Abstract
Background—Patients on total parenteral nutrition have an increased risk of developing gallstones because of gall bladder hypomotility. High dose amino acids may prevent biliary stasis by stimulating gall bladder emptying. Aims—To investigate whether intravenous amino acids also influence antroduodenal motility. Methods—Eight healthy volunteers received, on three separate occasions, intravenous saline (control), low dose amino acids (LDA), or high dose amino acids (HDA). Antroduodenal motility was recorded by perfusion manometry and duodenocaecal transit time (DCTT) using the lactulose breath hydrogen test. Results—DCTT was significantly prolonged during LDA and HDA treatment compared with control. The interdigestive motor pattern was maintained and migrating motor complex (MMC) cycle length was significantly reduced during HDA compared with control and LDA due to a significant reduction in phase II duration. Significantly fewer phase IIIs originated in the gastric antrum during LDA and HDA compared with control. Duodenal phase II motility index was significantly reduced during HDA, but not during LDA, compared with control. Conclusions—Separate intravenous infusion of high doses of amino acids in healthy volunteers: (1) modulates interdigestive antroduodenal motility; (2) shortens MMC cycle length due to a reduced duration of phase II with a lower contractile incidence both in the antrum and duodenum (phase I remains unchanged whereas the effect on phase III is diverse: in the antrum phase III is suppressed and in the duodenum the frequency is increased); and (3) prolongs interdigestive DCTT.
Keywords: amino acids; antroduodenal motility; small bowel transit time; total parenteral nutrition
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (115.3 KB).
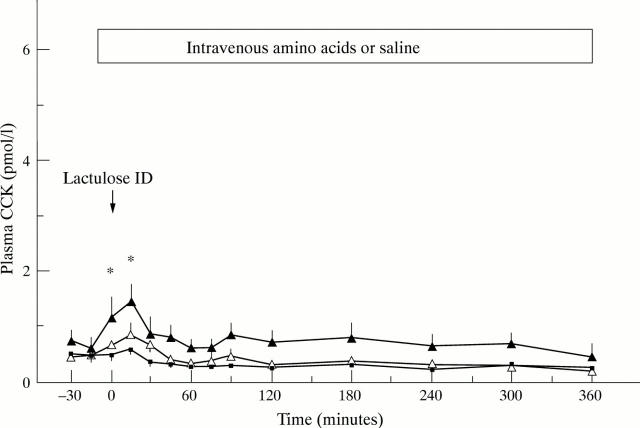
Figure 1 .
Plasma CCK concentrations (mean (SEM)) during LDA (open triangles) or HDA (closed triangles) compared with control (squares). *Significantly different (p<0.05) compared with basal.
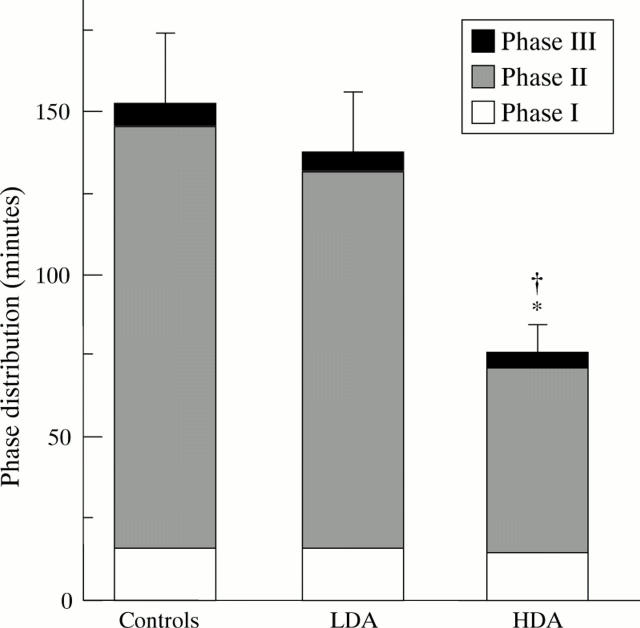
Figure 2 .
Data of mean MMC cycle length and its phase distribution (mean (SEM)) during LDA or HDA compared with control. *Significant (p<0.05) difference compared with control; †significant (p<0.05) difference between LDA and HDA.
