Abstract
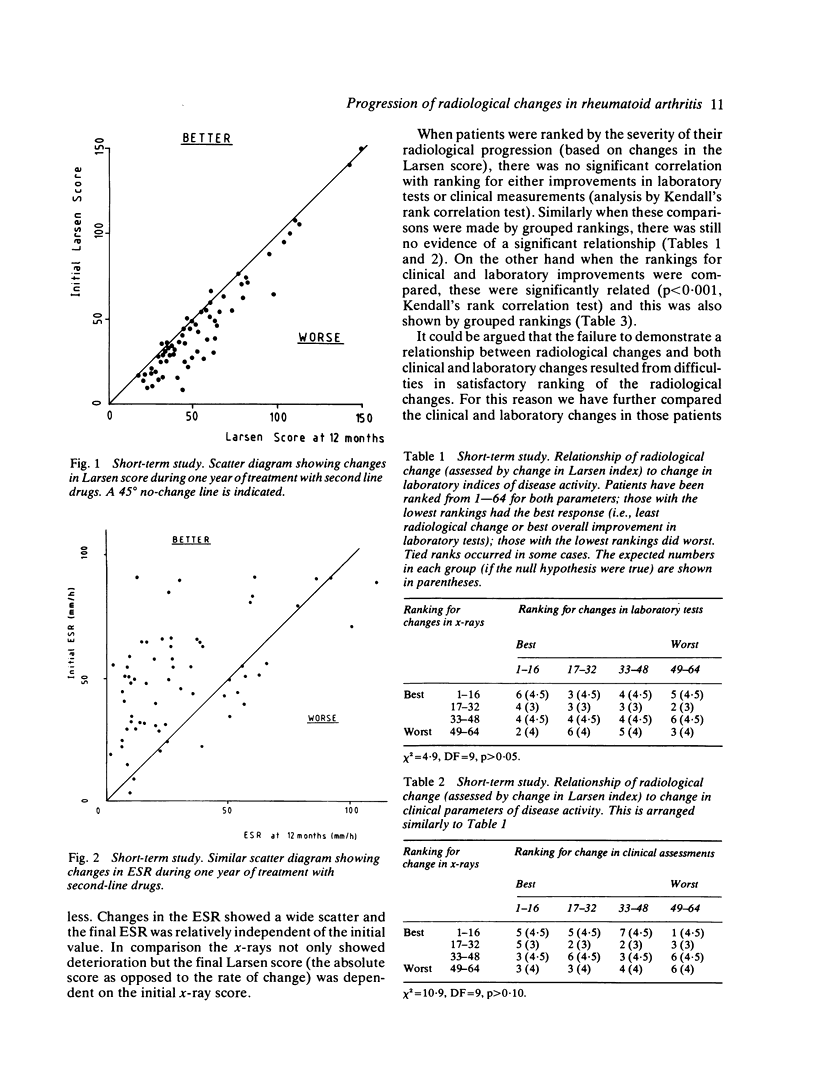
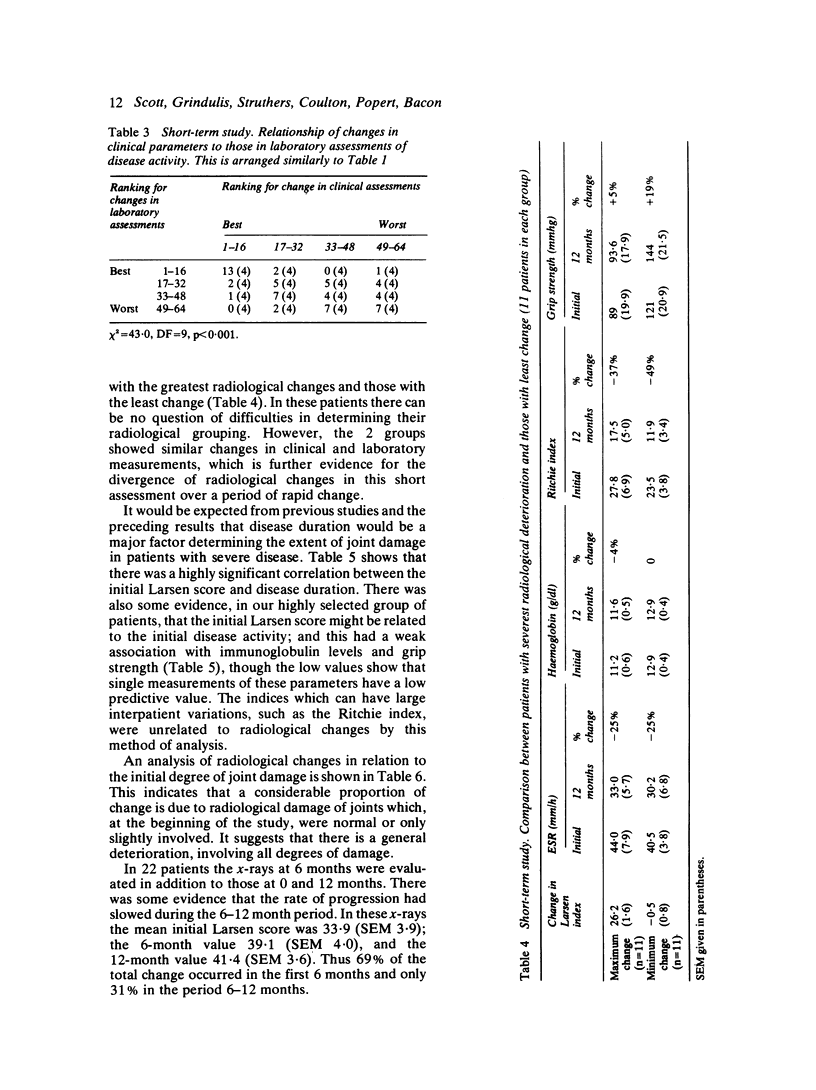
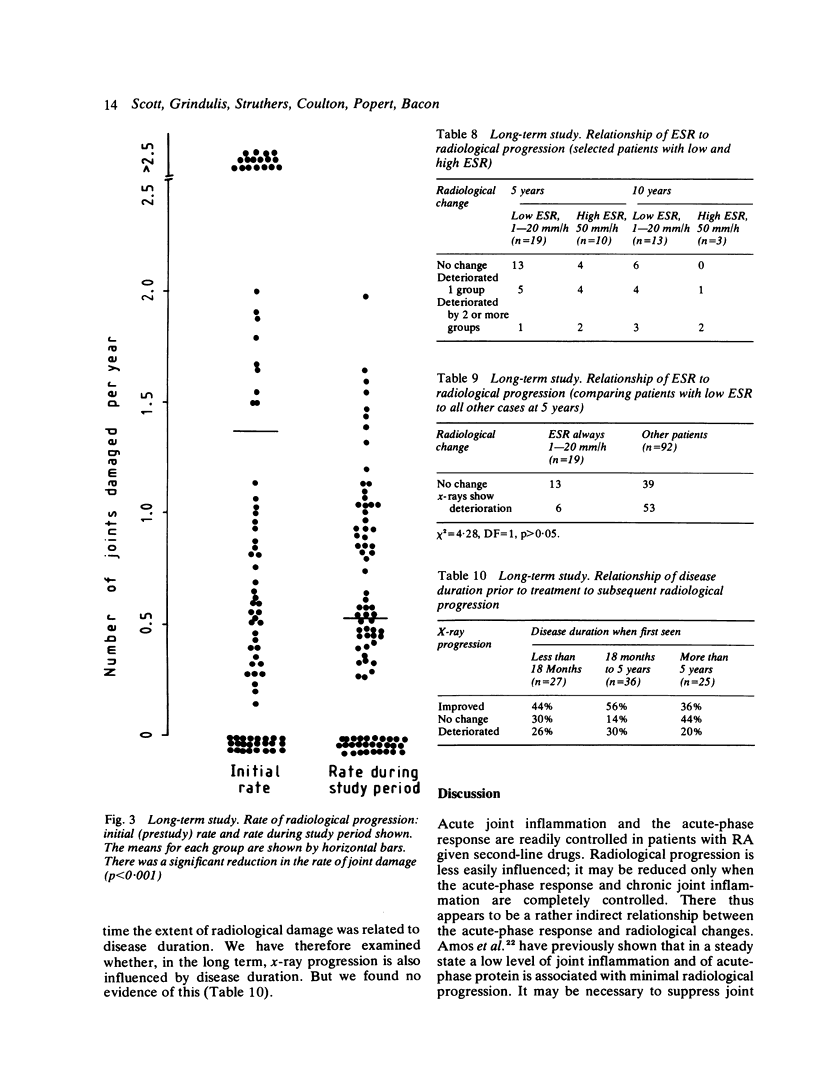
A prospective study over one year of patients who had active rheumatoid arthritis discovered 64 who had received treatment for an adequate time with second-line drugs. In these patients there was evidence of continuing joint destruction as shown by radiological progression. During the year there were highly significant correlations between improvements in clinical and laboratory measurements, but neither group of tests was related to the degree of radiological change. However, in the second 6 months of treatment there was evidence that radiological progression was reduced. In a second prospective study of 88 patients with rheumatoid arthritis given prolonged, intensive therapy with second-line drugs and followed up for 10 years two-thirds showed radiological progression. However, the number of joints damaged per year fell significantly during the study period. There was a divergence between deterioration in radiological features and improvements in the ESR and functional capacity, though patients with a persistently low ESR had less radiological progression. These studies provide evidence that treatment may be associated with a reduced rate of radiological progression but suggest that changes in radiological progression and clinical and laboratory measurements may result from different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aalto M., Kulonen E. Fractionation of connective-tissue-activating factors from the culture medium of silica-treated macrophages. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1979 Jun;87C(3):241–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aalto M., Kulonen E. Inhibition of protein synthesis in tendon cells by extracts from experimental granulation tissue. FEBS Lett. 1974 Dec 1;49(1):70–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80634-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aalto M., Turakainen H., Kulonen E. Effect of SiO2-liberated macrophage factor on protein synthesis in connective tissue in vitro. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1979 May;39(3):205–213. doi: 10.1080/00365517909106095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amos R. S., Constable T. J., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P., McConkey B. Rheumatoid arthritis: relation of serum C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rates to radiographic changes. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 22;1(6055):195–197. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6055.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amos R. S., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P., Walsh L., McConkey B. Rheumatoid arthritis: C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate during initial treatment. Br Med J. 1978 May 27;1(6124):1396–1396. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6124.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook A., Corbett M. Radiographic changes in early rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Feb;36(1):71–73. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evanson J. M., Jeffrey J. J., Krane S. M. Studies on collagenase from rheumatoid synovium in tissue culture. