Abstract
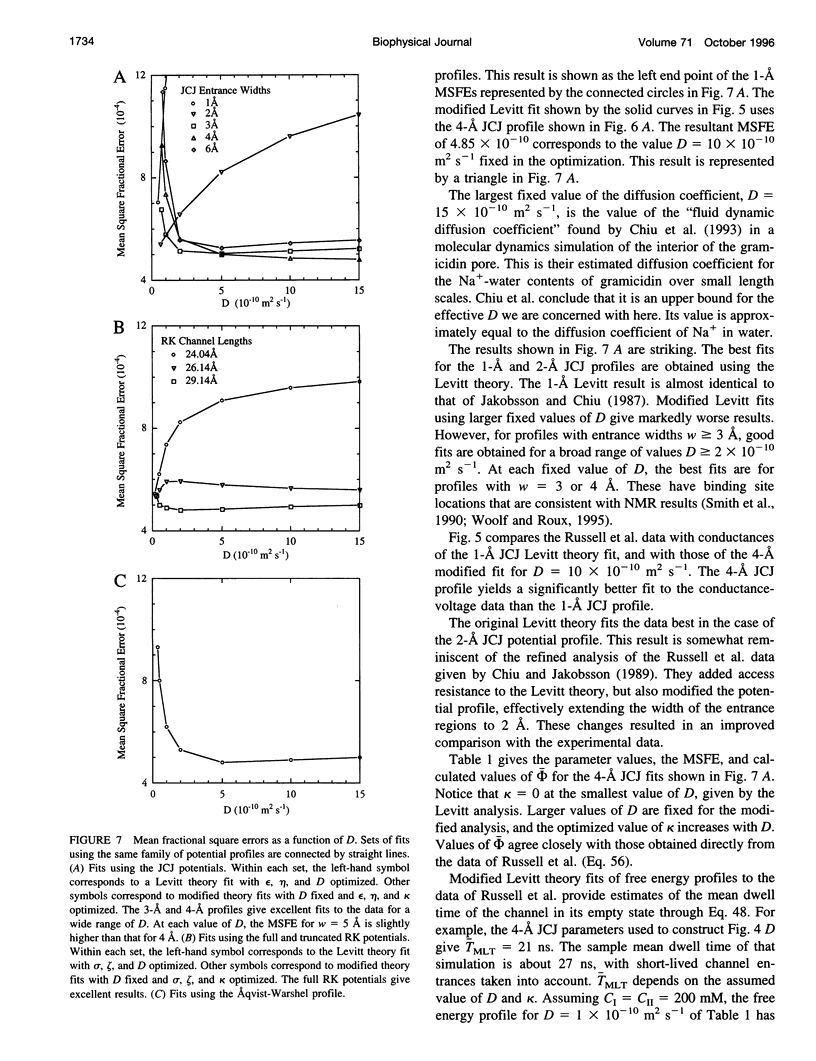
We have constructed a theory for diffusion through the pore of a single-ion channel by taking a limit of a random walk around a cycle of states. Similar to Levitt's theory of single-ion diffusion, one obtains boundary conditions for the Nernst-Planck equation that guarantee that the pore is occupied by at most one ion. Two of the terms in the boundary conditions are identical to those given by Levitt. However, the construction gives rise to a third term not found in Levitt's theory. With this term, the channel spends exponentially distributed intervals in the empty state. Ion sample paths have been simulated to help visualize trajectories near the channel entrances, with and without the new term. We use the modified Levitt theory to fit several potential profiles to the conductance data of Russell et al. In particular, we have analyzed the profile for Na+ in gramicidin calculated by Roux and Karplus. The peak-to-peak amplitude of their result must be reduced to at most 35% of its original value to fit the data. But with this reduction, excellent fits are obtained.
Full text
PDF


















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. Interfacial polarization effects on single-channel current measurements. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):135–146. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84415-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S., Koeppe R. E., 2nd Molecular determinants of channel function. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S89–158. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aqvist J., Warshel A. Energetics of ion permeation through membrane channels. Solvation of Na+ by gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1989 Jul;56(1):171–182. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82662-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. W., Jakobsson E. Stochastic theory of singly occupied ion channels. II. Effects of access resistance and potential gradients extending into the bath. Biophys J. 1989 Jan;55(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82786-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. W., Novotny J. A., Jakobsson E. The nature of ion and water barrier crossings in a simulated ion channel. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):98–109. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81344-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. E., Gates P. Y., Eisenberg R. S. Diffusion theory and discrete rate constants in ion permeation. J Membr Biol. 1988 Dec;106(2):95–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01871391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K., Jakobsson E., Wolynes P. The theory of ion transport through membrane channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;46(1):51–96. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani J. A., Levitt D. G. Diffusion and kinetic approaches to describe permeation in ionic channels. J Theor Biol. 1990 Oct 7;146(3):289–301. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80740-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elber R., Chen D. P., Rojewska D., Eisenberg R. Sodium in gramicidin: an example of a permion. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):906–924. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80267-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber S. S. Symmetry and asymmetry of permeation through toxin-modified Na+ channels. Biophys J. 1988 Nov;54(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83014-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Schwarz W. Potassium channels as multi-ion single-file pores. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Oct;72(4):409–442. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson E., Chiu S. W. Stochastic theory of ion movement in channels with single-ion occupancy. Application to sodium permeation of gramicidin channels. Biophys J. 1987 Jul;52(1):33–45. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83186-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. C. Electrostatic modeling of ion pores. Energy barriers and electric field profiles. Biophys J. 1982 Aug;39(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84503-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Interpretation of biological ion channel flux data--reaction-rate versus continuum theory. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:29–57. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Ion transport through pores: a rate-theory analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):423–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill P., Schumaker M. F. Orientation independence of single-vacancy and single-ion permeability ratios. Biophys J. 1995 Jul;69(1):84–93. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79878-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., Prod'hom B., Karplus M. Ion transport in the gramicidin channel: molecular dynamics study of single and double occupancy. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):876–892. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80264-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. W., Weiss L. B., Navetta F. I., Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Andersen O. S. Single-channel studies on linear gramicidins with altered amino acid side chains. Effects of altering the polarity of the side chain at position 1 in gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):673–686. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83694-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Thomas D. E., Atkins A. R., Separovic F., Cornell B. A. Solid-state 13C-NMR studies of the effects of sodium ions on the gramicidin A ion channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 24;1026(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90059-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


