Abstract
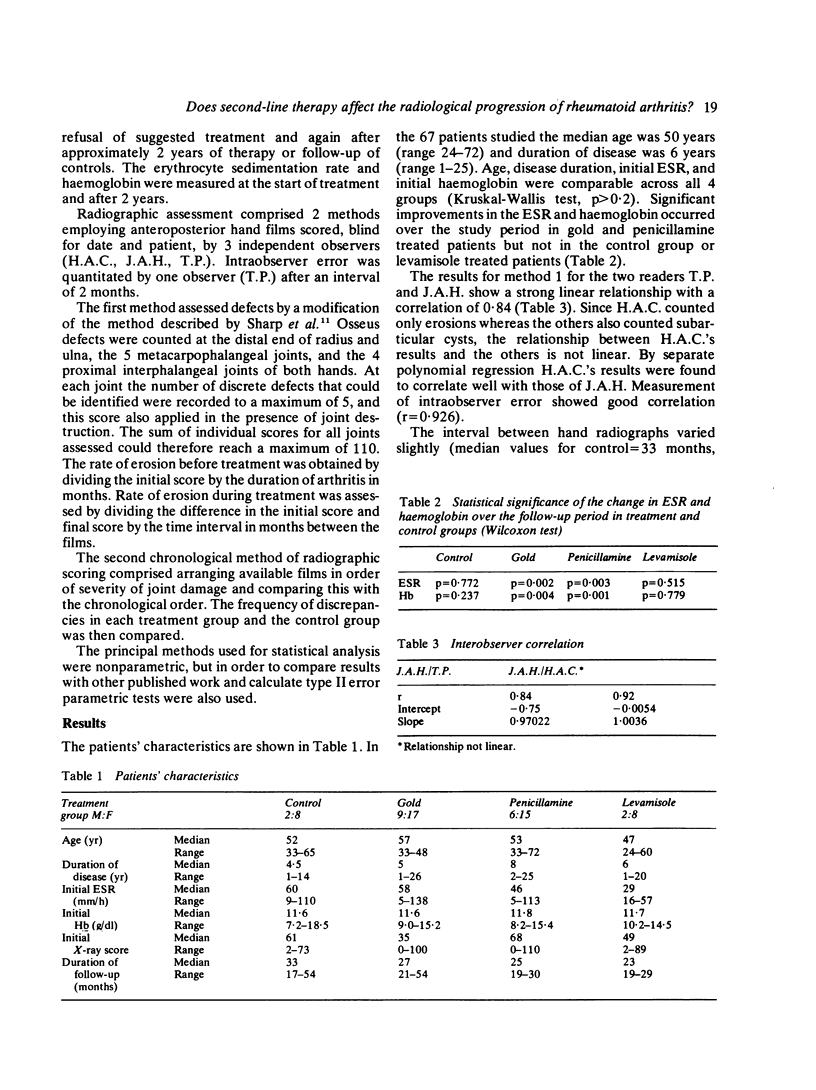
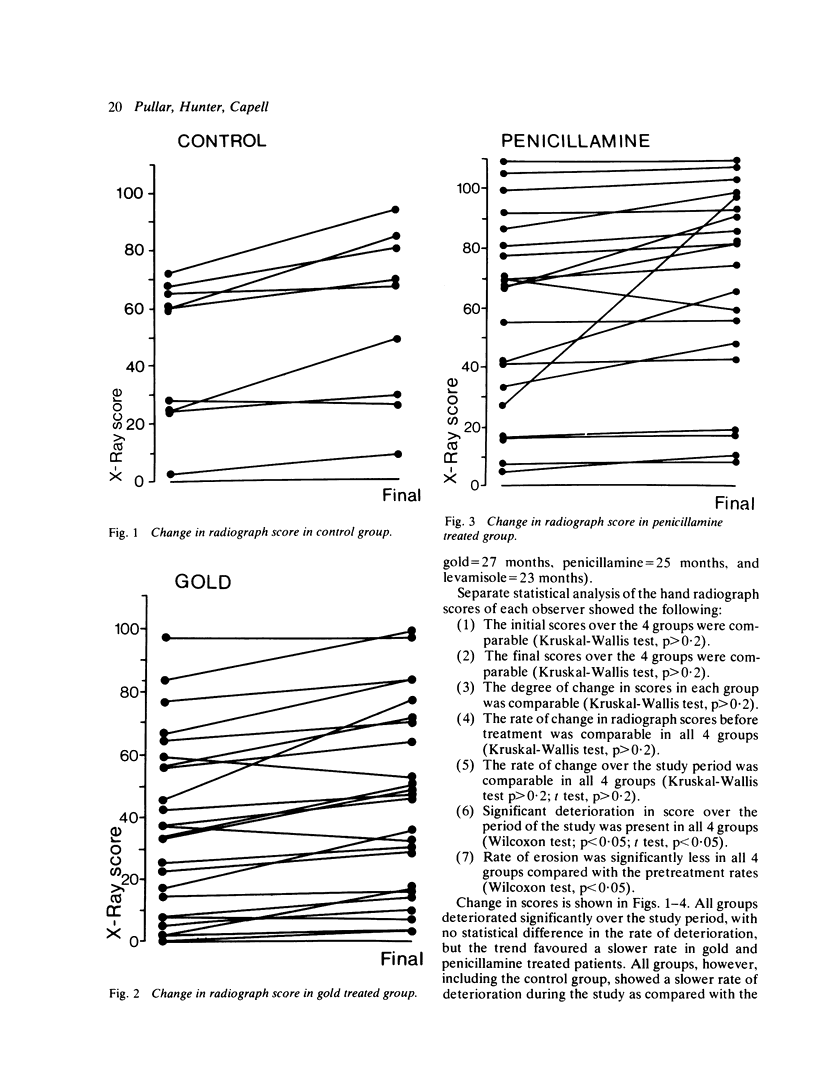
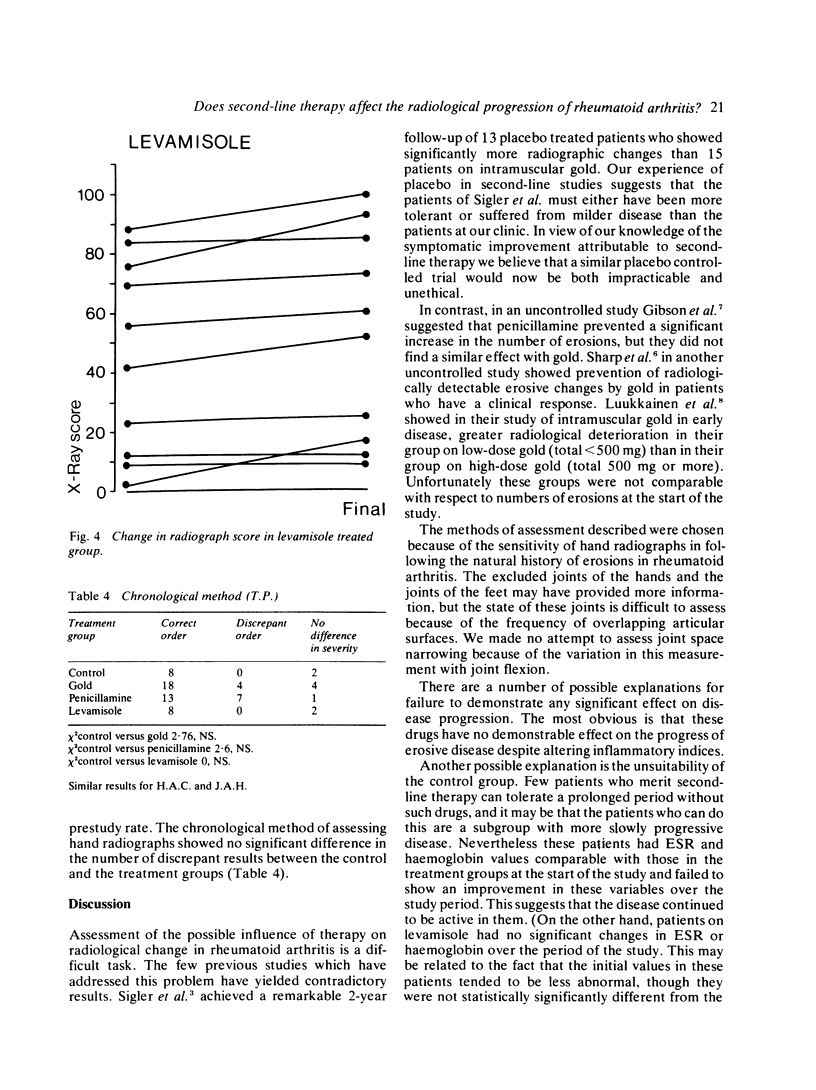
The effect of 'second-line' drugs on radiological progression in rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, and previous studies have yielded contradictory results. Sixty-seven patients with rheumatoid arthritis have been followed up clinically and radiologically for approximately 2 years (26 patients were receiving intramuscular gold, 21 penicillamine, 10 levamisole, and there were 10 controls who had consistently refused second-line therapy). Patients on gold and penicillamine showed improvement in erythrocyte sedimentation rate and haemoglobin over 2 years which was not seen in levamisole and control patients, but hand radiograph scores in all 4 groups showed statistically significant deterioration. There was a trend towards slowing of the rate of erosion in the gold and penicillamine groups in comparison with controls, but healing of erosions was extremely unusual.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bluhm G. B., Smith D. W., Mikulaschek W. M. Radiologic assessment of benoxaprofen therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Rheumatol Inflamm. 1982;5(2):186–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook A., Corbett M. Radiographic changes in early rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Feb;36(1):71–73. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capell H. A., Hunter J. A., Rennie J. A., Murdoch R. M. Levamisole - a possible alternative to gold and penicillamine in the longterm treatment of rheumatoid arthritis? J Rheumatol. 1981 Sep-Oct;8(5):730–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Controlled trial of D(-)penicillamine in severe rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1973 Feb 10;1(7798):275–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day A. T., Golding J. R., Lee P. N., Butterworth A. D. Penicillamine in rheumatoid disease: a long-term study. Br Med J. 1974 Feb 2;1(5900):180–183. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5900.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Huskisson E. C., Wojtulewski J. A., Scott P. J., Balme H. W., Burry H. C., Grahame R., Hart F. D. Evidence that D-penicillamine alters the course of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1976 Aug;15(3):211–215. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/15.3.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luukkainen R., Isomäki H., Kajander A. Effect of gold treatment on the progression of erosions in RA patients. Scand J Rheumatol. 1977;6(2):123–127. doi: 10.3109/03009747709095434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullar T., Hunter J. A., Capell H. A. Gold and penicillamine therapy: is shared care with general practitioners effective and safe? Rheumatol Rehabil. 1982 Aug;21(3):139–144. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/21.3.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothermich N. O., Thomas M. H., Phillips V. K., Bergen W. Clinical trial of penicillamine in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Dec;24(12):1473–1478. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. T., Lidsky M. D., Collins L. C., Moreland J. Methods of scoring the progression of radiologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of radiologic, clinical and laboratory abnormalities. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Nov-Dec;14(6):706–720. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. T., Lidsky M. D., Duffy J. Clinical responses during gold therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Changes in synovitis, radiologically detectable erosive lesions, serum proteins, and serologic abnormalities. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 May;25(5):540–549. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigler J. W., Bluhm G. B., Duncan H., Sharp J. T., Ensign D. C., McCrum W. R. Gold salts in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A double-blind study. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):21–26. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan R., Miller B. L., Paulus H. E. Long-term chrysotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Feb;22(2):105–110. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