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2639–2651. doi: 10.1172/JCI105947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. F. Penicillamine in rheumatoid arthritis: adverse effects. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1979;(28):94–99. doi: 10.3109/03009747909108247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KULKA J. P., BOCKING D., ROPES M. W., BAUER W. Early joint lesions of rheumatoid arthritis; report of eight cases, with knee biopsies of lesions of less than one year's duration. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Feb;59(2):129–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean W. F., Anastassiades T. P. Long term chrysotherapy: incidence of toxicity and efficacy during sequential time periods. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 May;22(5):495–501. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulonen E., Potila M. Macrophages and the synthesis of connective tissue components. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Feb;88(1):7–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Dale K., Eek M. Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1977 Jul;18(4):481–491. doi: 10.1177/028418517701800415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A. Radiological grading of rheumatoid arthritis. An interobserver study. Scand J Rheumatol. 1973;2(3):136–138. doi: 10.3109/03009747309098833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luukkainen R., Isomäki H., Kajander A. Effect of gold treatment on the progression of erosions in RA patients. Scand J Rheumatol. 1977;6(2):123–127. doi: 10.3109/03009747709095434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luukkainen R., Kajander A., Isomäki H. Effect of gold on progression of erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. Better results with early treatment. Scand J Rheumatol. 1977;6(3):189–192. doi: 10.3109/03009747709095448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B., Amos R. S., Billingham M. E., Constable T. J., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P., Forster P. J. Rheumatoid arthritis: effects of a new agent (ICI 55 897) on serum acute phase proteins and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980 Feb;39(1):18–21. doi: 10.1136/ard.39.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P. The assessment of rheumatoid arthritis. A study based on measurements of the serum acute-phase reactants. Q J Med. 1972 Apr;41(162):115–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P., Wilkinson A. R. The effects of some anti-inflammatory drugs on the acute-phase proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1973 Oct;42(168):785–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B., Davies P., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P., Butler M., Constable T. J., Amos R. S. Effects of gold, dapsone, and prednisone on serum C-reactive protein and haptoglobin and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979 Apr;38(2):141–144. doi: 10.1136/ard.38.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B., Davies P., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P., Butler M., Constable T. J. Dapsone in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1976 Aug;15(3):230–234. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/15.3.