Abstract
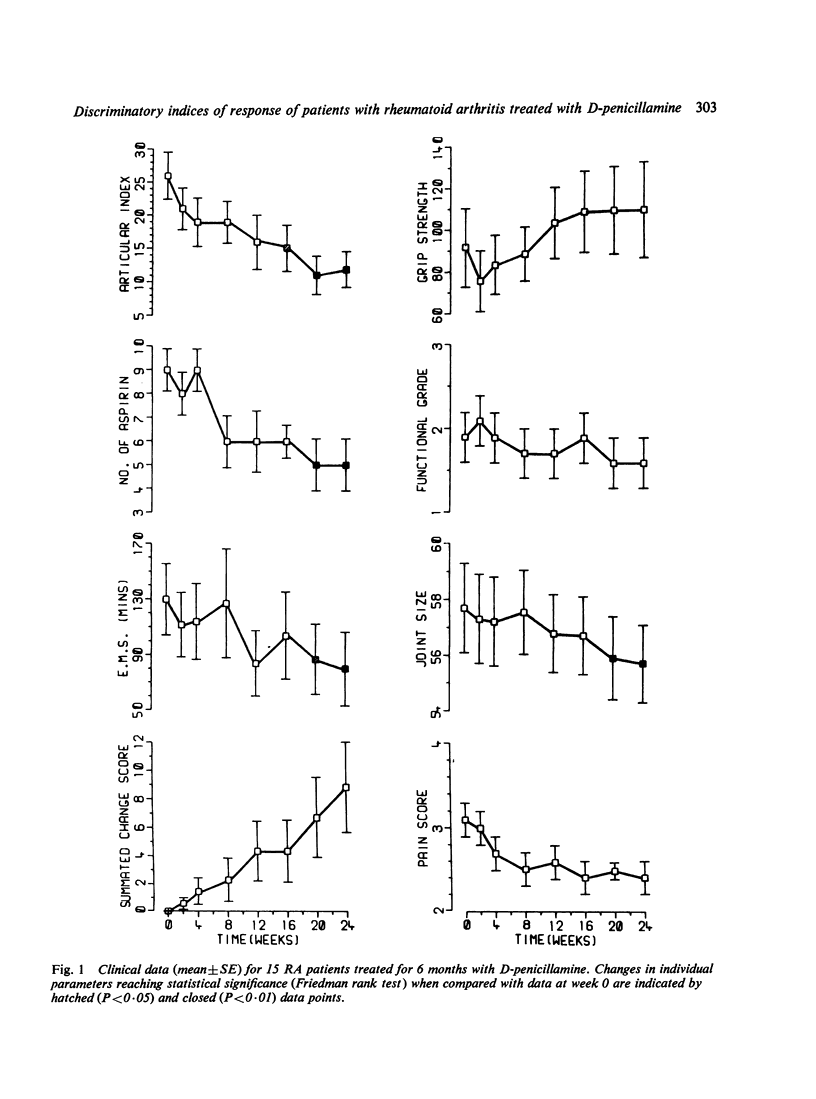
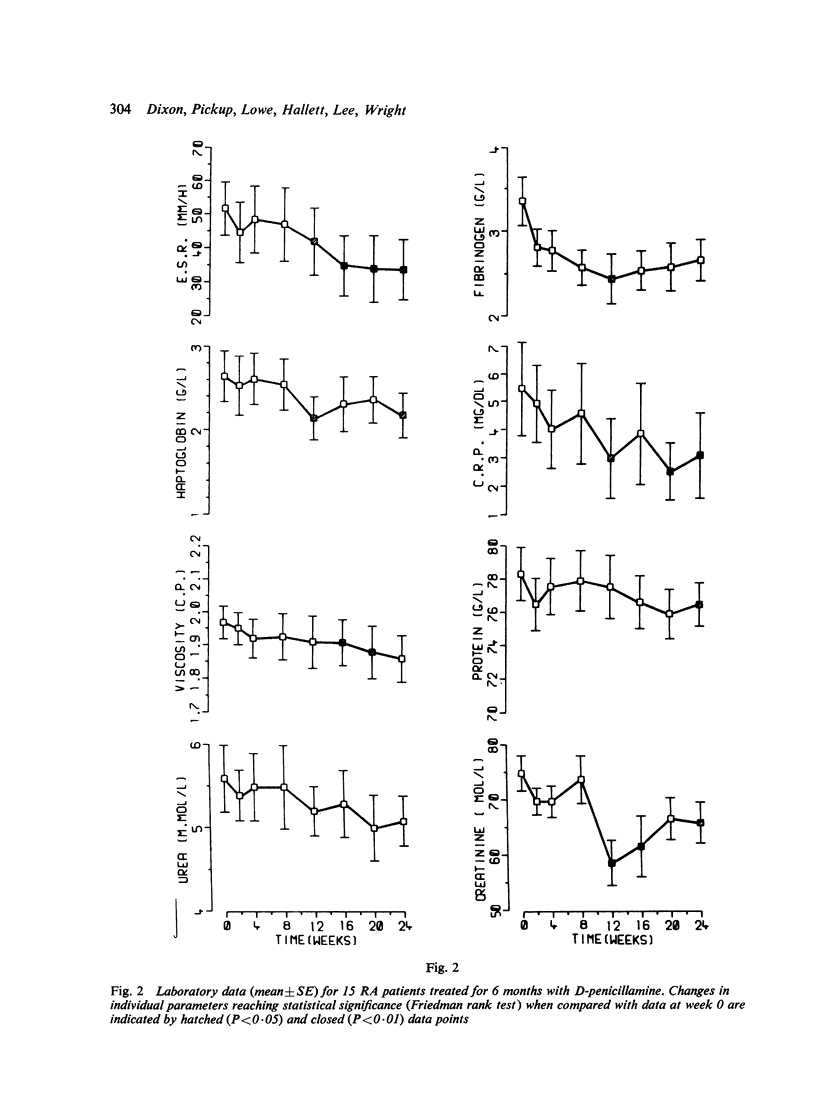
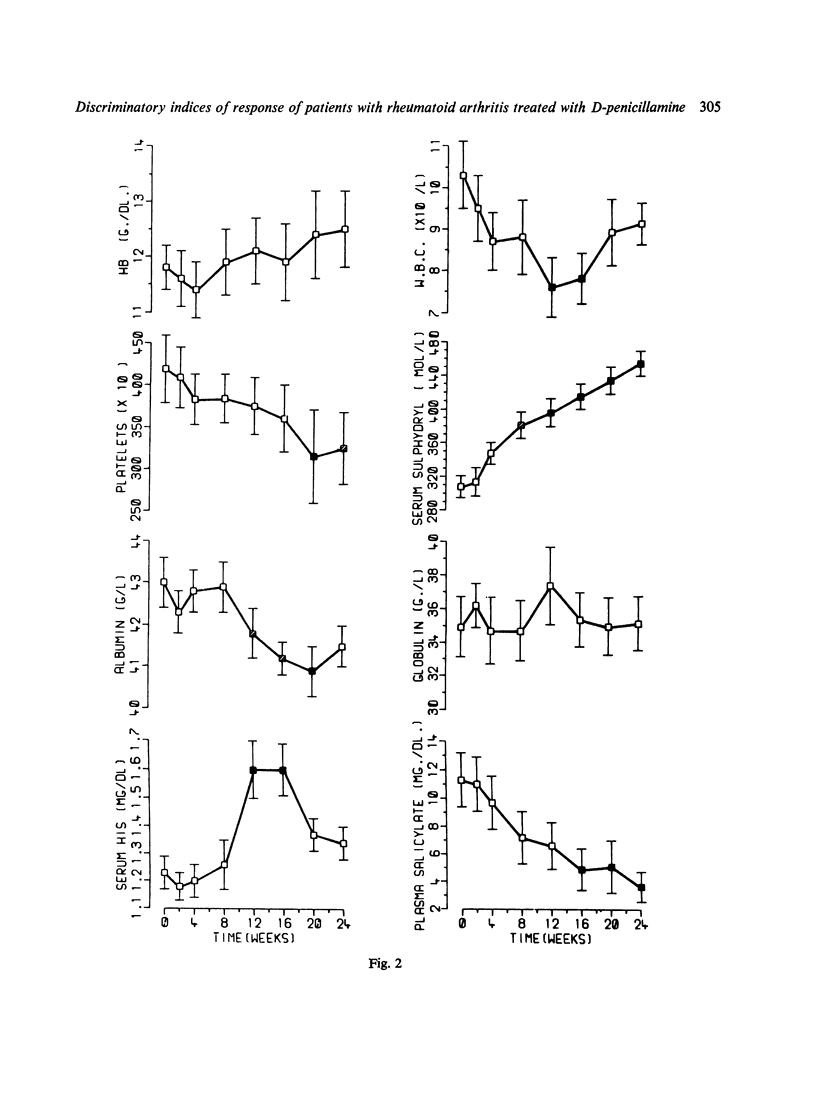
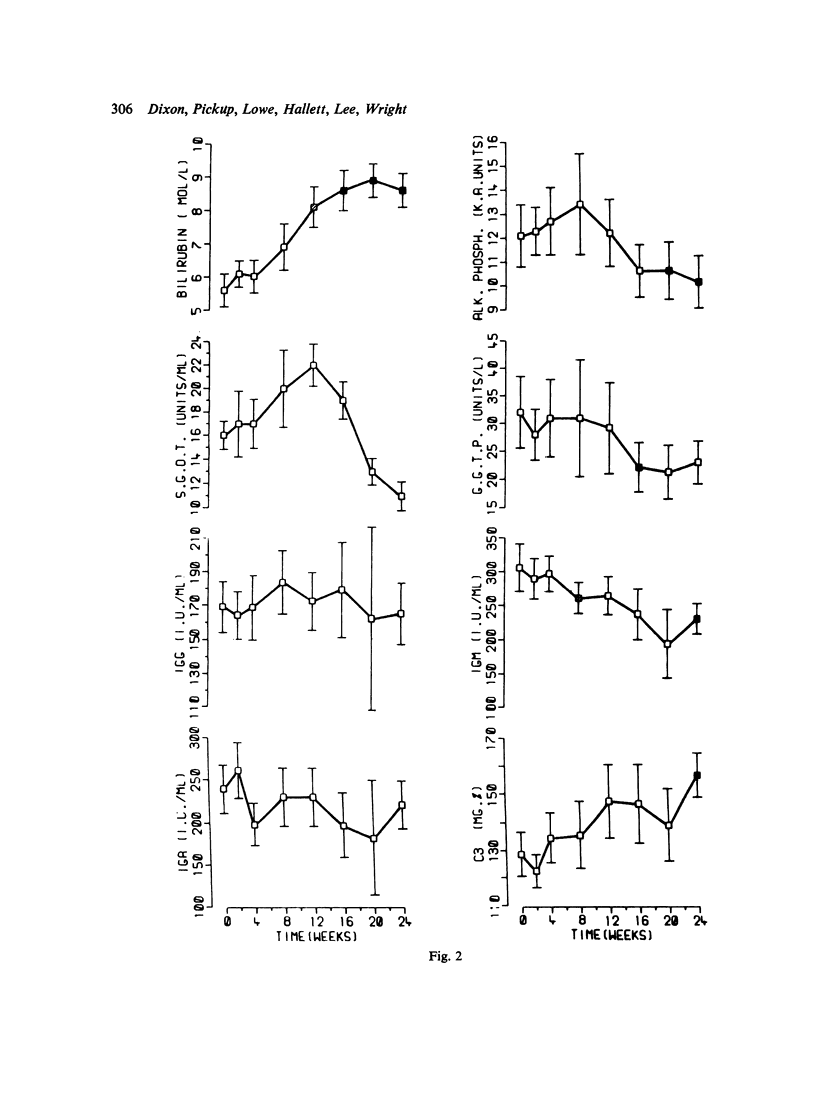
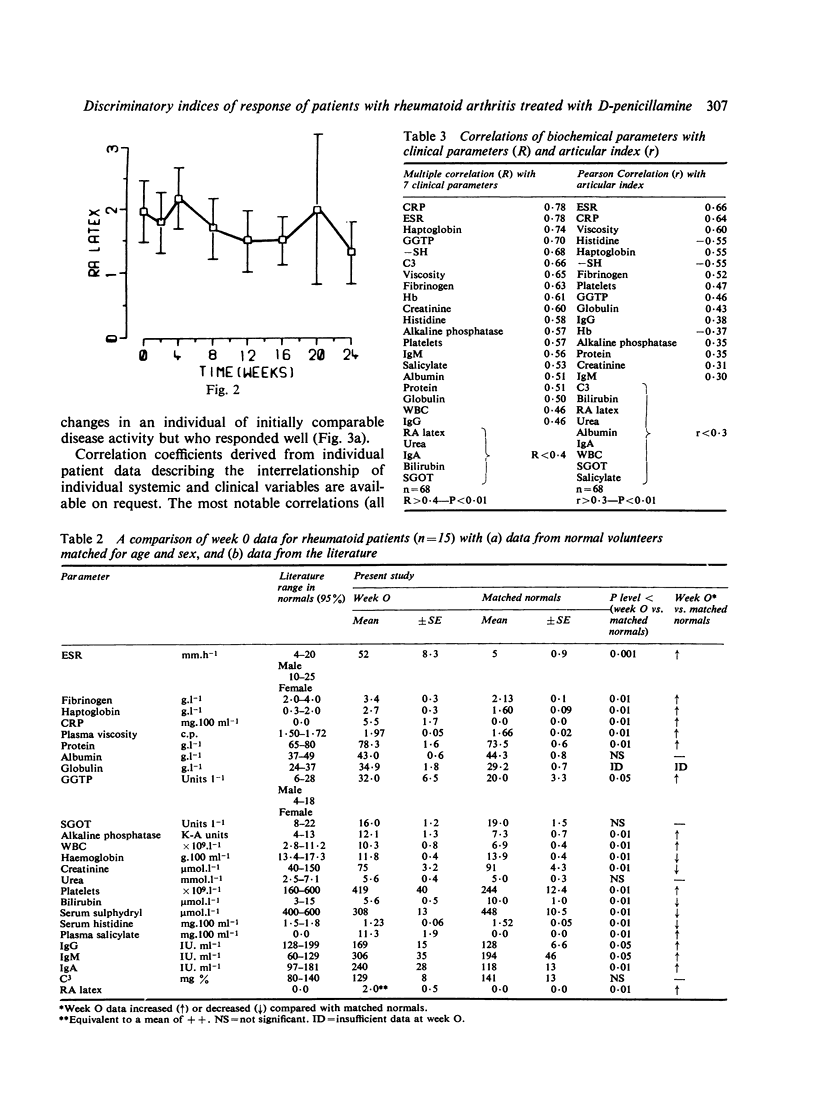
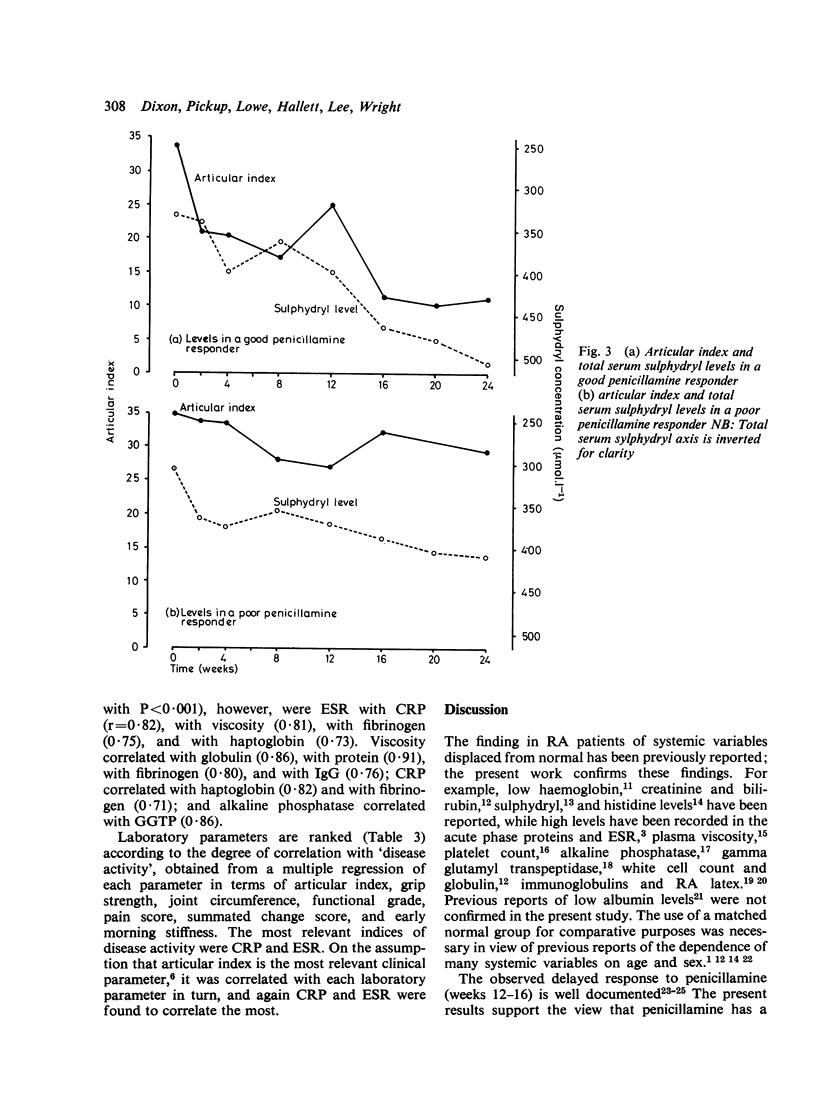
A long-term study is being undertaken to classify drugs used as specific agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in terms of their effects on biochemical and clinical characteristics of the disease. In particular is hoped to establish those indices which are most relevant to the response of RA to treatment. Fifteen patients were treated with D-penicillamine after an initial period of 2 weeks on aspirin alone, when the baseline investigations were made. The dose of penicillamine was increased gradually to a maximum of 500 mg a day over the period of 6 months, and changes in 8 clinical and 25 laboratory indices were measured on 8 separate occasions in the 6-month period. Marked clinical improvement took place, and this was mirrored by changes in a wide range of biochemical parametaers. ESR and C-reactive protein were shown to be the most suitable indices of disease improvement with penicillamine treatment.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aylward M., Maddock J., Wheeldon R., Parker R. J. A study of the influence of various antirheumatic drug regimens on serum acute-phase proteins, plasma tryptophan, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1975 May;14(2):101–114. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/14.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry H., Fernandes L., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Evans S. J., Hamilton E. B. Alclofenac and D-penicillamine. Comparative trial in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Feb;37(1):93–97. