Abstract
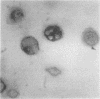
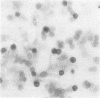
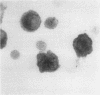
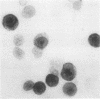
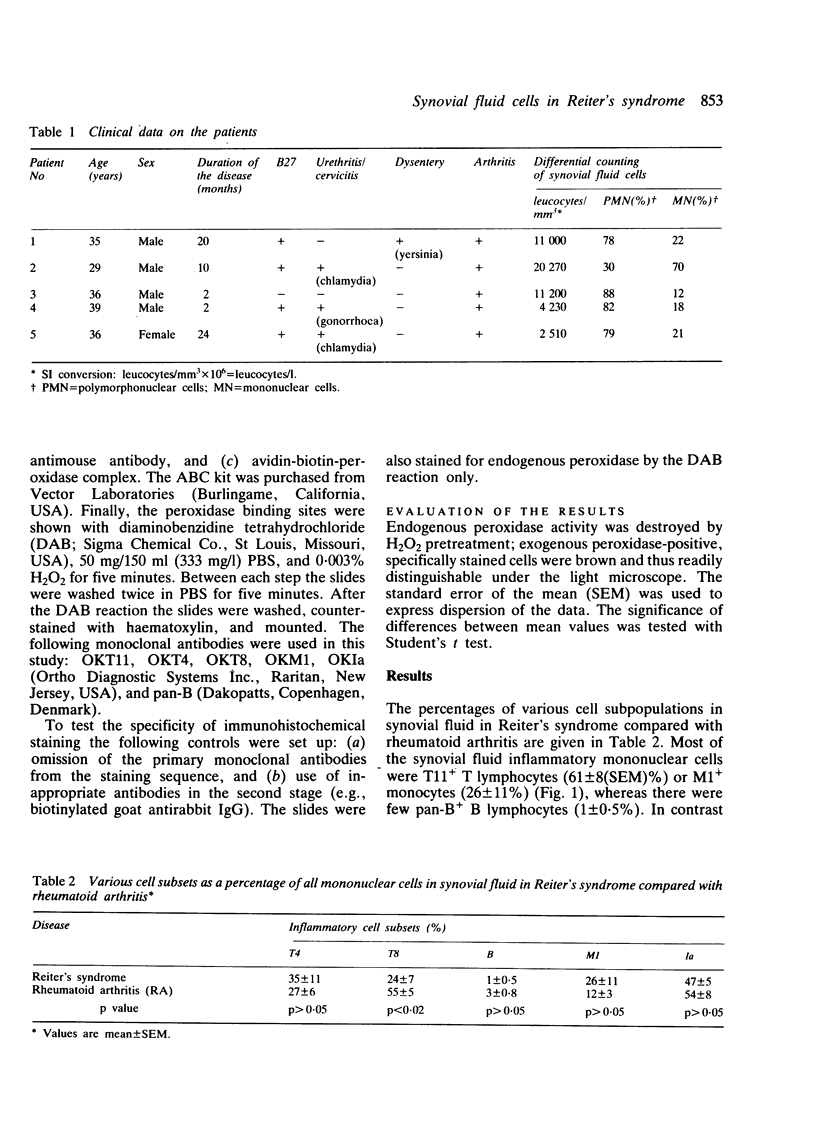
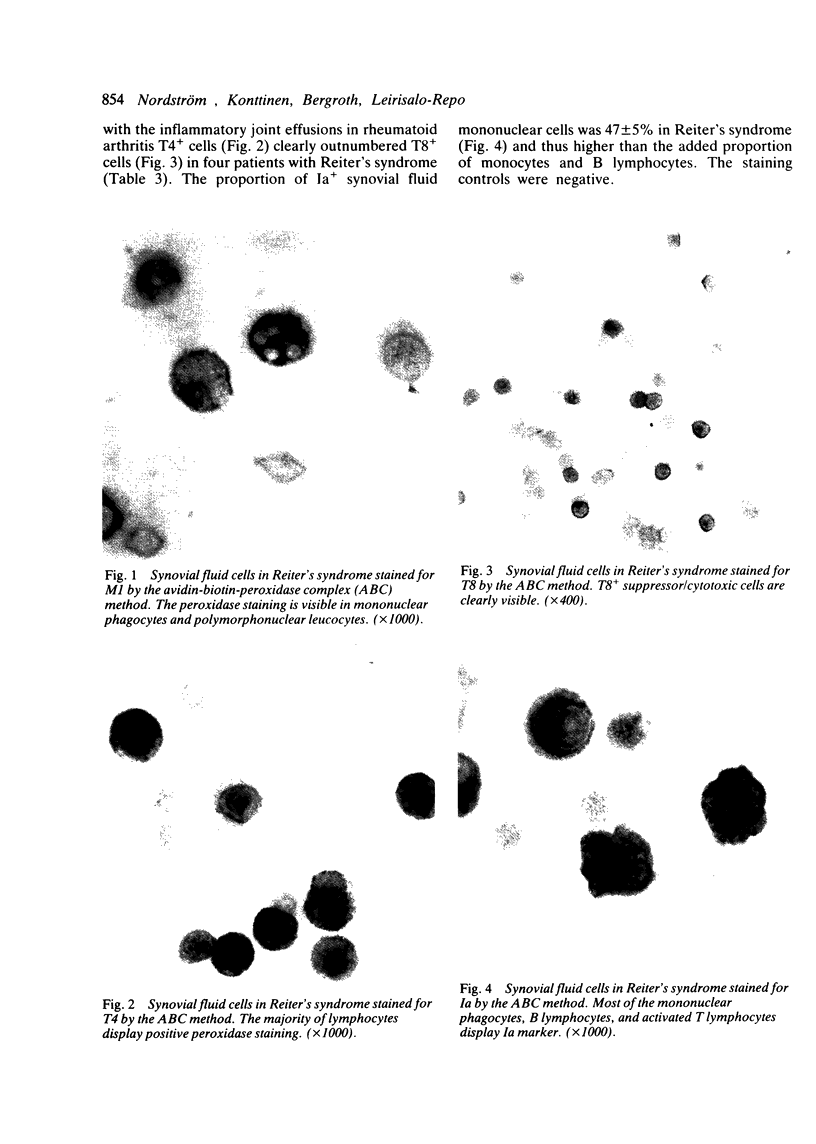
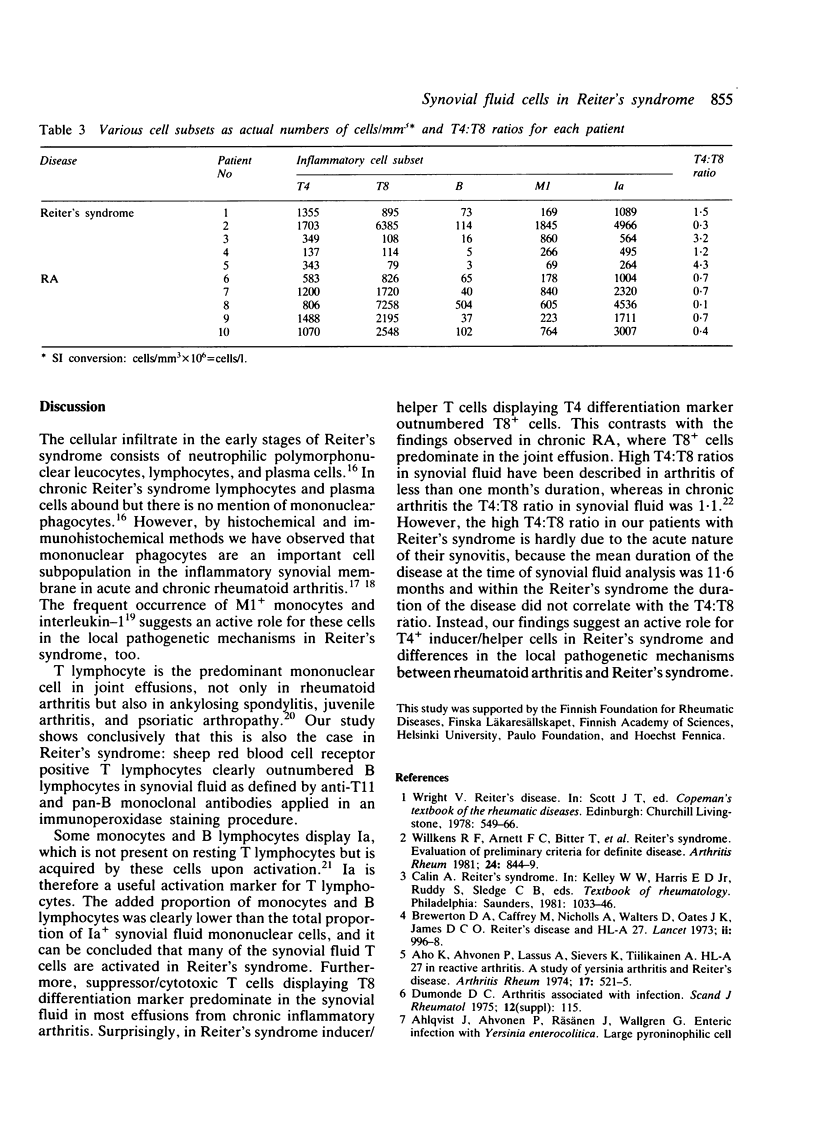
Synovial fluid cells in Reiter's syndrome were studied by cell subset specific monoclonal antibodies and avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex staining. Mean leucocyte count was 9842/mm3 (9.842 X 10(9)/l), and 71% of all cells were polymorphonuclear leucocytes. 26 +/- 11 (SEM)% and 47 +/- 5% of all mononuclear cells in synovial fluid were M1+ monocytes and Ia+ cells, respectively. T11+ T lymphocyte was the predominant synovial fluid mononuclear cell (61 +/- 8%) but, in contrast to the inflammatory joint effusions in rheumatoid arthritis, T4+ cells clearly outnumbered T8+ cells in Reiter's syndrome. Thus the synovial fluid in Reiter's syndrome contains the immunocompetent and accessory cells required for immune response, which in fact is activated as suggested by lymphocyte Ia expression. Furthermore, in contrast with rheumatoid arthritis inducer/helper cells with T4 phenotype seem to be involved preferentially in the local pathogenetic mechanisms in Reiter's syndrome.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K., Ahvonen P., Lassus A., Sievers K., Tiilikainen A. HL-A 27 in reactive arthritis. A study of Yersinia arthritis and Reiter's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Sep-Oct;17(5):521–526. