Abstract
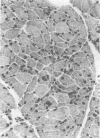
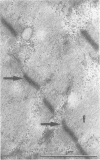
A 13 year old Greek girl with myasthenia gravis developed widespread muscle paralysis and atrophy after large parenteral doses of corticosteroids (5.48 g methylprednisolone). An electromyogram showed myopathy, creatine kinase concentration below normal, and a muscle biopsy showed severe myopathy with selective loss of the thick filaments (myosin). Previous reports of myopathy associated with large steroid doses have mostly been in patients who were also receiving non-depolarising neuromuscular blocking drugs. This patient is unique in that severe myopathy was associated with neuromuscular blockade caused by antibodies to acetylcholine receptors. The findings in this case suggest that high doses of parenteral corticosteroids in patients with myasthenia gravis may be dangerous and that blocking the neuromuscular junction with drugs or antibodies predisposes skeletal muscles to the injurious effects of corticosteroids.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afifi A. K., Bergman R. A. Steroid myopathy. A study of the evolution of the muscle lesion in rabbits. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1969 Feb;124(2):66–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastaglia F. L. Adverse effects of drugs on muscle. Drugs. 1982 Oct;24(4):304–321. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198224040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau G., Karpati G., Carpenter S., Soza M., Prescott S., Holland P. Glucocorticoid excess induces preferential depletion of myosin in denervated skeletal muscle fibers. Muscle Nerve. 1987 Jun;10(5):428–438. doi: 10.1002/mus.880100509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher J. H., Shafiq S. A., Schutta H. S. Acute myopathy with selective lysis of myosin filaments. Neurology. 1979 Jan;29(1):100–106. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.1.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Pennington R. J. Binding of dexamethasone and cortisol to cytosol receptors in rat extensor digitorum longus and soleus muscles. Exp Neurol. 1977 Nov;57(2):342–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(77)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Pennington R. J. The effect of cortisone on protein breakdown and synthesis in rat skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1977 Jan;6(3):159–169. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(77)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Marle W., Woods K. L. Acute hydrocortisone myopathy. Br Med J. 1980 Jul 26;281(6235):271–272. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6235.271-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]