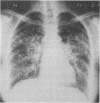
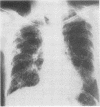
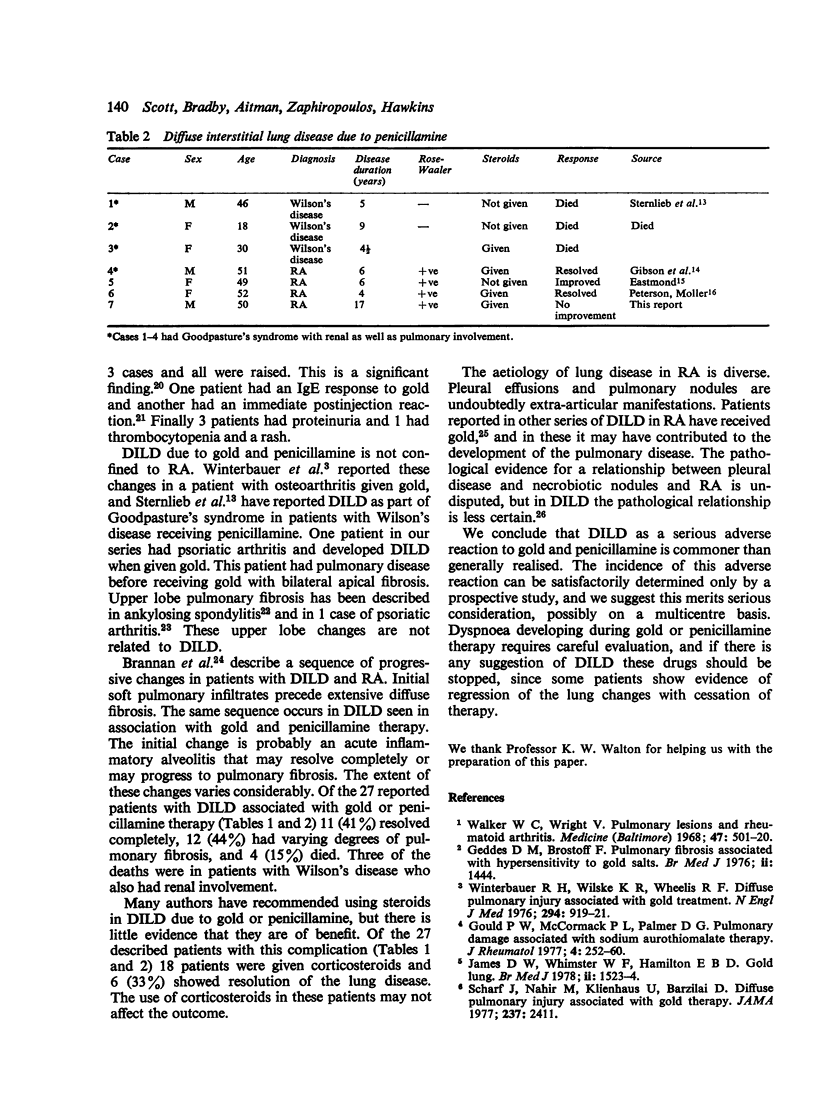
Abstract
Seven cases of diffuse interstitial lung disease (DILD) are reported with an unequivocal temporal relationship between the development of the lung disease and treatment with gold (6 cases) and penicillamine (1 case). They were characterised clinically by the sudden onset of dyspnoea and crepitations and radiologically by diffuse bilateral pulmonary shadowing. Most showed evidence of hypersensitivity such as eosinophilia, a raised serum IgE level in response to gold, proteinuria, thrombocytopenia, or an immediate postinjection reaction. DILD is a serious complication of treatment with gold and penicillamine that is commoner than generally realised.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRANNAN H. M., GOOD C. A., DIVERTIE M. B., BAGGENSTOSS A. H. PULMONARY DISEASE ASSOCIATED WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. JAMA. 1964 Sep 21;189:914–918. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070120036009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL A. H., MACDONALD C. B. UPPER LOBE FIBROSIS ASSOCIATED WITH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS. Br J Dis Chest. 1965 Apr;59:90–101. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(65)80017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codling B. W., Chakera T. M. Pulmonary fibrosis following therapy with Melphalan for multiple myeloma. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Aug;25(8):668–673. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.8.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P., Hughes G. R. Significance of eosinophilia during gold therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Nov-Dec;17(6):964–968. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastmond C. J. Diffuse alveolitis as complication of penicillamine treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1976 Jun 19;1(6024):1506–1506. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6024.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes D. M., Brostoff J. Pulmonary fibrosis associated with hypersensitivity to gold salts. Br Med J. 1976 Jun 12;1(6023):1444–1444. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6023.1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Burry H. C., Ogg C. Letter: Goodpasture syndrome and D-penicillamine. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Jan;84(1):100–100. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-1-100_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould P. W., McCormack P. L., Palmer D. G. Pulmonary damage associated with sodium aurothiomalate therapy. J Rheumatol. 1977 Autumn;4(3):252–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman L. R., Gall E. P., Pitt M., Lull G. Psoriatic spondylitis. Association with advanced nongranulomatous upper lobe pulmonary fibrosis. JAMA. 1978 Apr 3;239(14):1416–1417. doi: 10.1001/jama.239.14.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halla J. T., Hardin J. G., Linn J. E. Postinjection nonvasomotor reactions during chrysotherapy. Constitutional and rheumatic symptoms following injections of gold salts. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jul-Aug;20(6):1188–1191. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. W., Whimster W. F., Hamilton E. B. Gold lung. Br Med J. 1978 Jun 10;1(6126):1523–1524. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6126.1523-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R. L., Waite D. H. Progressive interstitial lung disease from prolonged methotrexate therapy. Arch Dermatol. 1978 Dec;114(12):1800–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limpisvasti P., Jones P. Report of a case: gold-associated pulmonary injury. Hawaii Med J. 1979 Feb;38(2):43–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON C. D., HARVILLE W. E., PIERCE J. A. RHEUMATOID LUNG DISEASE. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Apr;62:685–697. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-4-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen J., Møller I. Miliary pulmonary infiltrates and penicillamine. Br J Radiol. 1978 Nov;51(611):915–916. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-51-611-915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podell T. E., Klinenberg J. R., Kramer L. S., Brown H. V. Pulmonary toxicity with gold therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Mar;23(3):347–350. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G., Baume P., Vandenberg R. Azathioprin nd acute restrictive lung disese. Aust N Z J Med. 1972 Aug;2(3):272–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1972.tb03074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W., Ball G. V. Lung injury due to gold treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Mar;23(3):351–354. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlieb I., Bennett B., Scheinberg I. H. D-penicillamine induced Goodpasture's syndrome in Wilson's disease. Ann Intern Med. 1975 May;82(5):673–676. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-5-673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tala E., Jalava S., Nurmela T., Vuori K. Pulmonary infiltrates associated with gold therapy. Report of a case. Scand J Rheumatol. 1979;8(2):97–100. doi: 10.3109/03009747909105344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. C., Wright V. Pulmonary lesions and rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1968 Nov;47(6):501–520. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196811000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver L. T., Law J. S. Lung changes after gold salts. Br J Dis Chest. 1978 Jul;72(3):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(78)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbauer R. H., Wilske K. R., Wheelis R. F. Diffuse pulmonary injury associated with gold treatment. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 22;294(17):919–921. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604222941703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]