Abstract
Tyrosine as a solid, but not in solution, caused human erythrocyte haemolysis. Haemolysis was increased with higher tyrosine concentrations and extended incubation times; it was greater at 37degrees than 4degreesC, and decreased by higher erythrocyte concentrations. Titration of phenolic groups on the surface of di-iodotyrosine crystals altered the extent of di-iodotyrosine-induced haemolysis. Haemolysis induced by tyrosine was inhibited by polyethylene glycol (mol.wt. 6000 or 20000) in a competitive fashion; polyoxyethylene/polyoxypropylene non-ionic detergents, polyvinylpyrrolidone (mol.wt. 40000 or 360000), 0.25--1.0M-NaC1, 0.25--1.0 M-KC1 and 0.25 M-NaSCN also inhibited haemolysis. H+-ion donation from the phenolic groups of tyrosine is suggested as part of the mechanism of haemolysis. Non-ionic detergents may inhibit tyrosine-crystal-induced haemolysis by binding the phenolic groups at the surface of the crystal.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ELWORTHY P. H., MACFARLANE C. B. FURTHER ASPECTS OF THE PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY OF SOME NON-IONIC DETERGENTS. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1965 Mar;17:129–143. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1965.tb07632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
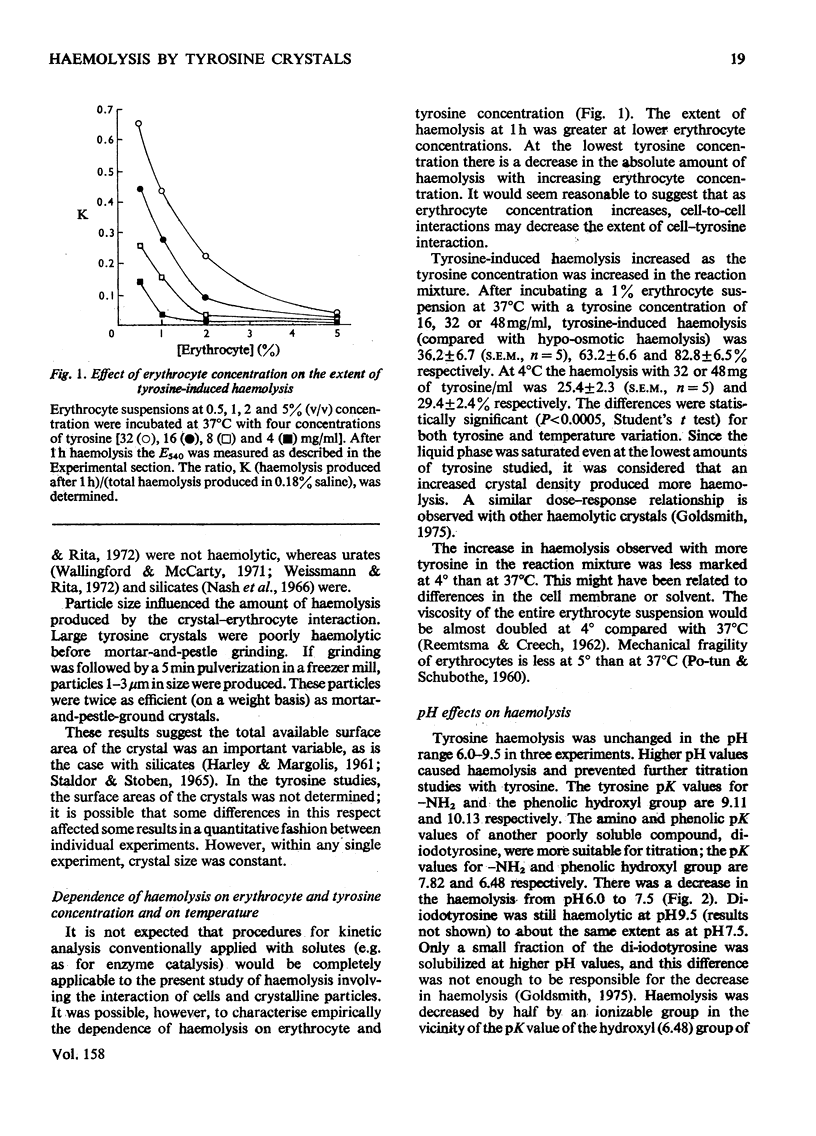
- Goldsmith L. A. Hemolysis and lysosomal activation by solid state tyrosine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 19;64(2):558–565. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90358-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARLEY J. D., MARGOLIS J. Haemolytic activity of colloidal silica. Nature. 1961 Mar 25;189:1010–1011. doi: 10.1038/1891010a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harington J. S., Miller K., Macnab G. Hemolysis by asbestos. Environ Res. 1971 Apr;4(2):95–117. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(71)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. J., Anderson R. A., Watson T. R. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of interactions between cetomacrogol and phenol. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;23(10):786–793. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. V., Jr, Thompson E. B. Radioactive assay for tyrosine aminotransferase. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jun;47(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T., Allison A. C., Harington J. S. Physico-chemical properties of silica in relation to its toxicity. Nature. 1966 Apr 16;210(5033):259–261. doi: 10.1038/210259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson G. J. Lipid composition of erythrocytes in various mammalian species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEMTSMA K., CREECH O., Jr Viscosity studies of blood, plasma, and plasma substitutes. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1962 Nov;44:674–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer R. J., Bunescu G., Baden V. Interactions of mineral fiber surfaces with cells in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 20;172(23):759–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer R. J., Pundsack F. L. Asbestos hemolysis. Environ Res. 1970 Jan;3(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(70)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallingford W. R., McCarty D. J. Differential membranolytic effects of microcrystalline sodium urate and calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):100–112. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Rita G. A. Molecular basis of gouty inflammation: interaction of monosodium urate crystals with lysosomes and liposomes. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 6;240(101):167–172. doi: 10.1038/newbio240167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


