Abstract
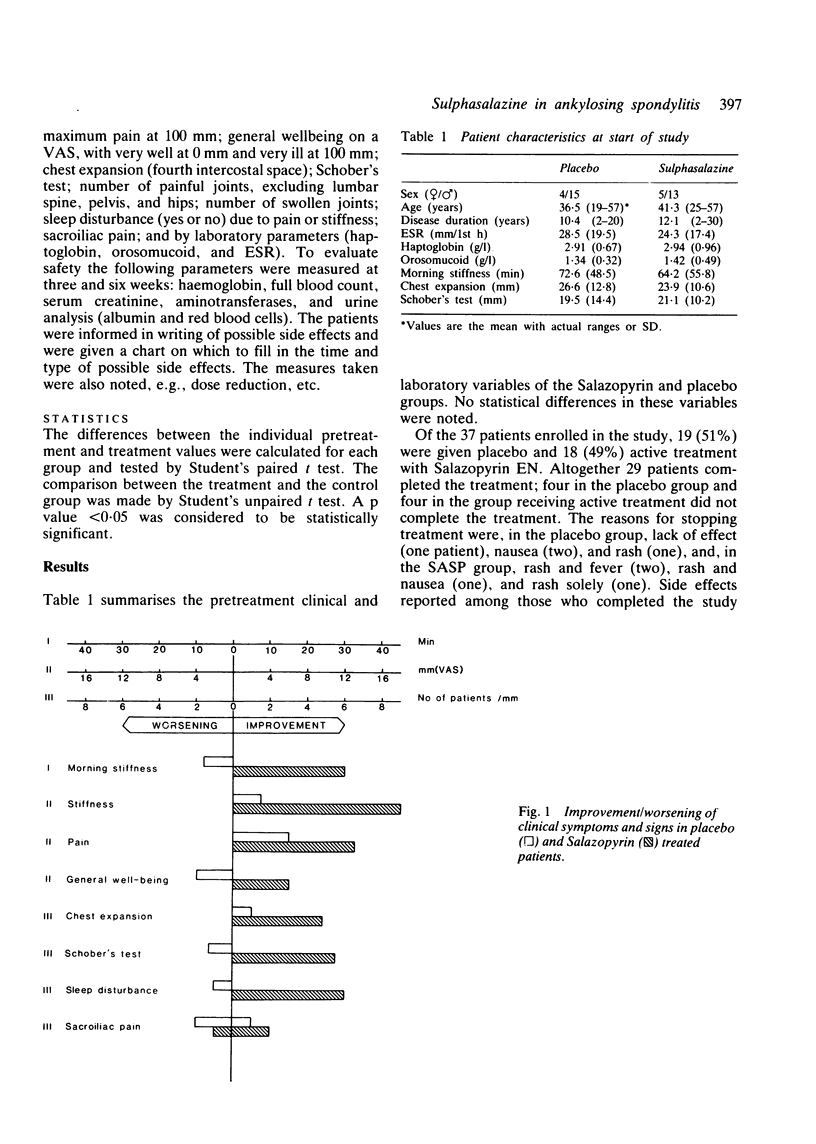
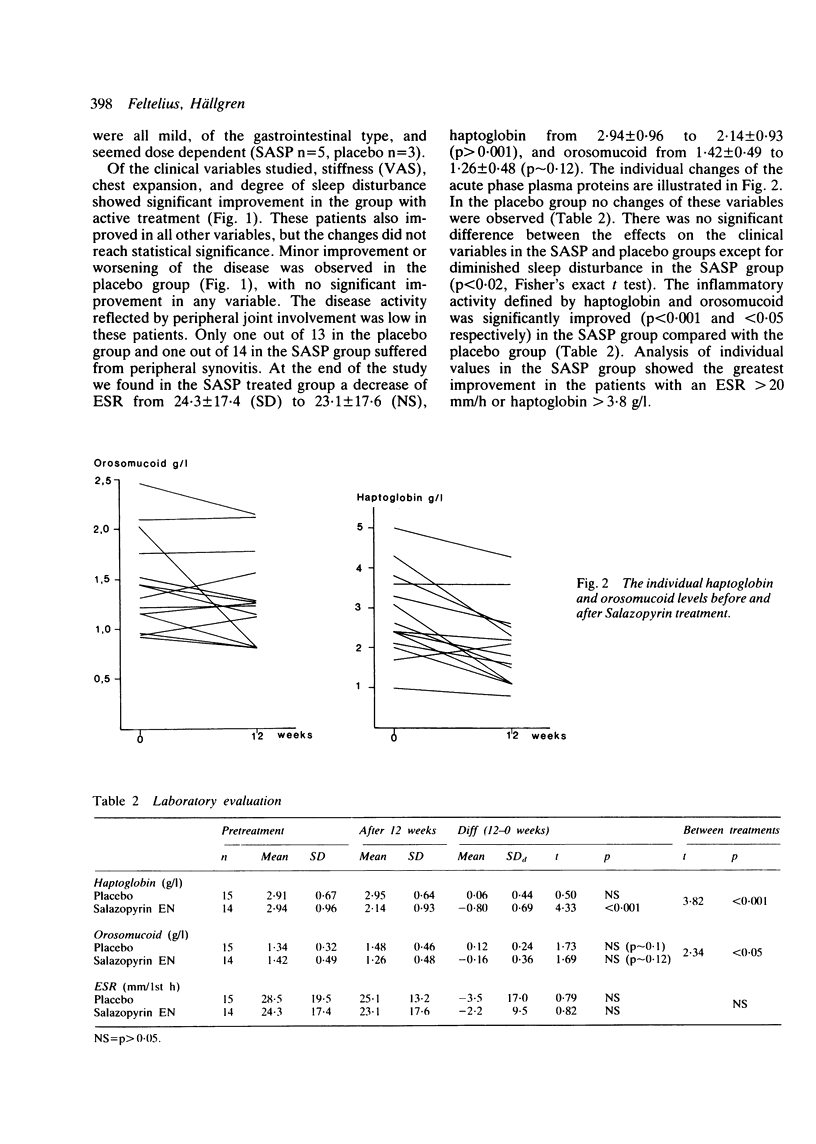
In recent years sulphasalazine has gained acceptance as an effective agent for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ankylosing spondylitis is a disease where remission inducing drugs so far have been lacking. In this double blind trial sulphasalazine was compared with placebo in 37 patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Evaluation after three months' treatment showed reduction of inflammatory activity and improvement of clinical variables. The side effects were mild. The results suggest that sulphasalazine is a potentially effective and safe drug in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird H. A., Dixon J. S., Pickup M. E., Rhind V. M., Lowe J. R., Lee M. R., Wright V. A biochemical assessment of sulphasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1982 Jan-Feb;9(1):36–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastmond C. J., Calguner M., Shinebaum R., Cooke E. M., Wright V. A sequential study of the relationship between faecal Klebsiella aerogenes and the common clinical manifestations of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Feb;41(1):15–20. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. L. "Postinfectious" arthritis. New look at an old concept with particular attention to disseminated gonococcal infection. Am J Med. 1983 Jun;74(6):925–928. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90782-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoult J. R., Moore P. K. Effects of sulphasalazine and its metabolites on prostaglandin synthesis, inactivation and actions on smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Apr;68(4):719–730. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keat A. Reiter's syndrome and reactive arthritis in perspective. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 29;309(26):1606–1615. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312293092604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen M. L. The influence of salicyl-azo-sulfapyridine on the immune response to antigenic tumour cells inoculated into the coecal lumen of C3H mice. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1978;13(8):991–997. doi: 10.3109/00365527809181381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B., Amos R. S., Durham S., Forster P. J., Hubball S., Walsh L. Sulphasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1980 Feb 16;280(6212):442–444. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6212.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein A., Das K. M., Melamed J., Murphy R. A. Comparative analysis of systemic immunological parameters in ulcerative colitis and idiopathic proctitis: effects of sulfasalazine in vivo and in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Aug;33(2):217–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenson W. F., Lobos E. Inhibition of platelet thromboxane synthetase by sulfasalazine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Jul 15;32(14):2205–2209. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUELOVE S. C., WATKINSON G., DRAPER G. Comparison of corticosteroid and sulphasalazine therapy in ulcerative colitis. Br Med J. 1962 Dec 29;2(5321):1708–1711. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5321.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


