Abstract
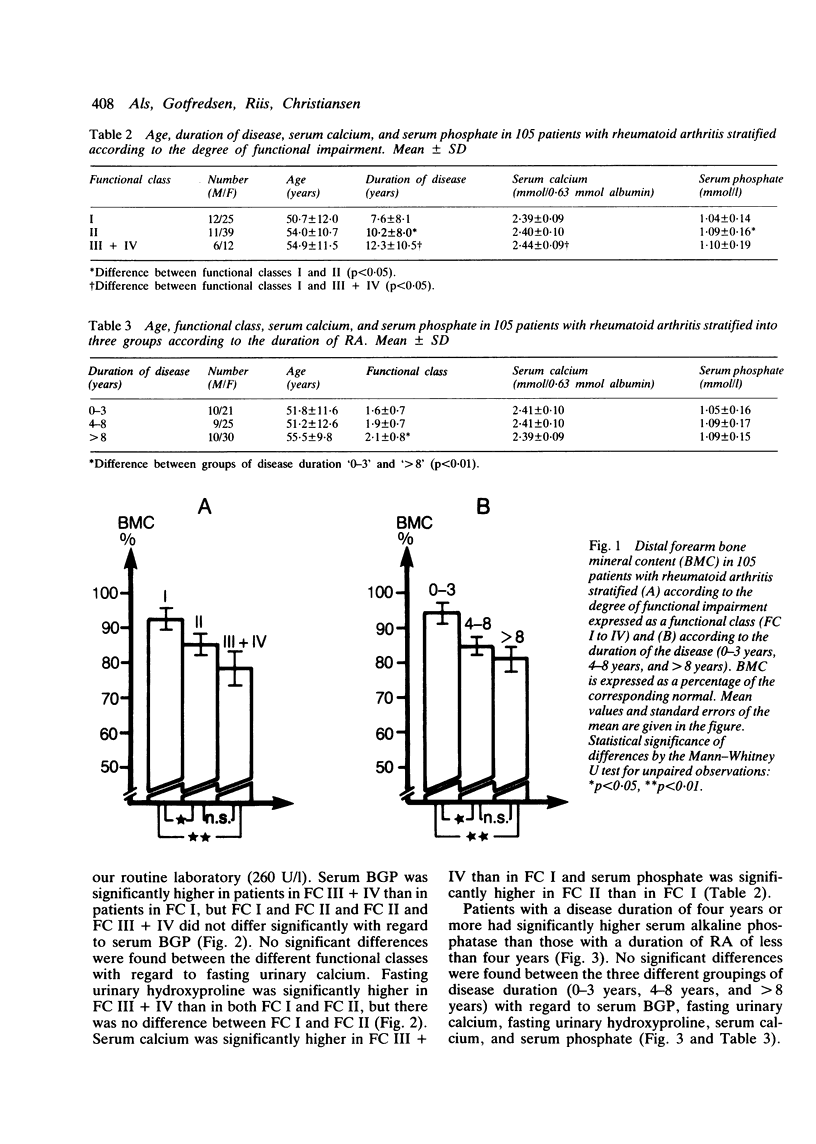
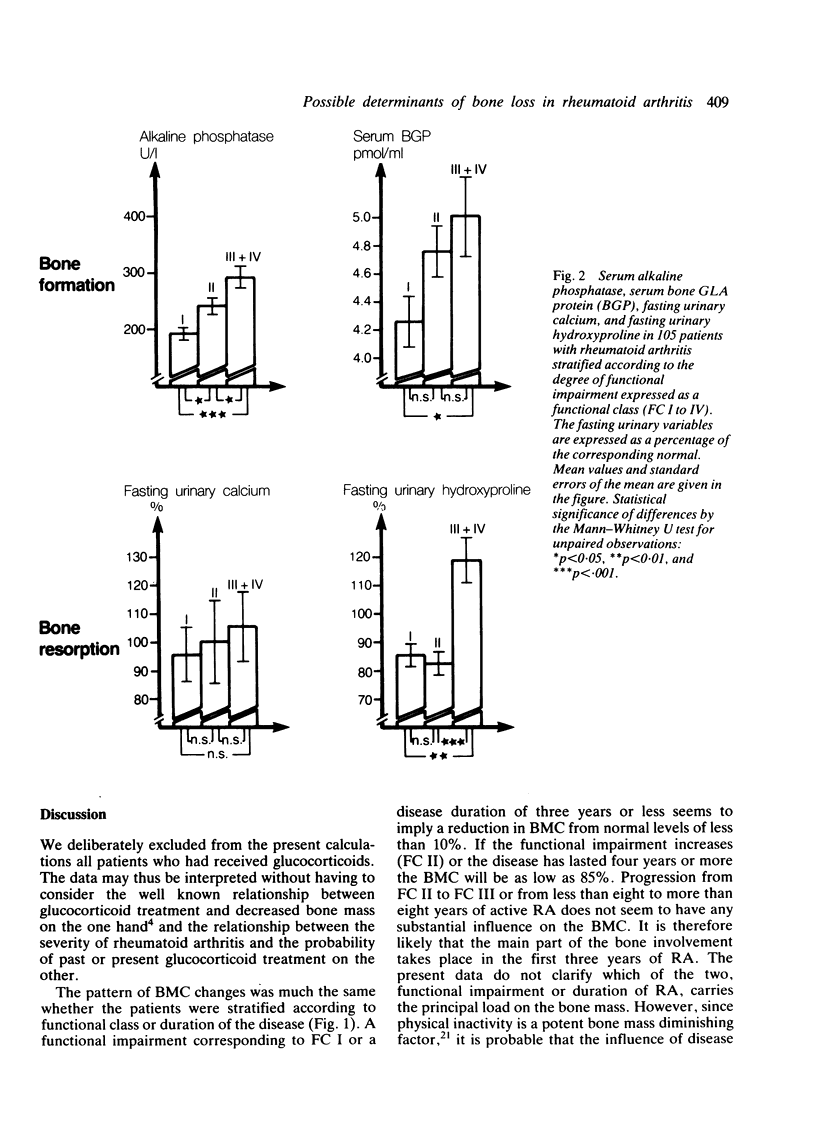
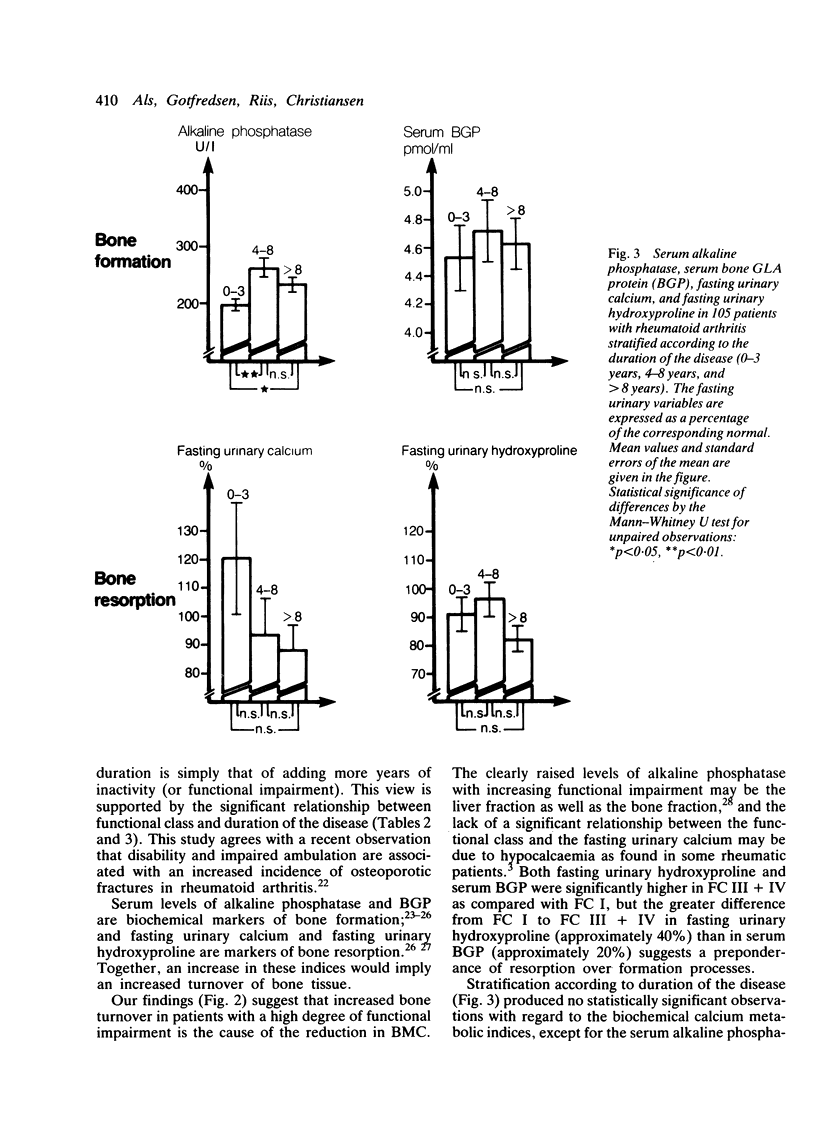
One hundred and five patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with a variety of antirheumatic drugs, excepting glucocorticoids, were stratified according to the degree of functional impairment (functional classes I to IV) and duration of the disease (0-3 years; 4-8 years; and greater than 8 years). The variables investigated were distal forearm bone mineral content (BMC), biochemical markers of bone formation: serum alkaline phosphatase and serum bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid containing protein (BGP) and biochemical markers of bone resorption: fasting urinary calcium and fasting urinary hydroxyproline. Significant relationships were found between BMC and functional impairment and duration of the disease. Indices of bone formation and bone resorption rose with increasing functional impairment, particularly those of bone resorption. It is concluded that disability induces osteopenia in rheumatoid arthritis by increasing the bone turnover with a more marked increased in resorption than in the formation processes. The effect of the disease duration is merely that of adding more years of functional impairment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Als O. S., Christiansen C., Hellesen C. Prevalence of decreased bone mass in rheumatoid arthritis. Relation to anti-inflammatory treatment. Clin Rheumatol. 1984 Jun;3(2):201–208. doi: 10.1007/BF02030755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Delmas P. D., Malaval L., Edouard C., Chapuy M. C., Meunier P. J. Serum bone Gla-protein: a specific marker for bone formation in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Lancet. 1984 May 19;1(8386):1091–1093. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92506-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi Z. S. [Treatment of diabetes with insulin]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1984 Mar;64(3):142–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen C., Naestoft J., Hvidberg E. F., Larsen N. E., Petersen B. An easy procedure for in vivo estimation of protein binding and correction of elevated serum values induced by venous stasis. