Abstract
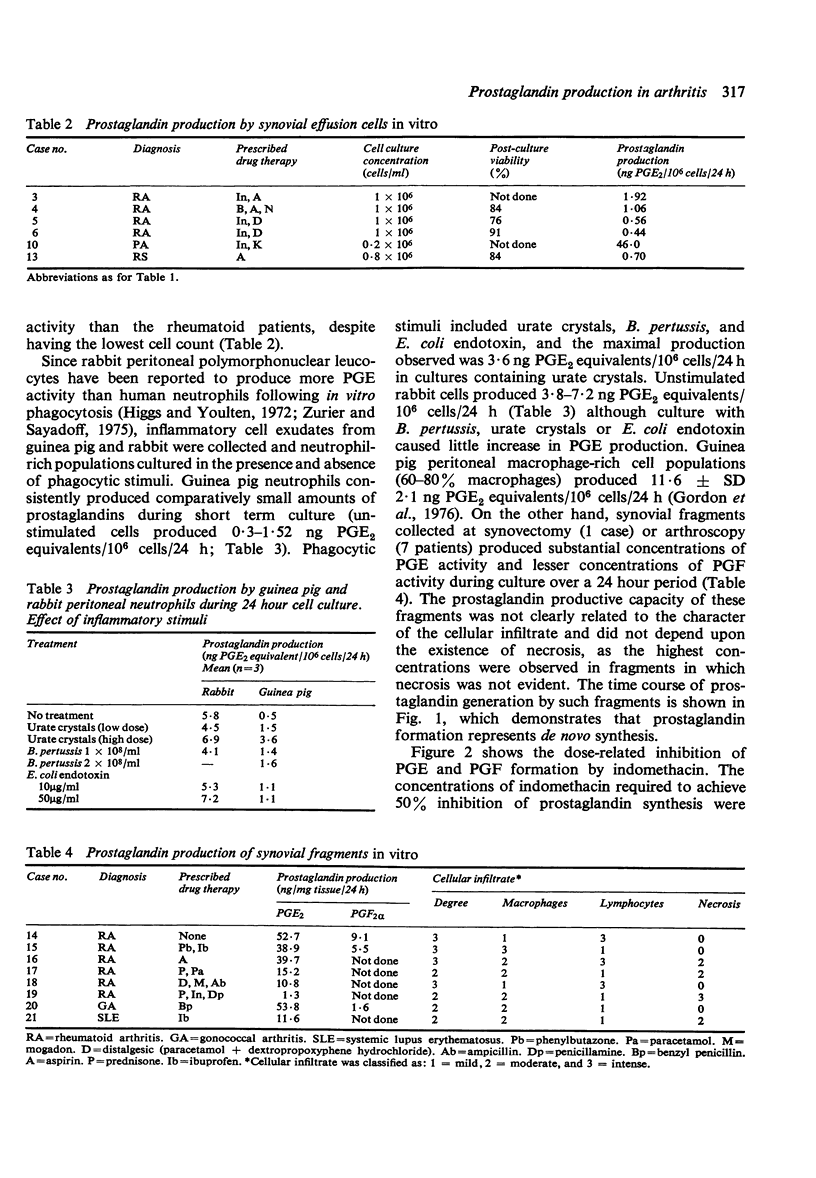
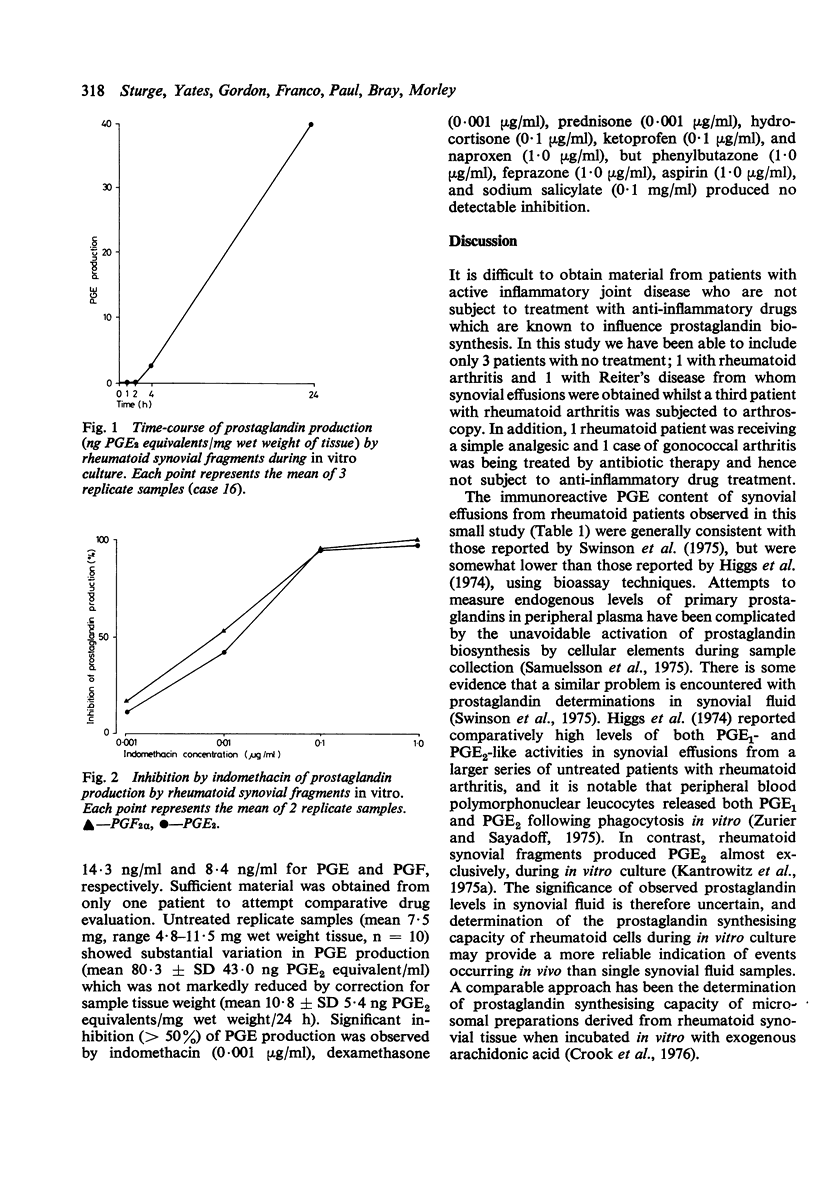
Inflammatory cell populations from synovial effusions or synovial villi in rheumatoid arthritis have been cultured in vitro. Prostaglandin productive capacity, measured by radioimmunoassay, showed the polymorphonuclear leucocyte rich populations from synovial effusions to be poor sources of PGE production whereas the synovial fragments produced substantial amounts of PGE activity. It is suggested that the macrophage is the major source of local prostaglandin formation both in gout and rheumatoid arthritis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackham A., Farmer J. B., Radziwonik H., Westwick J. The role of prostaglandins in rabbit monoarticular arthritis. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 May;51(1):35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09629.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Transformation of arachidonic acid and homo-gamma-linolenic acid by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Monohydroxy acids from novel lipoxygenases. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7816–7820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray M. A., Gordon D. Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on macrophage prostaglandin biosynthesis [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;57(3):466P–467P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray M. A., Gordon D., Morley J. Proceedings: Role of prostaglandins in reactions of cellular immunity. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Nov;52(3):453P–453P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook D., Collins A. J., Bacon P. A., Chan R. Prostaglandin synthetase activity from human rheumatoid synovial microsomes. Effect of 'aspirin-like' drug therapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Aug;35(4):327–332. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.4.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Krane S. M., Russell R. G., Robinson D. R. Production of collagenase and prostaglandins by isolated adherent rheumatoid synovial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):945–949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori H. W., Champion G. D., Bluestone R., Paulus H. E. Simultaneous pharmacokinetics of indomethacin in serum and synovial fluid. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Sep;32(5):433–435. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.5.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris V. A., DeRubertis F. R. Release of prostaglandin by mitogen- and antigen-stimulated leukocytes in culture. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):378–386. doi: 10.1172/JCI107773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):237–239. doi: 10.1038/newbio231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatt M., Peskar B., Brune K. Leukocytes and prostaglandins in acute inflammation. Experientia. 1974 Nov 15;30(11):1257–1259. doi: 10.1007/BF01945171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D., Bray M. A., Morley J. Control of lymphokine secretion by prostaglandins. Nature. 1976 Jul 29;262(5567):401–402. doi: 10.1038/262401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Svensson J., Samuelsson B. Thromboxanes: a new group of biologically active compounds derived from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., McCall E., Youlten L. J. A chemotactic role for prostaglandins released from polymorphonuclear leucocytes during phagocytosis. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Apr;53(4):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Youlten L. J. Proceedings: Prostaglandin production by rabbit peritoneal polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;44(2):330P–330P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantrowitz F., Robinson D. R., McGuire M. B., Levine L. Corticosteroids inhibit prostaglandin production by rheumatiod synovia. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):737–739. doi: 10.1038/258737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L. Antibodies to pharmacologically active molecules: specificities and some applications of antiprostaglandins. Pharmacol Rev. 1973 Jun;25(2):293–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortel R. W., Newcombe D. S. Acute gouty arthritis and response to colchicine in the virtual absence of synovial-fluid leukocytes. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 13;290(24):1363–1364. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406132902406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Acetylation of prostaglandin synthase by aspirin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3073–3076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Granström E., Green K., Hamberg M., Hammarström S. Prostaglandins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:669–695. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Phelps P., Agudelo C. A. Urate crystal induced inflammation in dog joints: sequence of synovial changes. J Rheumatol. 1974 Mar;1(1):102–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Willis A. L. Aspirin selectively inhibits prostaglandin production in human platelets. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):235–237. doi: 10.1038/newbio231235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