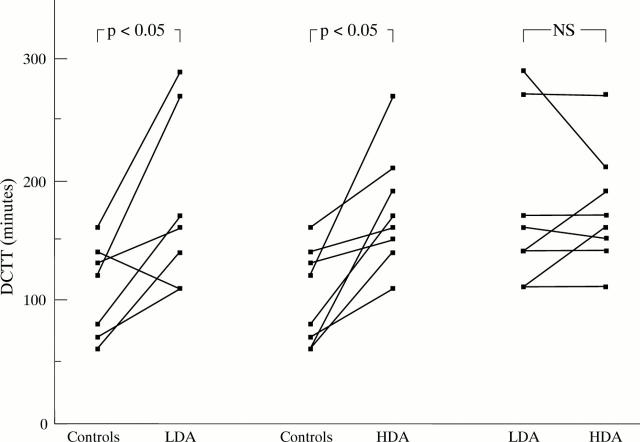
Figure 3 .
Individual data of duodenocaecal transit time (DCTT) during LDA or HDA compared with control.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bond J. H., Jr, Levitt M. D., Prentiss R. Investigation of small bowel transit time in man utilizing pulmonary hydrogen (H2) measurements. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):546–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotti M., Barbara L. Interdigestive gastroduodenal motor activity in subjects with increased gastric acid secretion. Digestion. 1988;41(3):156–160. doi: 10.1159/000199768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursztein-De Myttenaere S., Gil K. M., Heymsfield S. B., Fürst P., Askanazi J., D'Attellis N., Elwyn D. H. Gastric emptying in humans: influence of different regimens of parenteral nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994 Aug;60(2):244–248. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/60.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cano N., Cicero F., Ranieri F., Martin J., di Costanzo J. Ultrasonographic study of gallbladder motility during total parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterology. 1986 Aug;91(2):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90562-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer S. Y., Masclee A. A., Lam W. F., Jansen J. B., Lamers C. B. Effect of intravenous glucose on intravenous amino acid-induced gallbladder contraction and CCK secretion. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Feb;39(2):268–274. doi: 10.1007/BF02090196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doty J. E., Pitt H. A., Porter-Fink V., DenBesten L. The effect of intravenous fat and total parenteral nutrition on biliary physiology. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1984 May-Jun;8(3):263–268. doi: 10.1177/0148607184008003263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doty J. E., Pitt H. A., Porter-Fink V., Denbesten L. Cholecystokinin prophylaxis of parenteral nutrition-induced gallbladder disease. Ann Surg. 1985 Jan;201(1):76–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelbroek M., Sun W. M., Horowitz M., Dent J., Smout A., Akkermans L. Stereospecific effects of intraduodenal tryptophan on pyloric and duodenal motility in humans. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994 Dec;29(12):1088–1095. doi: 10.3109/00365529409094893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga J. D. The effect of amino acids on intestinal smooth muscle related to their content in blood and tissue. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 3;67(1):91–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussaini S. H., Pereira S. P., Veysey M. J., Kennedy C., Jenkins P., Murphy G. M., Wass J. A., Dowling R. H. Roles of gall bladder emptying and intestinal transit in the pathogenesis of octreotide induced gall bladder stones. Gut. 1996 May;38(5):775–783. doi: 10.1136/gut.38.5.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg J. I., Maxwell V. Intravenous infusion of amino acids stimulates gastric acid secretion in man. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 5;298(1):27–29. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801052980106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. B., Lamers C. B. Radioimmunoassay of cholecystokinin in human tissue and plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jul 15;131(3):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katschinski M., Schirra J., Begliner C., Langbein S., Wank U., D'Amato M., Arnold R. Intestinal phase of human antro-pyloro-duodenal motility: cholinergic and CCK-mediated regulation. Eur J Clin Invest. 1996 Jul;26(7):574–583. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.1996.1790522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Borody T. J., Phillips S. F., Tucker R. L., Haddad A. C. Human interdigestive motility: variations in patterns from esophagus to colon. Gastroenterology. 1986 Aug;91(2):386–395. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90573-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlin P., Zinsmeister A., Phillips S. Relationship of motility to flow of contents in the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1982 Apr;82(4):701–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek J. W., Thor P., Domschke W. Effects of nitric oxide on antral motility and gastric emptying in humans. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995 Feb;7(2):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfertheiner P., Domínguez-Muñoz J. E. Effect of exogenous pancreatic enzymes on gastrointestinal and pancreatic hormone release and gastrointestinal motility. Digestion. 1993;54 (Suppl 2):15–20. doi: 10.1159/000201098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S. N., Heaton K. W. Intestinal transit, deoxycholic acid and the cholesterol saturation of bile--three inter-related factors. Gut. 1986 May;27(5):550–558. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.5.