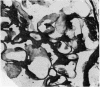Abstract
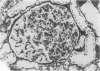
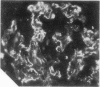
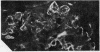
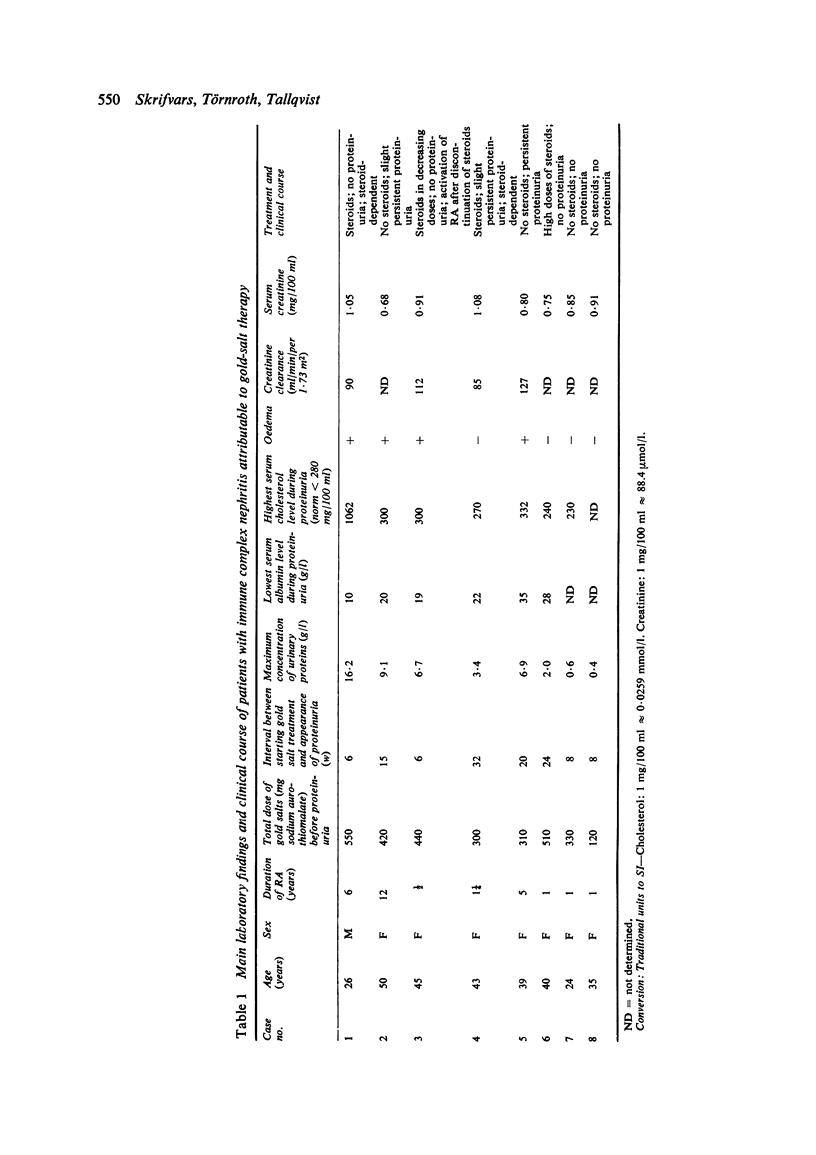
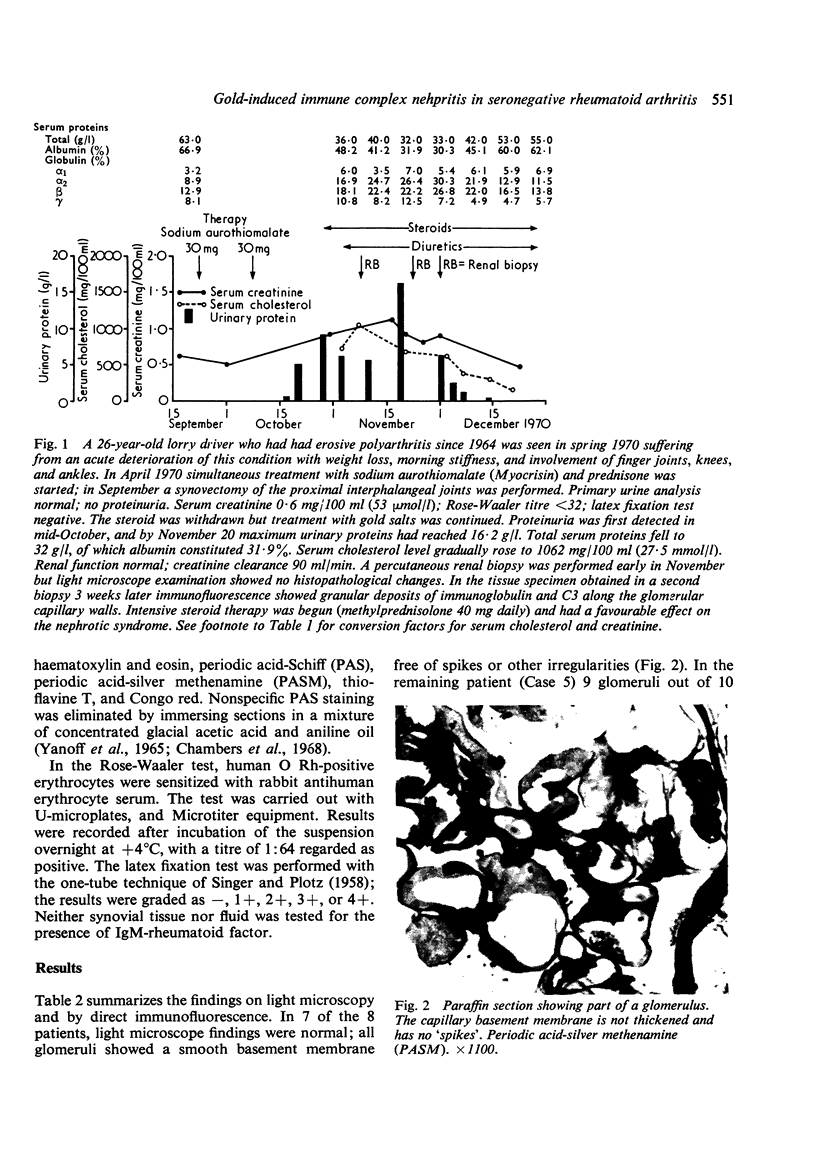
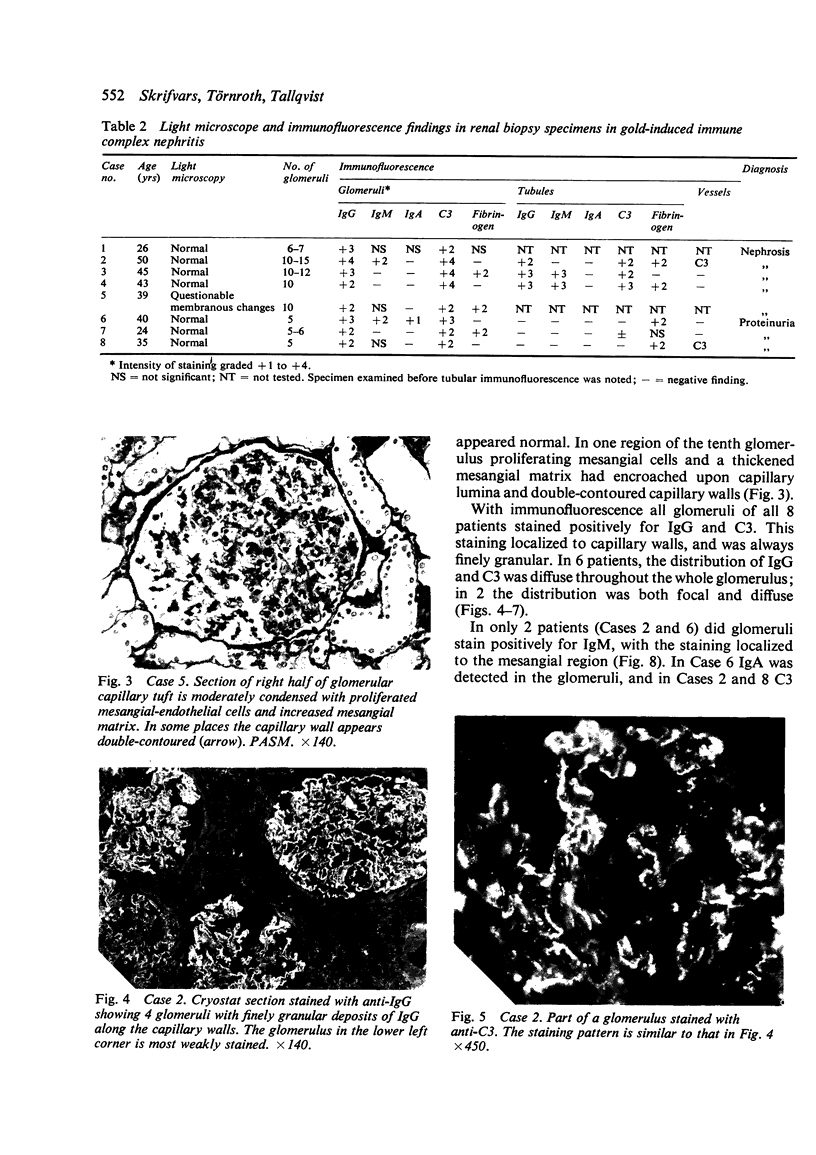
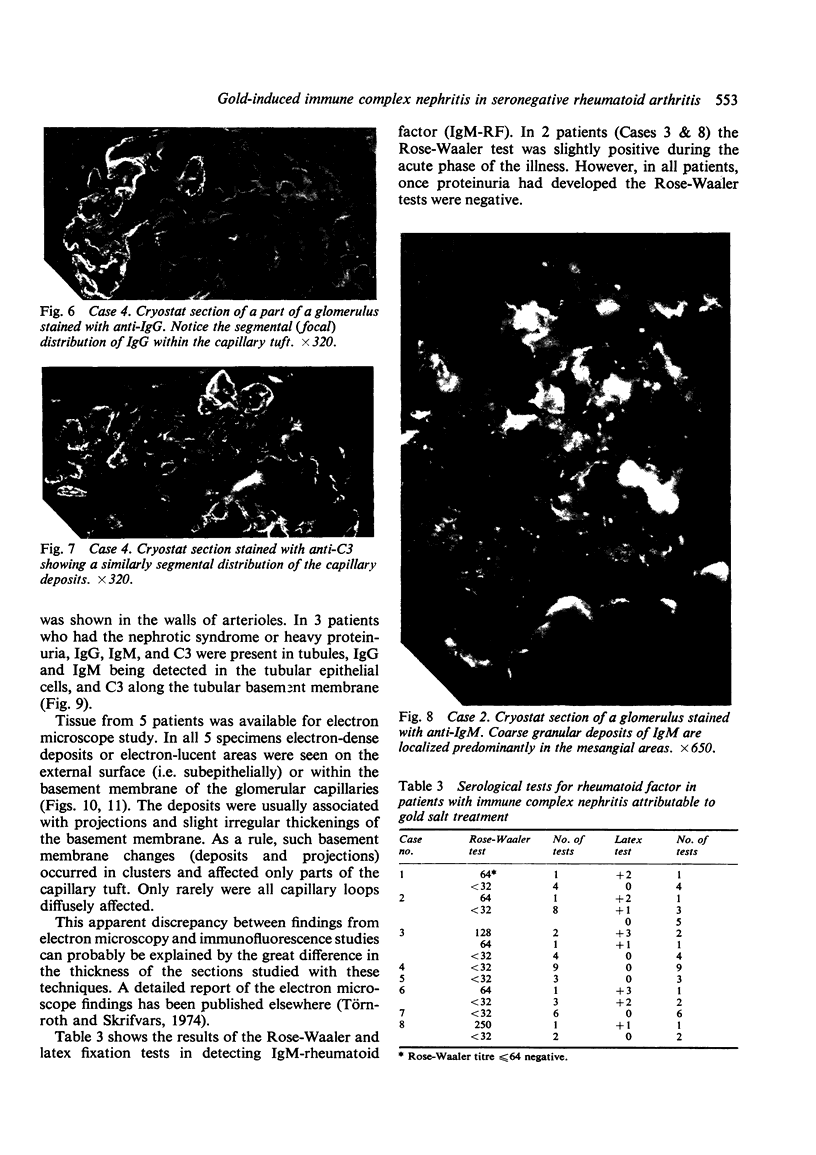
Proteinuria, with or without the nephrotic syndrome, developed in 8 patients with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis after the institution of gold therapy. Light microscope examination of renal biopsies showed normal findings in 7, and a focal increase in the mesangial matrix of one glomerulus in the eighth. In all patients immunofluorescence showed deposits of IgG and C3 along the glomerular basement membrane, indicative of immune complex nephritis. The renal biopsies of 5 patients were studied with the electron microscope and subepithelial deposits were detected in all. The Rose-Waaler test for the detection of IgM-rheumatoid factor (IgM-RF) was repeatedly negative in all patients. These results suggest that the development of gold nephropathy may be related to an absence of IgM-RF in serum.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRUN C., OLSEN S., RAASCHOU F., SORENSEN A. W. THE LOCALIZATION OF GOLD IN THE HUMAN KIDNEY FOLLOWING CHRYSOTHERAPY: A BIOPSY STUDY. Nephron. 1964;1:265–276. doi: 10.1159/000179340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton M. C., Schur P. H. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. II. Intracytoplasmic inclusions of immunoglobulins and complement. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Jan-Feb;14(1):87–95. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. M. Immune complex disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 May;32(3):265–271. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers R. W., Bowling M. C., Grimley P. M. Glutaraldehyde fixation in routine histopathology. Arch Pathol. 1968 Jan;85(1):18–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEROT M., KAHN J., MAZALTON A., PEYRAFORT J. Néphrite anurique aiguë mortelle après traitement aurique, chrysocyanose associée. 1954 Feb 26-Mar 5Bull Mem Soc Med Hop Paris. 70(7-8):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganote C. E., Beaver D. L., Moses H. L. Renal gold inclusions. A light and electron microscopic study. Arch Pathol. 1966 May;81(5):429–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb N. L., Smith P. M., Smith E. M. Tissue gold concentration in a rheumatoid arthritic receiving chrysotherapy. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jan-Feb;15(1):16–22. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMANN W., HACKEL D. B., HARWOOD S., WILSON S. G., HUNTER J. L. Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund's adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Apr;100(4):660–664. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Little A. H. Gold nephropathy. An immunopathologic study. Arch Pathol. 1973 Aug;96(2):133–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusius F. E., Markkanen A., Peltola P. Plasma levels and urinary excretion of gold during routine treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 May;29(3):232–235. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.3.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE J. C., DUSHKIN M., EYRING E. J., ENGLEMAN E. P., HOPPER J., Jr RENAL LESIONS ASSOCIATED WITH GOLD THERAPY; LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES. Arthritis Rheum. 1965 Feb;8:1–13. doi: 10.1002/art.1780080102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey R. T., Klassen J. Immunologically mediated glomerular, tubular and interstitial renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 15;288(11):564–570. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303152881108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER R. L., SCHMID F. R. Phagocytosis of particulate complexes of gamma-globulin and rheumatoid factor. J Immunol. 1962 Apr;88:519–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persellin R. H., Hess E. V., Ziff M. Effect of a gold salt on the immune response. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Apr;10(2):99–106. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER J. M., PLOTZ C. M. The latex fixation test for rheumatoid arthritis using patients' own gamma globulin. Arthritis Rheum. 1958 Apr;1(2):142–146. doi: 10.1002/art.1780010206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg D. S., Kidd E. G., Shnitka T. K., Ulan R. A. Gold nephropathy. A clinical and pathologic study. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):812–825. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk S. W., Ziff M. Ultrastructural studies of the passage of gold thiomalate across the renal glomerular capillary wall. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Jan-Feb;13(1):39–52. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tönroth T., Skrifvars B. Gold nephropathy prototype of membranous glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1974 Jun;75(3):573–590. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wager O., Räsänen J. A., Haltia K., Wasastjerna C. M components with antibody activity. Anti-smooth muscle, anti-thyroglobulin and anti-streptolysin-O activity in five M component sera. Ann Clin Res. 1971 Apr;3(2):86–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Diagnosis of immunopathologic renal disease. Kidney Int. 1974 Jun;5(6):389–401. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YANOFF M., ZIMMERMAN L. E., FINE B. S. GLUTARALDEHYDE FIXATION OF WHOLE EYES. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Aug;44:167–171. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/44.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]