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Jul 9;62(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen C., Rödbro P., Jensen H. Bone mineral content in the forearm measured by photon absorptiometry. Principles and reliability. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1975 Jul;35(4):323–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen C., Rödbro P. Long-term reproducibility of bone mineral content measurements. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Jun;37(4):321–323. doi: 10.3109/00365517709092636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockel R., Kendall M. J., Becker J. F., Hawkins C. F. Serum biochemical values in rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 Mar;30(2):166–170. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy A. C., Smith D. A., Buchanan W. W., Anderson J. B., Jasani M. K. Bone loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1975;4(2):73–79. doi: 10.3109/03009747509095618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffenburger T., Olah A. J., Dambacher M. A., Guncaga J., Lentner C., Haas H. G. Bone remodeling and calcium metabolism: a correlated histomorphometric, calcium kinetic, and biochemical study in patients with osteoporosis and Paget's Disease. Metabolism. 1977 Jun;26(6):589–606. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazess R. B., Whedon G. D. Immobilization and bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 1983 May;35(3):265–267. doi: 10.1007/BF02405043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordin B. E. Diagnostic procedures in disorders of calcium metabolism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1978 Jan;8(1):55–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1978.tb01350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka M., Rekonen A., Kuikka J., Anttinen J. Bone mineral density in rheumatoid arthritis measured by the gamma transmission method. Scand J Rheumatol. 1975;4(1):28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Williamson M. K., Lothringer J. W. Origin of the vitamin K-dependent bone protein found in plasma and its clearance by kidney and bone. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12760–12766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pødenphant J., Larsen N. E., Christiansen C. An easy and reliable method for determination of urinary hydroxyproline. Clin Chim Acta. 1984 Sep 15;142(1):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(84)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. M., Kennedy N. S., Smith M. A., Tothill P., Nuki G. Total body calcium in rheumatoid arthritis: effects of disease activity and corticosteroid treatment. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jul 31;285(6338):330–332. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6338.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickers H., Balslev I., Foltved H., Rødbro P. Bone mineral content before and after intestinal bypass operation in obese patients. Acta Med Scand. 1981;209(3):203–207. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1981.tb11577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringe J. D., Kuhlencordt F., Kruse H. P. Proceedings: Bone mineral determinations on long-term diabetics. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976 Jun;126(6):1300–1301. doi: 10.2214/ajr.126.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saville P. D., Kharmosh O. Osteoporosis of rheumatoid arthritis: influence of age, sex and corticosteroids. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Oct;10(5):423–430. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skibsted Als O., Gotfredsen A., Christiansen C. Relationship between local and total bone mineral in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and normal subjects. Clin Rheumatol. 1983 Sep;2(3):265–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02041401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtama P., Helelä T., Kalliomäki J. L. Osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis. A follow-up study. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1968;14(4):276–284. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1968.14.issue-1-4.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J., Whaley K., MacSween R. N., Nuki G., Dick W. C., Buchanan W. W. Liver disease in rheumatoid arthritis and Sjøgren's syndrome. Prospective study using biochemical and serological markers of hepatic dysfunction. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Feb;34(1):70–81. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


