Abstract
Transmission electron microscopic studies of synthetic and natural monosodium urate crystals dried on formvar coated grids showed identical internal structures in all crystals. At higher magnification the crystals' surface showed angular or wavy irregularities, and more rarely some crystals appeared to have other tiny crystals on the surface. Protein-like surface coating was not observed except in crystals from one asymptomatic patient in whom synovial fluid was loaded with monosodium urate crystals, but no inflammatory cells were present. Heated synthetic monosodium urate crystals retained the ultrastructural characteristics in their interior but they lost their needle or rod-like shape. Transmission electron microscopic study of monosodium urate crystals dried on formvar coated grids provides a quick method of investigating crystal ultrastructure.
Full text
PDF


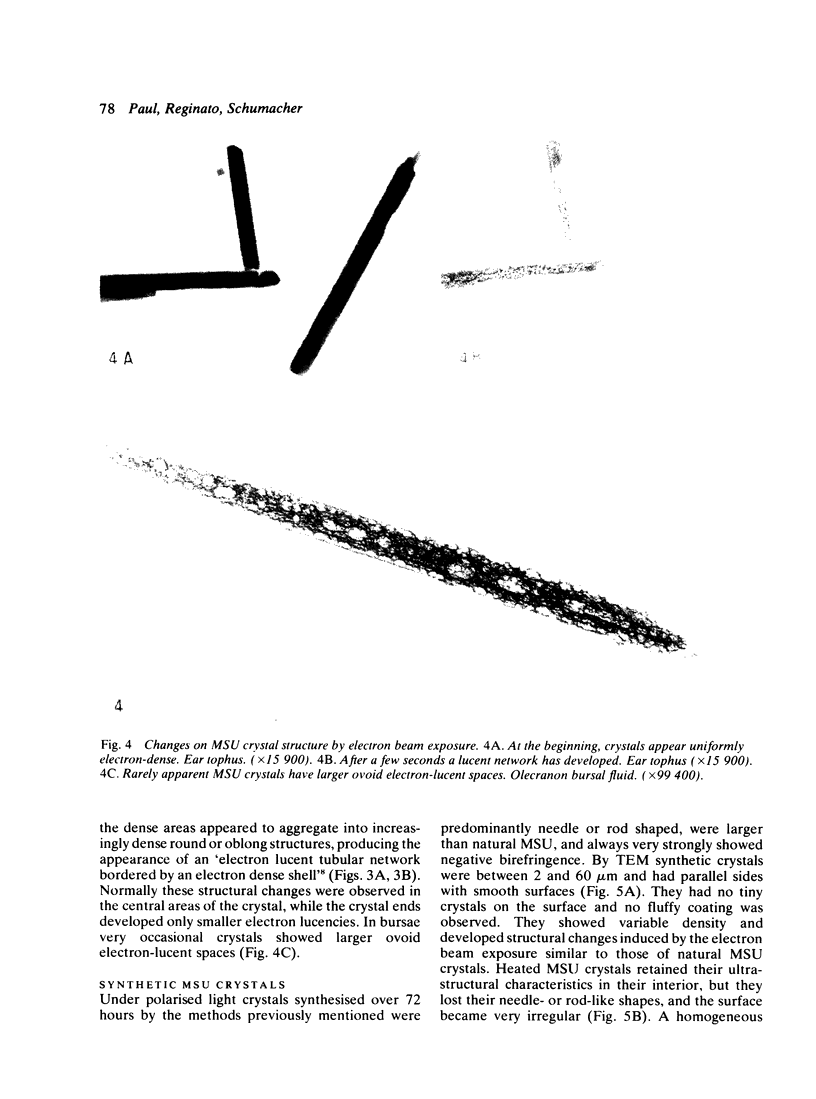



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agudelo C. A., Schumacher H. R. The synovitis of acute gouty arthritis. A light and electron microscopic study. Hum Pathol. 1973 Jun;4(2):265–279. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(73)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campion D. S., Bluestone R., Klinenberg J. R. Displacement by uricosuric agents of sodium urate bound to human serum albumin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 May 1;23(11):1653–1657. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90378-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Dieppe P. A., Tyler G., Chapman S. K., Willoughby D. A. The identification of particulate matter in biological tissues and fluids. J Pathol. 1977 Jan;121(1):37–40. doi: 10.1002/path.1711210106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Doyle D. V., Levison D. A. A practical method for the identification of particulate and crystalline material in paraffin--embedded tissue specimens. J Pathol. 1980 Jun;131(2):165–173. doi: 10.1002/path.1711310209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denko C. W., Whitehouse M. W. Experimental inflammation induced by naturally occurring microcrystalline calcium salts. J Rheumatol. 1976 Mar;3(1):54–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure G., Netter P., Malaman B., Steinmetz J., Duheille J., Gaucher A. Scanning electron microscopic study of microcrystals implicated in human rheumatic diseases. Scan Electron Microsc. 1980;(3):163–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Kozin F., Chow D., May J., Skosey J. L. Adsorption of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomal enzymes to monosodium urate crystals. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Nov-Dec;20(8):1538–1542. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon G. V., Schumacher H. R. Electron microscopic study of depot corticosteroid crystals with clinical studies after intra-articular injection. J Rheumatol. 1979 Jan-Feb;6(1):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL R. R., SEEGMILLER J. E. Uricolysis by human leukocytes. Nature. 1962 Nov 3;196:482–483. doi: 10.1038/196482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbacher P., Schumacher H. R. Immunoglobulin in tophi and on the surface of monosodium urate crystals. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Apr;21(3):353–361. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig S., Gorevic P., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Crystal deposition disease. Diagnosis by electron microscopy. Am J Med. 1977 Jul;63(1):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLERMEYER R. W., BRECKENRIDGE R. T. THE INFLAMMATORY PROCESS IN ACUTE GOUTY ARTHRITIS. I. ACTIVATION OF HAGEMAN FACTOR BY SODIUM URATE CRYSTALS. