Abstract
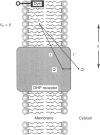
1. Voltage changes and intramembrane charge movements in the transverse tubule membranes (T-system) of frog fast twitch muscle fibres were compared using the potentiometric dye WW-375 and a Vaseline-gap voltage clamp. As shown previously, the potentiometric dye reports a dynamic surface potential change that occurs on the myoplasmic face of the T-system membranes when the macroscopic potential applied across the surface membrane exceeds the mechanical threshold (about -60 mV). 2. The voltage dependence of the extra surface potential change and charge movement were found to be similar. Both activated with a sigmoid voltage dependence centred around -35 to -40 mV, and saturated at voltages above 0 mV. Both processes inactivated upon sustained depolarization, with a mid-point for inactivation of -40 mV. 3. Pharmacological agents which alter charge movement and excitation-contraction (E-C) coupling altered the non-linear surface potential change in a parallel manner. Perchlorate, which potentiates charge movement and E-C coupling, slowed the activation and deactivation of both charge movement and the non-linear surface potential change at voltages above -40 mV, and shifted the voltage dependence of both processes by 13 14 mV to more negative voltages. Dantrolene, which depresses charge movement and E-C coupling, shifted the voltage dependence of both processes to more positive voltages. Nifedipine, which suppresses charge movement and E-C coupling, reduced the magnitude of both charge movement and the non-linear surface potential change. 4. The non-linear surface potential change remained after the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) was depleted of Ca2+, suggesting that it is not a consequence of Ca2+ release. 5. These results suggest that the non-linear surface potential change is closely associated with movements of the voltage sensor (dihydropyridine (DHP) receptor) that control E-C coupling and/or signal transduction across the triadic junction. We propose that the movement of charged intramembrane domains of the DHP receptor which generate charge movement drive a subsequent movement of charged intracellular molecular domains that move within about 1 nm of the T-system membrane to generate a measurable change in surface charge. For example, the postulated mobile surface charges could be on an intracellular domain of the voltage sensor or closely associated protein, or could be a charged molecular domain of a protein that associates/dissociates with T-system membrane or DHP receptor during E-C coupling.
Full text
PDF





















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F. Charge movement and mechanical repriming in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):361–388. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Heiny J. A., Vergara J. Inward rectification in the transverse tubular system of frog skeletal muscle studied with potentiometric dyes. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:269–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block B. A., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P., Franzini-Armstrong C. Structural evidence for direct interaction between the molecular components of the transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum junction in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2587–2600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Fitts R., Pizarro G., Ríos E. Voltage sensors of the frog skeletal muscle membrane require calcium to function in excitation-contraction coupling. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:475–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Rios E. Intramembrane charge movement in frog skeletal muscle fibres. Properties of charge 2. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:489–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Hui C. S. Membrane capacitance in frog cut twitch fibers mounted in a double vaseline-gap chamber. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Aug;96(2):225–256. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. A non-linear voltage dependent charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):245–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis K. O., Carpenter J. F. Studies on the mechanism of action of dantrolene sodium. A skeletal muscle relaxant. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;275(1):83–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00505069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmeyer D., Zöllner P., Pohl B., Melzer W. Calcium current reactivation after flash photolysis of nifedipine in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1995 Aug 15;487(1):51–56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Ríos E. Perchlorate enhances transmission in skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Sep;102(3):373–421. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Potassium contractures in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiny J. A., Jong D. S. A nonlinear electrostatic potential change in the T-system of skeletal muscle detected under passive recording conditions using potentiometric dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jan;95(1):147–175. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiny J. A., Valle J. R., Bryant S. H. Optical evidence for a chloride conductance in the T-system of frog skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1990 May;416(3):288–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00392065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Campbell D. T. An improved vaseline gap voltage clamp for skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):265–293. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. 'Off' tails of intramembrane charge movements in frog skeletal muscle in perchlorate-containing solutions. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:491–509. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Kinetic separation of charge movement components in intact frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1994 Dec 1;481(Pt 2):357–369. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Voltage-dependent block of charge movement components by nifedipine in frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Sep;96(3):535–557. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.3.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S. Pharmacological studies of charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:509–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong D. S., Pape P. C., Chandler W. K. Effect of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium depletion on intramembranous charge movement in frog cut muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Oct;106(4):659–704. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Schneider M. F. Increased optical transparency associated with excitation--contraction coupling in voltage-clamped cut skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1977 Feb 10;265(5594):556–560. doi: 10.1038/265556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Schümperli R. A., Szücs G. Comparison of birefringence signals and calcium transients in voltage-clamped cut skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:579–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Herrmann-Frank A., Lüttgau H. C. The role of Ca2+ ions in excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal muscle fibres. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 May 8;1241(1):59–116. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(94)00014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K. G., Bryant S. H. The mechanism of action of dantrolene sodium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Apr;201(1):138–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape P. C., Jong D. S., Chandler W. K. Calcium release and its voltage dependence in frog cut muscle fibers equilibrated with 20 mM EGTA. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Aug;106(2):259–336. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D. The sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules of the frog's sartorius. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):209–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro G., Csernoch L., Uribe I., Rodríguez M., Ríos E. The relationship between Q gamma and Ca release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1991 May;97(5):913–947. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.5.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakowski R. F. Immobilization of membrane charge in frog skeletal muscle by prolonged depolarization. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:129–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rios E., Brum G. Involvement of dihydropyridine receptors in excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):717–720. doi: 10.1038/325717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Pizarro G. Voltage sensor of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jul;71(3):849–908. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.3.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirokova N., Pizarro G., Ríos E. A damped oscillation in the intramembranous charge movement and calcium release flux of frog skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Sep;104(3):449–476. doi: 10.1085/jgp.104.3.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Beam K. G., Powell J. A., Numa S. Restoration of excitation-contraction coupling and slow calcium current in dysgenic muscle by dihydropyridine receptor complementary DNA. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):134–139. doi: 10.1038/336134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano M., el-Hayek R., Ikemoto N. Effects of perchlorate on depolarization-induced conformational changes in the junctional foot protein and Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1995 Oct 3;34(39):12584–12589. doi: 10.1021/bi00039a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Hayek R., Parness J., Valdivia H. H., Coronado R., Hogan K. Dantrolene and azumolene inhibit [3H]PN200-110 binding to porcine skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):894–900. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91281-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]