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blades A. N., Coyer A. B., Flavell H. C. Plasma viscosity with particular reference to its estimation in cases of rheumatoid-type arthritis. Ann Phys Med. 1966 May;8(6):214–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestone R., Goldberg L. S. Effect of D-penicillamine on serum immunoglobulins and rheumatoid factor. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jan;32(1):50–52. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttiger L. E., Svedberg C. A. Normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate and age. Br Med J. 1967 Apr 8;2(5544):85–87. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5544.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N., Merrill D. Serum immunoglobulins in rheumatoid arthritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 May;67(5):850–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockel R., Kendall M. J., Becker J. F., Hawkins C. F. Serum biochemical values in rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 Mar;30(2):166–170. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P. Relationship of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate to viscosity and plasma proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Jan;33(1):53–56. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon A. J., Davies J., Dormandy T. L., Hamilton E. B., Holt P. J., Mason R. M., Thompson M., Weber J. C., Zutshi D. W. Synthetic D(-)penicillamine in rheumatoid arthritis. Double-blind controlled study of a high and low dosage regimen. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Oct;34(5):416–421. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.5.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld M., Penchas S., Eliakim M. Thrombocytosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Recurrent arterial thromboembolism and death. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Dec;36(6):579–581. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.6.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans P. H. Serum sulphydryl levels in rheumatoid patients treated with alclofenac. Curr Med Res Opin. 1975;3(5):268–275. doi: 10.1185/03007997509114777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr M., Kendall M. J., Young D. W., Meynell M. J., Hawkins C. F. Assessment of rheumatoid activity based on clinical features and blood and synovial fluid analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Apr;35(2):163–167. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber D. A. Determination of histidine in serum with o-phthaldialdehyde. Anal Biochem. 1970 Apr;34(2):500–504. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber D. A., Gerber M. G. Specificity of a low free serum histidine concentration for rheumatoid arthritis. J Chronic Dis. 1977 Feb;30(2):115–127. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(77)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Huskisson E. C., Wojtulewski J. A., Scott P. J., Balme H. W., Burry H. C., Grahame R., Hart F. D. Evidence that D-penicillamine alters the course of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1976 Aug;15(3):211–215. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/15.3.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grennan D. M., Anderson J. A., Kennedy A. C., Mitchell W., Dick W. C., Buchanan W. W. Relationship between haemoglobin and the other clinical and laboratory parameters in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Med Res Opin. 1975;3(2):104–108. doi: 10.1185/03007997509113656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haataja M., Kalliomäki J. L. Laboratory scale for evaluating the activity of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1978 May;17(2):83–85. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/17.2.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness J. The viscosity of human blood plasma; its measurement in health and disease. Biorheology. 1971 Dec;8(3):171–193. doi: 10.3233/bir-1971-83-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huskisson E. C., Berry H. Some immunological changes in rheumatoid arthritis among patients receiving penicillamine and gold. Postgrad Med J. 1974 Aug;50 (Suppl 2):59–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs W. L. A colorimetric assay for gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Jan;31(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90375-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall M. J., Cockel R., Becker J., Hawkins C. F. Raised serum alkaline phosphatase in rheumatoid disease. An index of liver dysfunction? Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Sep;29(5):537–540. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.5.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORBER A., PEARSON C. M., MEREDITH W. L., GANTZ-MANDELL L. E. SERUM SULFHYDRYL DETERMINATIONS AND SIGNIFICANCE IN CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISEASES. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Sep;61:423–434. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-61-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber A., Chang C. C., Masuoka D., Meacham I. Effect of thiols in biological systems on protein sulfhydryl content. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 May;19(5):1551–1560. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J. R., Pickup M. E., Dixon J. S., Leatham P. A., Rhind V. M., Wright V., Downie W. W. Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase levels in arthritis: a correlation with clinical and laboratory indices of disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Oct;37(5):428–431. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.5.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddock J., Rees P., Holly F., Aylward M. The influence of alclofenac treatment on acute-phase proteins, plasma tryptophan, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Med Res Opin. 1975;3(5):286–297. doi: 10.1185/03007997509114779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcolongo R., Jr, Carcassi A., Frullini F., Bianco G., Bravi A. Levels of serum immunoglobulins in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1967 Sep;26(5):412–418. doi: 10.1136/ard.26.5.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P. The assessment of rheumatoid arthritis. A study based on measurements of the serum acute-phase reactants. Q J Med. 1972 Apr;41(162):115–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P., Wilkinson A. R. The effects of some anti-inflammatory drugs on the acute-phase proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1973 Oct;42(168):785–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkisara P., Nissilä M., Kajander A., Martio J., von Essen R., Anttila P., Mäkisara G. L. Comparison of penicillamine and gold treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1978;7(3):166–170. doi: 10.3109/03009747809095648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATCLIFF A. P., HARDWICKE J. ESTIMATION OF SERUM HAEMOGLOBIN-BINDING CAPACITY (HAPTOGLOBIN) ON SEPHADEX G.100. J Clin Pathol. 1964 Nov;17:676–679. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.6.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEARN M. A., EPSTEIN W. V., ENGLEMAN E. P., TAYLOR W. F. Relationship of serum proteins and rheumatoid factor to serum viscosity in rheumatic diseases. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Apr;61:677–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanworth D. R., Williamson J. P., Shadforth M., Felix-Davies D., Thompson R. Drug-induced IgA deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1977 May 7;1(8019):1001–1002. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S., Hamilton E. B., Williams R. Rheumatoid arthritis and liver involvement. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1978 Oct;12(5):416–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swannell A. J., Watkins J. The influence of drug therapy on serum immunoglobulin profiles in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc R Soc Med. 1977;70 (Suppl 3):140–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRINDER P. Rapid determination of salicylate in biological fluids. Biochem J. 1954 Jun;57(2):301–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0570301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veys E. M., Claessens H. E. Serum levels of IgG, IgM, and IgA in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 Sep;27(5):431–440. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.5.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilding P., Kendall M. J., Holder R., Grimes J. A., Farr M. The influence of drugs and disease activity on biochemical and haematological data in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Oct 15;64(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