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassare A. R., Weiss T. D., Tsai C. C., Arthur R. E., Moore T. L., Zuckner J. Immunoprotein deposition in synovial tissue in Reiter's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Jun;40(3):281–285. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewerton D. A., Caffrey M., Nicholls A., Walters D., Oates J. K., James D. C. Reiter's disease and HL-A 27. Lancet. 1973 Nov 3;302(7836):996–998. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Viljanen M., Tiilikainen A., Toivanen A. Persistence of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies to Yersinia in yersinia arthritis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):424–429. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konttinen Y. T., Bergroth V., Nordström D., Koota K., Skrifvars B., Hagman G., Friman C., Hämäläinen M., Slätis P. Cellular immunohistopathology of acute, subacute, and chronic synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Aug;44(8):549–555. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.8.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konttinen Y. T., Reitamo S., Ranki A., Häyry P., Kankaanapä U., Wegelius O. Characterization of the immunocompetent cells of rheumatoid synovium from tissue sections and eluates. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Jan;24(1):71–79. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leino R., Vuento R., Koskimies S., Viander M., Toivanen A. Depressed lymphocyte transformation by yersinia and Escherichia coli in yersinia arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Apr;42(2):176–181. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.2.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson E., Biberfeld G. T lymphocyte subpopulations defined by monoclonal antibodies in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatic disease. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1982 Nov;9(2):93–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Pesando J. M., Ritz J., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Ia determinants on human T-cell subsets defined by monoclonal antibody. Activation stimuli required for expression. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1472–1482. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuento R., Eskola J., Leino R., Koskimies S., Viander M. IgM, IgG, and IgA synthesis in vitro in persons suffering from yersinia arthritis and in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Apr;43(2):186–191. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINBERGER H. W., ROPES M. W., KULKA J. P., BAUER W. Reiter's syndrome, clinical and pathologic observations. A long term study of 16 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1962 Feb;41:35–91. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196202000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willkens R. F., Arnett F. C., Bitter T., Calin A., Fisher L., Ford D. K., Good A. E., Masi A. T. Reiter's syndrome. Evaluation of preliminary criteria for definite disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Jun;24(6):844–849. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. D., Ihrie E. J., Dinarello C. A., Cohen P. L. Isolation of an interleukin-1-like factor from human joint effusions. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Aug;26(8):975–983. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]