Abstract
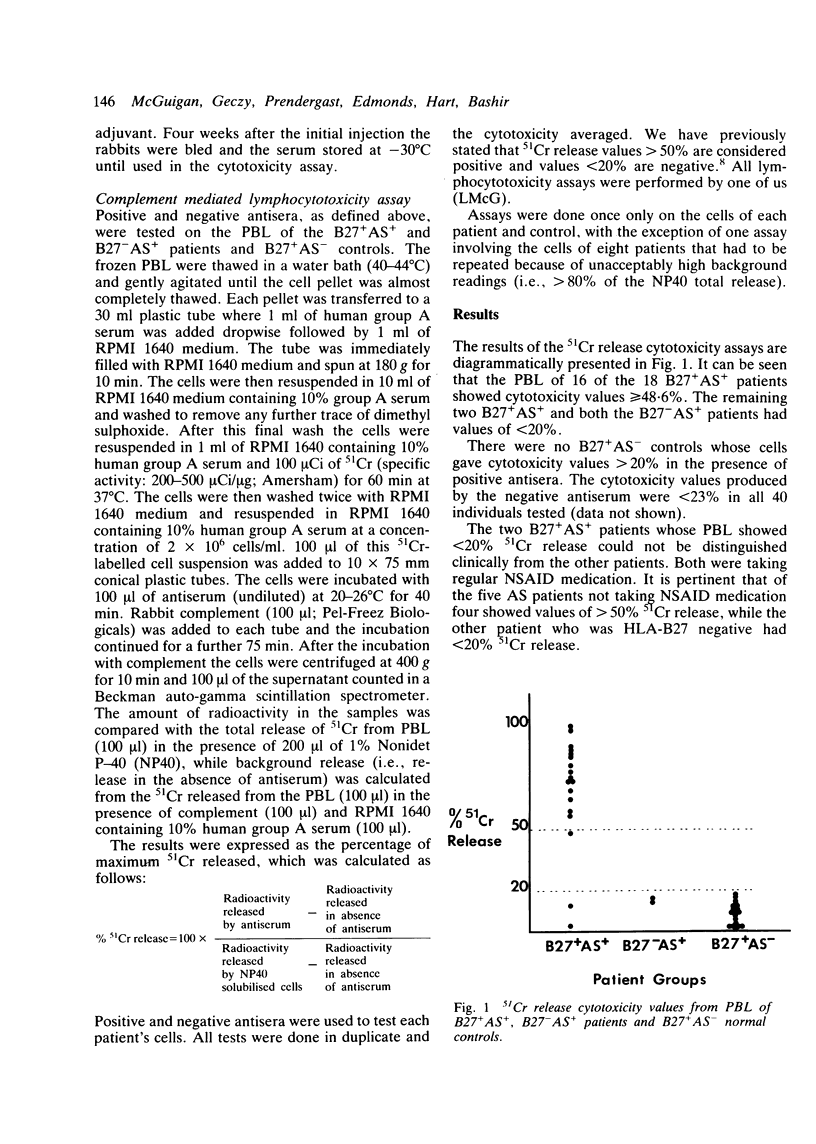
We have previously shown that antibodies raised in rabbits to certain enteric bacteria will specifically lyse, in a 51Cr release assay, the peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) of 80% of HLA-B27 positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis (B27+ AS+) but not the PBL of HLA-B27 positive normal controls (B27+ AS-). Other laboratories have been unable to reproduce these findings. This study was designed to ascertain whether this lack of reproducibility was due to a peculiarity of our B27+ AS+ patients or to technical difficulties in the complement mediated 51Cr release assay. We have shown in this blind study that the PBL of 16 out of 18 B27+ AS+ patients from a New Zealand population were lysed by our antisera but none of the PBL of 20 B27+ AS- normal controls were lysed. The phenomenon of 'cross reactivity' between certain enteric bacteria and B27+ AS+ PBL is not confined to the Sydney AS population.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer J. R., Stubbs M. M., Currey H. L., Geczy A. F. Antiserum to Klebsiella K43 BTS 1 specifically lyses lymphocytes of HLA-B27-positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis from a London population. Lancet. 1985 Feb 9;1(8424):344–345. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu A. D., Rousseau F., Israël-Assayag E., Roy R. Klebsiella related antigens in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1983 Feb;10(1):102–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds J., Geczy A. F., Sullivan J. S., Prendergast J. K., Upfold L. I., Bashir H. V. Enteric bacteria and HLA-B27 associated cell surface modification in patients with seronegative spondarthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1983 Nov;22(4 Suppl 2):75–82. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/xxii.suppl_2.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geczy A. F., Alexander K., Bashir H. V., Edmonds J. A factor(s) in Klebsiella culture filtrates specifically modifies an HLA-B27 associated cell-surface component. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):782–784. doi: 10.1038/283782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella T. D., Fritzler M. J., McNeil D. J. Ankylosing spondylitis. A disease in search of microbes. J Rheumatol. 1983 Feb;10(1):2–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella T. D., Lanteigne C., Fritzler M. J., Lewkonia R. M. Absence of impaired lymphocyte transformation to Klebsiella spp. in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Aug;43(4):590–593. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.4.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuigan L. E., Hart H. H., Gow P. J., Kidd B. L., Grigor R. R., Moore T. E. Employment in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Aug;43(4):604–606. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.4.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll J. M., Wright V. Normal range of spinal mobility. An objective clinical study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 Jul;30(4):381–386. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.4.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast J. K., Sullivan J. S., Geczy A., Upfold L. I., Edmonds J. P., Bashir H. V., Reiss-Levy E. Possible role of enteric organisms in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis and other seronegative arthropathies. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):935–941. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.935-941.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seager K., Bashir H. V., Geczy A. F., Edmonds J., de Vere-Tyndall A. Evidence for a specific B27-associated cell surface marker on lymphocytes of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Nature. 1979 Jan 4;277(5691):68–70. doi: 10.1038/277068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


