Abstract
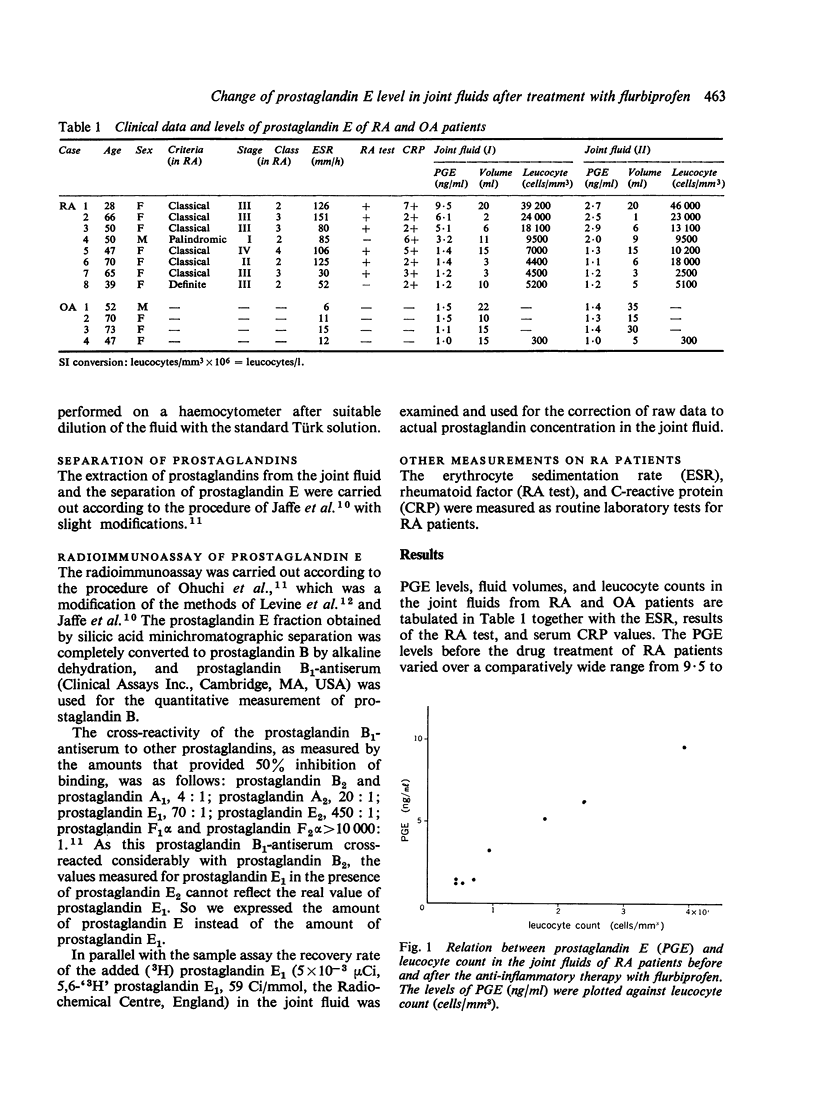
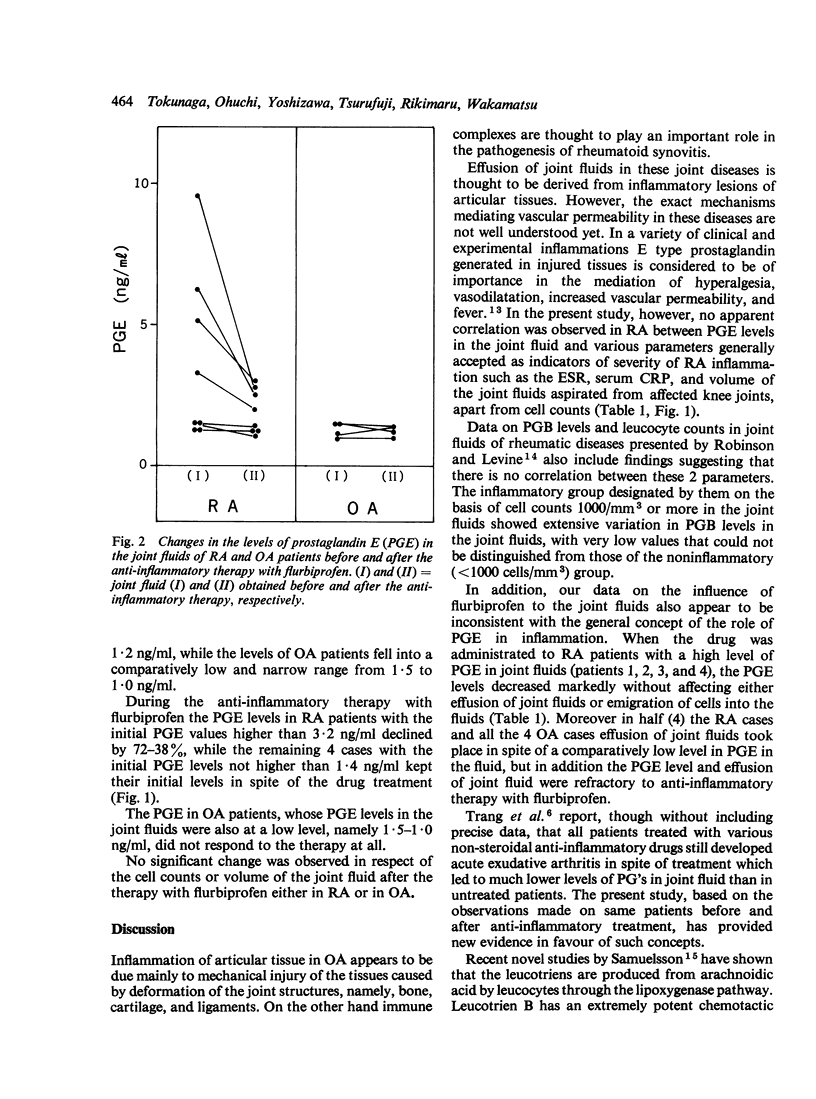
The prostaglandin E (PGE) level in the knee joint fluid was determined by radioimmunoassay before and after anti-inflammatory therapy with flurbiprofen in 8 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and 4 patients with osteoarthritis (OA). The level of PGE in RA joint fluids before the anti-inflammatory treatment was 9.5-1.2 ng/ml and in proportion with the leucocyte count in the joint fluid. A marked decrease of the PGE level was attained with flurbiprofen treatment in 4 patients whose initial PGE levels had been higher than 3.2 ng/ml, while 4 patients with lower PGE levels, namely, 1.4-1.2 ng/ml, did not respond to the drug treatment. In all the OA patients the PGE levels was no higher than 1.5 ng/ml and refractory to the anti-inflammatory therapy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crook D., Collins A. J., Rose A. J. A comparison of the effect of flurbiprofen on prostaglandin synthetase from human rheumatoid synovium and enzymatically active animal tissues. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;28(6):535–535. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb02787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby G., Bankhurst A. D., Williams R. C., Jr Immunohistochemical localization of prostaglandin E in rheumatoid synovial tissues. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Apr;20(3):785–791. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe B. M., Behrman H. R., Parker C. W. Radioimmunoassay measurement of prostaglandins E, A, and F in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):398–405. doi: 10.1172/JCI107196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Gjtierrez Cernosek R. M., Van Vunakis H. Specificities of prostaglandins B 1 , F 1 , and F 2 antigen-antibody reactions. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6782–6785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi K., Sato H., Tsurufuji S. The content of prostaglandin E and prostaglandin F2alpha in the exudate of carrageenin granuloma of rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 26;424(3):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Stepney R. J., Higgs G. A., Eakins K. E. Chemokinetic activity of arachidonic and lipoxygenase products on leuocyctes of different species. Prostaglandins. 1980 Aug;20(2):411–418. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(80)80058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Levine L. Prostaglandin-stimulated bone resorption by rheumatoid synovia. A possible mechanism for bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1181–1188. doi: 10.1172/JCI108195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturge R. A., Yates D. B., Gordon D., Franco M., Paul W., Bray A., Morley J. Prostaglandin production in arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Aug;37(4):315–320. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.4.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trang L. E., Granström E., Lövgren O. Levels of prostaglandins F2 alpha and E2 and thromboxane B2 in joint fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1977;6(3):151–154. doi: 10.3109/03009747709095440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