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArthur K. E., Isenberg J. I., Hogan D. L., Dreier S. J. Intravenous infusion of L-isomers of phenylalanine and tryptophan stimulate gastric acid secretion at physiologic plasma concentrations in normal subjects and after parietal cell vagotomy. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1254–1262. doi: 10.1172/JCI110875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing B., Bories C., Kunstlinger F., Bernier J. J. Does total parenteral nutrition induce gallbladder sludge formation and lithiasis? Gastroenterology. 1983 May;84(5 Pt 1):1012–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealon W. H., Upp J. R., Jr, Alexander R. W., Gomez G., Townsend C. M., Jr, Thompson J. C. Intravenous amino acids stimulate human gallbladder emptying and hormone release. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):G173–G178. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.2.G173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederau C., Sonnenberg A., Erckenbrecht J. Effects of intravenous infusion of amino acids, fat, or glucose on unstimulated pancreatic secretion in healthy humans. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 May;30(5):445–455. doi: 10.1007/BF01318177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I., Svenberg T., Hellström P. M., Theodorsson E., Hedenborg G., Modlin I. M. Pancreaticobiliary juice releases motilin during phase I of the migrating motor complex in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Jan;28(1):80–84. doi: 10.3109/00365529309096049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penagini R., Misiewicz J. J., Frost P. G. Effect of jejunal infusion of bile acids on small bowel transit and fasting jejunal motility in man. Gut. 1988 Jun;29(6):789–794. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.6.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pijl H., Koppeschaar H. P., Cohen A. F., Iestra J. A., Schoemaker H. C., Frölich M., Onkenhout W., Meinders A. E. Evidence for brain serotonin-mediated control of carbohydrate consumption in normal weight and obese humans. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1993 Sep;17(9):513–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt H. A., King W., 3rd, Mann L. L., Roslyn J. J., Berquist W. E., Ament M. E., DenBesten L. Increased risk of cholelithiasis with prolonged total parenteral nutrition. Am J Surg. 1983 Jan;145(1):106–112. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qvist N., Oster-Jørgensen E., Pedersen S. A., Rasmussen L., Hovendal C., Holst J. J. Increases in plasma motilin follow each episode of gallbladder emptying during the interdigestive period, and changes in serum bile acid concentration correlate to plasma motilin. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995 Feb;30(2):122–127. doi: 10.3109/00365529509093249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Membrilla A., Martínez V., Jiménez M., Goñalons E., Vergara P. Is nitric oxide the final mediator regulating the migrating myoelectric complex cycle? Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 1):G207–G214. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.268.2.G207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roslyn J. J., Pitt H. A., Mann L. L., Ament M. E., DenBesten L. Gallbladder disease in patients on long-term parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jan;84(1):148–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitzmann J. V., Pitt H. A., Steinborn P. A., Pasha Z. R., Sanders R. C. Cholecystokinin prevents parenteral nutrition induced biliary sludge in humans. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1990 Jan;170(1):25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snape W. J., Jr, Yoo S. Effect of amino acids on isolated colonic smooth muscle from the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Dec;235(3):690–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenberg T., Nilsson I., Samuelson K., Welbourn R. D. Studies on the causal relationship between gall-bladder emptying and motilin release in man. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1984;520:59–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vantrappen G., Janssens J., Peeters T. L., Bloom S. R., Christofides N. D., Hellemans J. Motilin and the interdigestive migrating motor complex in man. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Jul;24(7):497–500. doi: 10.1007/BF01489315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto O., Matsunaga Y., Haga N., Mizumoto A., Itoh Z. Inhibition of phase III activity by acidifying stomach in vagally denervated and innervated dogs with gastric pouches. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jun;106(6):1533–1541. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90407-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoli G., Ballinger A., Healy J., O'Donnell L. J., Clark M., Farthing M. J. Promotion of gallbladder emptying by intravenous aminoacids. Lancet. 1993 May 15;341(8855):1240–1241. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91146-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]