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B. New drugs for inflammation - a clinical viewpoint for their assessment. Agents Actions. 1976 Sep;6(5):593–595. doi: 10.1007/BF01971575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moberg E., Wassen E., Kjellberg S. R., Zettergren L., Scheller S., Aschan W. The early pathologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1966;357:142–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothermich N. O., Philips V. K., Bergen W., Thomas M. H. Chrysotherapy. A prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Nov-Dec;19(6):1321–1327. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothermich N. O., Philips V. K., Bergen W., Thomas M. H. Followup study of chrysotherapy. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Apr;22(4):423–423. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothermich N. O., Thomas M. H., Phillips V. K., Bergen W. Clinical trial of penicillamine in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Dec;24(12):1473–1478. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., Delamere J. P., Walton K. W. The distribution of fibronectin in the pannus in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Aug;62(4):362–368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., Wainwright A. C., Walton K. W., Williamson N. Significance of fibronectin in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Apr;40(2):142–153. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.2.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. T., Lidsky M. D., Collins L. C., Moreland J. Methods of scoring the progression of radiologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of radiologic, clinical and laboratory abnormalities. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Nov-Dec;14(6):706–720. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiokawa Y., Horiuchi Y., Honma M., Kageyama T., Okada T., Azuma T. Clinical evaluation of D-penicillamine by multicentric double-blind comparative study in chronic rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Nov-Dec;20(8):1464–1472. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigler J. W., Bluhm G. B., Duncan H., Sharp J. T., Ensign D. C., McCrum W. R. Gold salts in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A double-blind study. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):21–26. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W., Bluhm G. B. Rater reliability in reading PA films of hands for bone and cartilage changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Rheumatol Inflamm. 1982;5(2):198–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman M. H., Hannifin D. M. Management of rheumatoid arthritis with oral gold. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Aug;22(8):922–925. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley D. E., Crossley M. J., Evanson J. M. Collagenase at sites of cartilage erosion in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jul-Aug;20(6):1231–1239. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright V., Amos R. Do drugs change the course of rheumatoid arthritis? Br Med J. 1980 Apr 5;280(6219):964–966. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6219.964-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


