme J., Lew V. L. Uniform ionophore A23187 distribution and cytoplasmic calcium buffering in intact human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 22;692(3):431–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90394-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiffert T., Garcia-Sancho J., Lew V. L. Irreversible ATP depletion caused by low concentrations of formaldehyde and of calcium-chelator esters in intact human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 13;773(1):143–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90559-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