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kippen I., Klinenberg J. R., Weinberger A., Wilcox W. R. Factors affecting urate solubility in vitro. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Jul;33(4):313–317. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozin F., McCarty D. J. Protein adsorption to monosodium urate, calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate, and silica crystals: relationship to the pathogenesis of crystal-induced inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19 (Suppl 3):433–438. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197605/06)19:3+<433::aid-art1780190718>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTY D. J., Jr, FAIRES J. S. A comparison of the duration of local anti-inflammatory effect of several adrenocorticosteroid esters--a bioassay technique. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1963 May;5:284–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel N. S. Structural changes in sodium urate crystals on heating. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jun;23(6):772–776. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naff G. B., Byers P. H. Complement as a mediator of inflammation in acute gouty arthritis. I. Studies on the reaction between human serum complement and sodium urate crystals. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 May;81(5):747–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker F., Odland G. F. Ultrastructural and lipid biochemical comparisons of human eruptive, tuberous and planar xanthomas. Isr J Med Sci. 1973 Apr;9(4):395–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P., Steele A. D., McCarty D. J., Jr Compensated polarized light microscopy. Identification of crystals in synovial fluids from gout and pseudogout. JAMA. 1968 Feb 12;203(7):508–512. doi: 10.1001/jama.203.7.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritzker K. P., Phillips H., Luk S. C., Koven I. H., Kiss A., Houpt J. B. Pseudotumor of temporomandibular joint: destructive calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate arthropathy. J Rheumatol. 1976 Mar;3(1):70–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritzker K. P., Zahn C. E., Nyburg S. C., Luk S. C., Houpt J. B. The ultrastructure of urate crystals in gout. J Rheumatol. 1978 Spring;5(1):7–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle J. M., Bluhm G. B., Barnhart M. I. Ultrastructural study of leucocytes and urates in gouty arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1967 Sep;26(5):389–401. doi: 10.1136/ard.26.5.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R. Ultrastructural findings in chondrocalcinosis and pseudogout. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19 (Suppl 3):413–425. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197605/06)19:3+<413::aid-art1780190715>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak H. K., Cooper S. M., Wilcox W. R. Studies on the nucleation of monosodium urate at 37 degrees c. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 May;23(5):574–580. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallingford W. R., McCarty D. J. Differential membranolytic effects of microcrystalline sodium urate and calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):100–112. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]