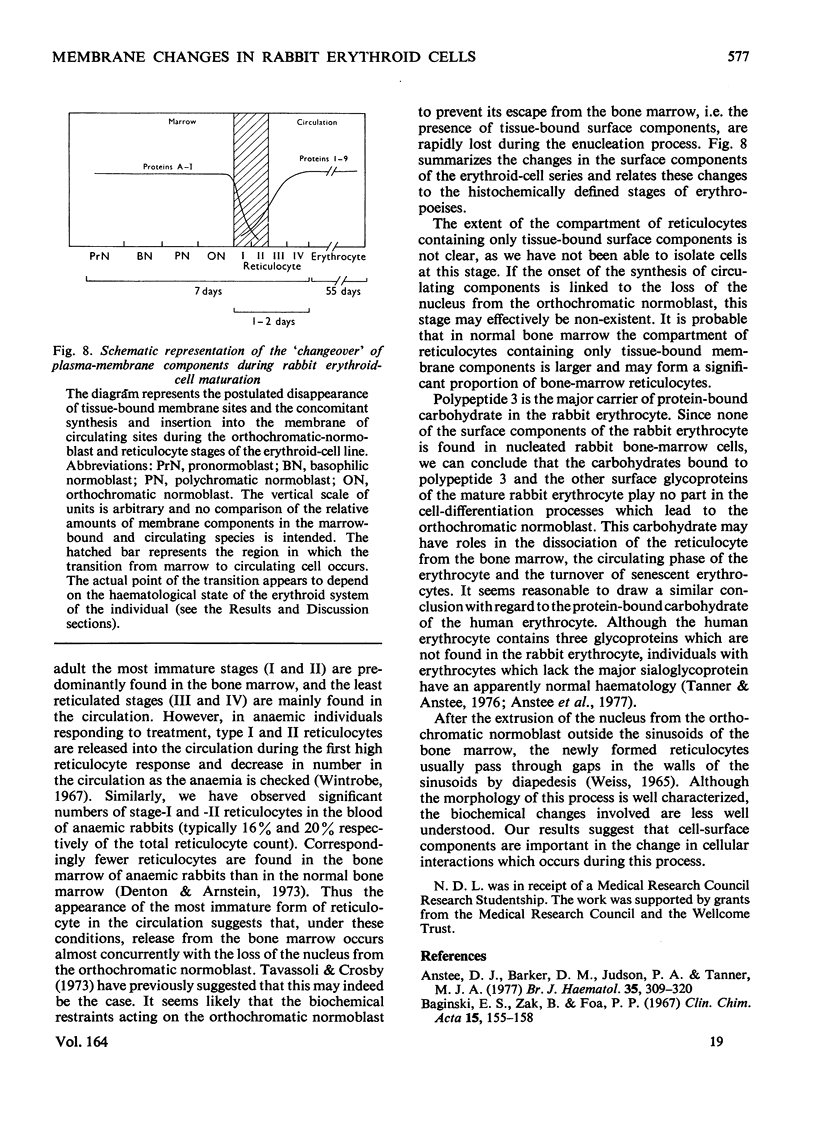
Abstract
The membrane components of rabbit bone-marrow-bound erythroid cells were characterized and compared with those of circulating rabbit erythroid cells. By the criteria of sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, radioiodination with lactoperoxidase and binding of radioiodinated lectins, the two circulating forms of erythroid cells (the reticulocyte and erythrocyte) have the same surface components. In contrast, bone-marrow-bound nucleated erythroid cells have a unique set of membrane surface components which are completely different from those found on circulating cells. Of the ten Coomassie-Blue-staining proteins present in nucleated erythroid-cell plasma-membrane preparations, eight are accessible at the extracellular surface, and all of these are lectin-binding glycoproteins. Bone-marrow erythroid cells separated according to age by velocity sedimentation were also studied. The changeover in surface components occurs after the last nucleated stage of the erythroid cells (the orthochromatic normoblast). We discuss the alterations in membrane surface components observed during the differentiation of the erythroid-cell series in relation to the transition from bone-marrow-bound to circulating forms of these cells. We suggest that the change in membrane surface components may be linked to the loss of the nucleus from the normoblast and the entry of the erythroid cell into the circulation.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anstee D. J., Barker D. M., Judson P. A., Tanner M. J. Inherited sialoglycoprotein deficiencies in human erythrocytes of type En[a-]. Br J Haematol. 1977 Feb;35(2):309–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfield A., Goldberg D. M. Inhibition of the nucleotidase effect of alkaline phosphatase by beta-glycerophosphate. Nature. 1968 Jul 6;219(5149):73–75. doi: 10.1038/219073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer D. H., Jenkins R. E., Tanner M. J. The organization of the major protein of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):531–534. doi: 10.1042/bj1370531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. Membrane proteins related to anion permeability of human red blood cells. I. Localization of disulfonic stilbene binding sites in proteins involved in permeation. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(3):207–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01870088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L. Covalent labeling of membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 29;415(4):379–410. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton M. J., Arnstein H. R. Characterization of developing adult mammalian erythroid cells separated by velocity sedimentation. Br J Haematol. 1973 Jan;24(1):7–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb05722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diepenhorst P., Sprokholt R., Prins H. K. Removal of leukocytes from whole blood and erythrocyte suspensions by filtration through cotton wool. I. Filtration technique. Vox Sang. 1972;23(4):308–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1972.tb03465.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDEN C. Glutamic dehydrogenase. II. The effect of various nucleotides on the association-dissociation and kinetic properties. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):815–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlmann M., Lafleur L., Marceau N. Major changes in surface membrane proteins during erythropoiesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):322–327. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80331-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch P. A., Gardner F. H., Gartrell J. E., Jr, Carter J. R., Jr Biogenesis of erythrocyte membrane proteins. In vitro studies with rabbit reticulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 21;389(1):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Small B. Membrane proteins synthesized by rabbit reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):51–64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Phillips R. A. Separation of cells by velocity sedimentation. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Jun;73(3):191–201. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseroff A. R., Robbins P. W., Burger M. M. The cell surface membrane: biochemical aspects and biophysical probes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:647–682. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.003243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. Molecular biology of cellular membranes with applications to immunology. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):1–66. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner M. J., Anstee D. J. A method for the direct demonstration of the lectin-binding components of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):265–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1530265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavassoli M., Crosby W. H. Fate of the nucleus of the marrow erythroblast. Science. 1973 Mar 2;179(4076):912–913. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4076.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. R., Gutfreund H. The kinetics of the reaction of nitrophenyl phosphates with alkaline phosphatase from Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):455–460. doi: 10.1042/bj1060455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. The structure of bone marrow. Functional interrelationships of vascular and hematopoietic compartments in experimental hemolytic anemia: an electron microscopic study. J Morphol. 1965 Nov;117(3):467–537. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051170308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


