Abstract
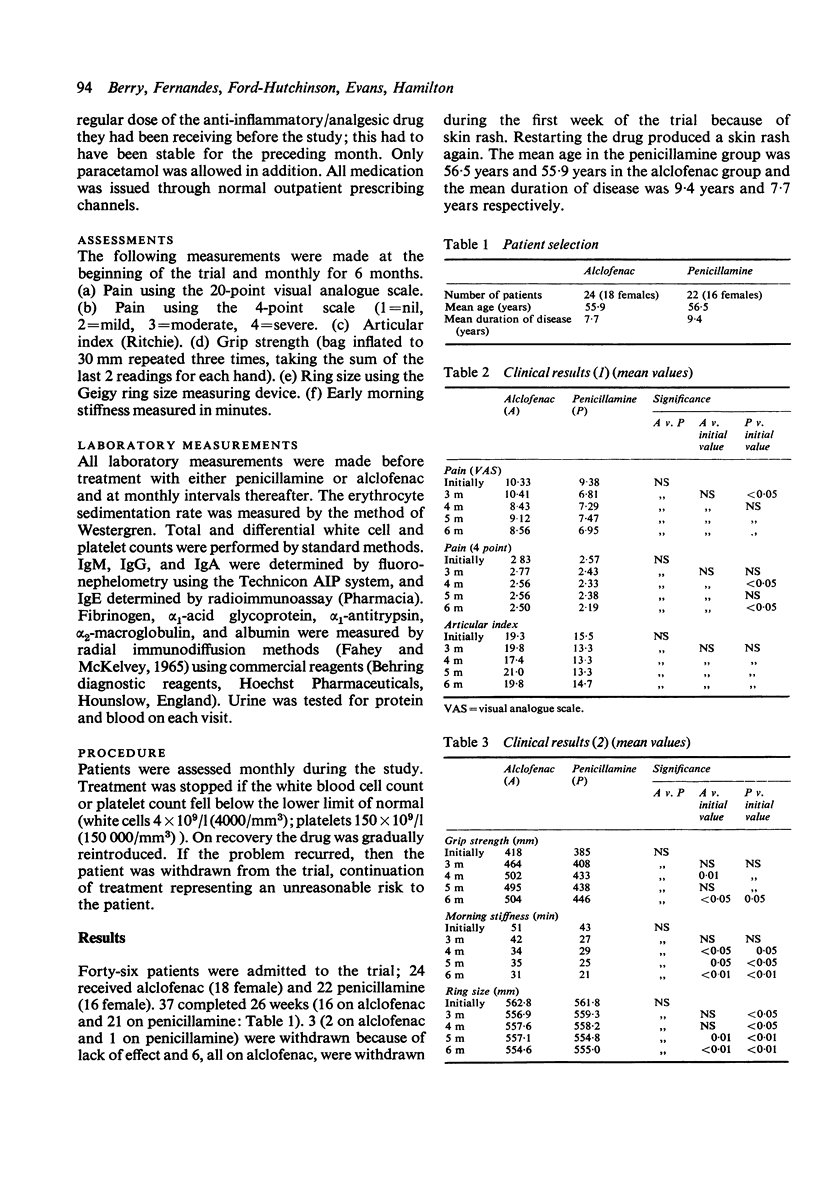
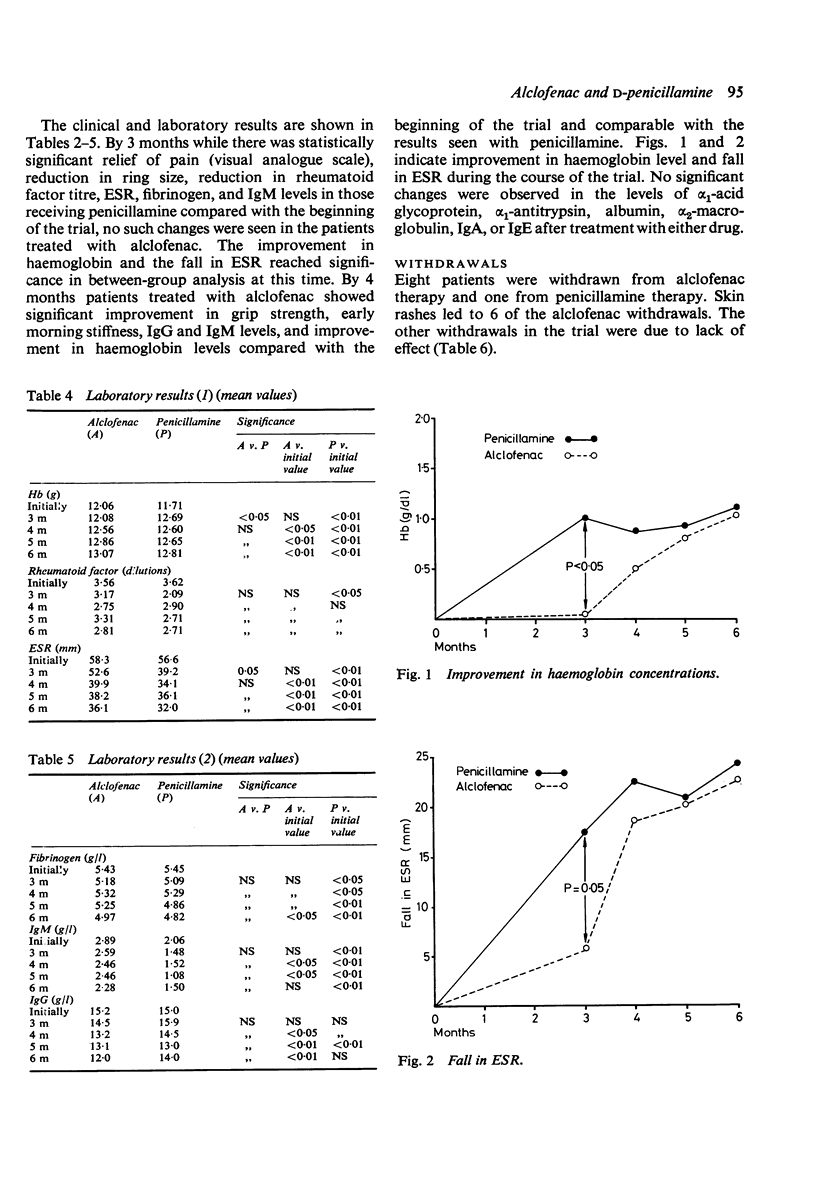
Forty-six patients with rheumatoid arthritis, 22 receiving D-penicillamine and 2j alclofenac, took part in a 6-month single-bind external observer trial to compare the efficacy and toxicity of these drugs in the treatment of severe rheumatoid arthritis. Both drugs were active and similar in their efficacy at 6 months as judged by clinical and laboratory measurements. Penicillamine was active therapeutically by 3 months, one month before alclofenac. 9 patients, 8 on alclofenac and one on D-penicillamine, had to stop treatment because of lack of effect or toxic effects. Skin rashes within the first week of treatment were a major problem with alclofenac and led to 6 withdrawals.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aylward M. Alclofenac in rheumatoid arthritis: an evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Br J Clin Pract. 1973 Jul;27(7):255–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aylward M., Parker R. J., Holly F., Maddock J., Davies D. B. Long-term study of indomethacin and alclofenac in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1975 Apr 5;2(5961):7–9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5961.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aylward M., Parker R. J., Maddock J. Studies on 4-allyloxy-3 chlorophenylacetic acid (Alcofenac). A double-blind comparison of Alcofenac and aspirin in rheumatoid arthritis, and effects of therapy on serum immunoglobulins and rheumatoid factor. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 May;33(3):268–272. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.3.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry H., Liyanage S. P., Durance R. A., Barnes C. G., Berger L. A., Evans S. Azathioprine and penicillamine in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled trial. Br Med J. 1976 May 1;1(6017):1052–1054. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6017.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billings R. A., Burry H. C., Emaslie F. S., Kerr G. D. Vasculitis with alclofenac therapy. Br Med J. 1974 Nov 2;4(5939):263–265. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5939.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Controlled trial of D(-)penicillamine in severe rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1973 Feb 10;1(7798):275–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCKELVEY E. M. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF SERUM IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN ANTIBODY-AGAR PLATES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huskisson E. C., Gibson T. J., Balme H. W., Berry H., Burry H. C., Grahame R., Hart F. D., Henderson D. R., Wojtulewski J. A. Trial comparing D-penicillamine and gold in rheumatoid arthritis. Preliminary report. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Nov;33(6):532–535. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.6.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSHE J. M. Wilson's disease; new oral therapy. Lancet. 1956 Jan 7;270(6906):25–26. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91859-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


