Abstract
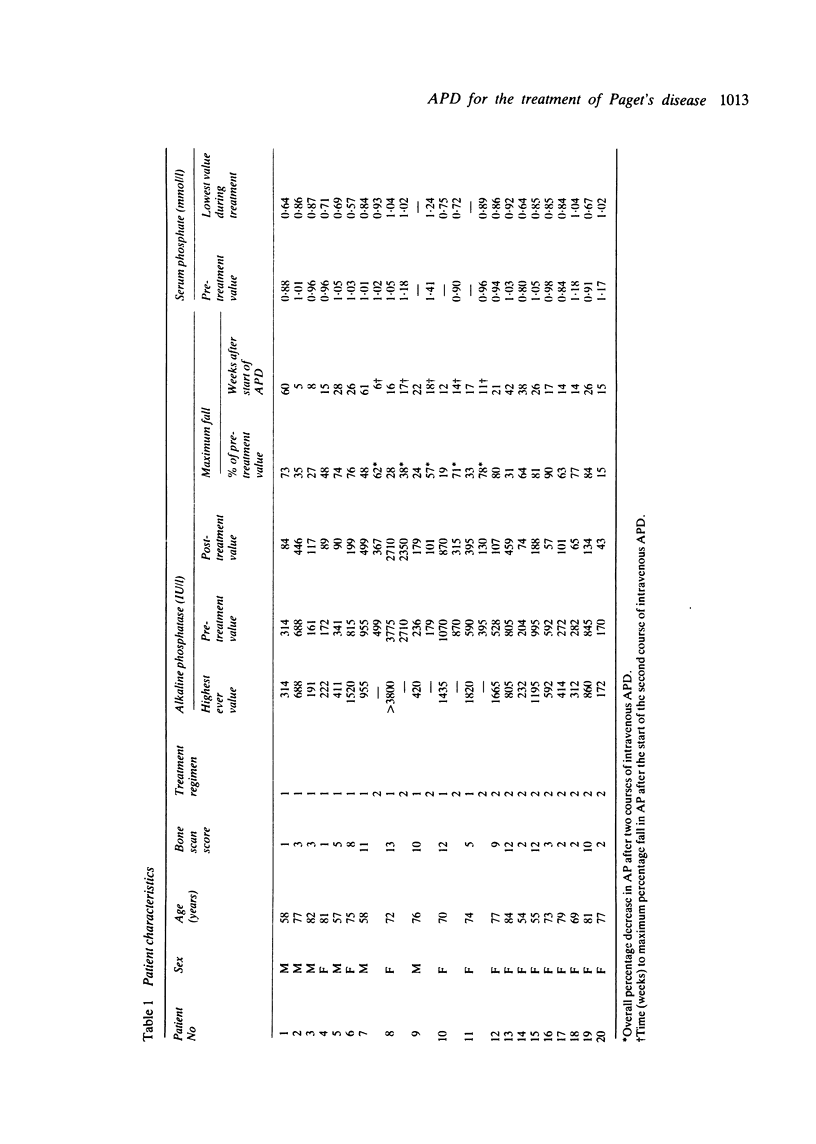
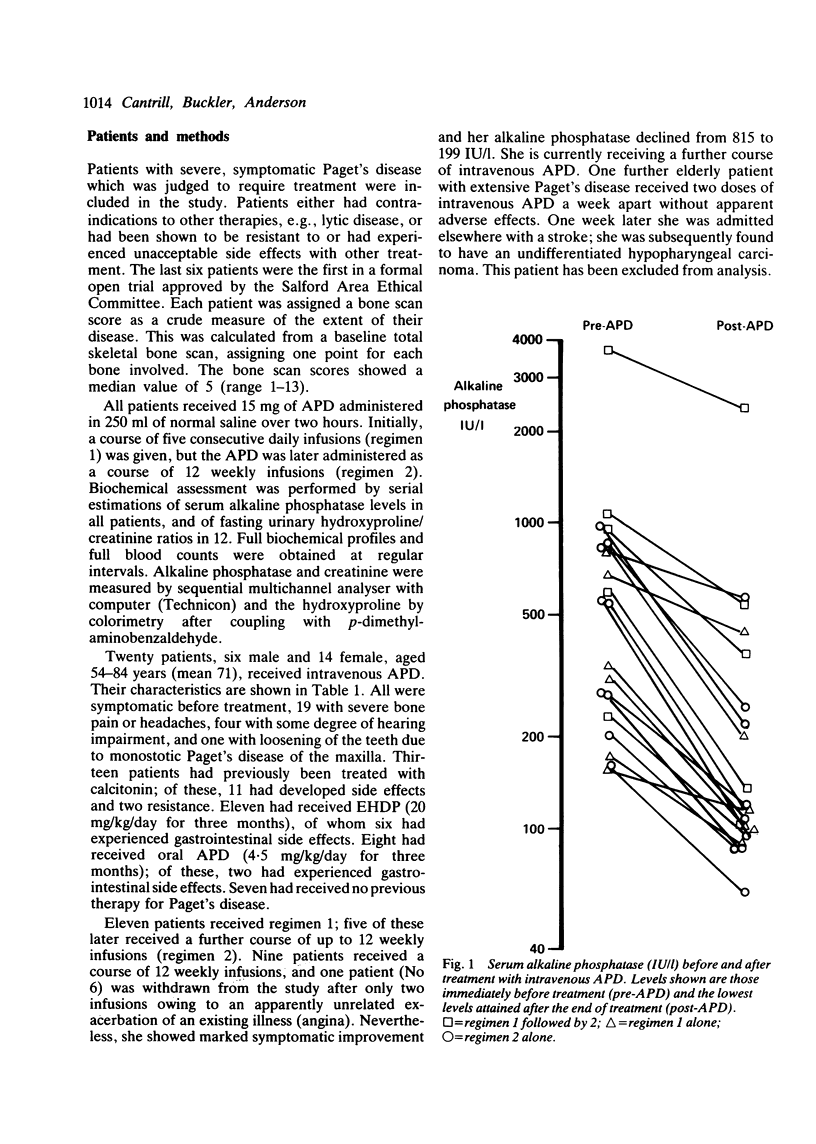
Twenty patients with severe symptomatic Paget's disease were treated with a series of 15 mg intravenous infusions of 3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate (APD). A regimen of either five consecutive days of treatment (regimen 1) or a course of 12 weekly infusions was administered (regimen 2). In five cases regimen 2 followed regimen 1 after a three month interval. Alkaline phosphatase levels fell in all patients and returned to the normal range in 12. All but one of the patients obtained symptomatic improvement. There was a median fall in alkaline phosphatase activity of 63%. Eight patients observed a transient increase in bone pain starting about 24 hours after the first infusion. Intravenous APD was well tolerated, and we conclude that it is an effective treatment for Paget's disease; this route of administration avoids the problem of poor and unpredictable gastrointestinal absorption seen when a bisphosphonate is given orally. The optimal dose and duration of APD therapy, frequency of relapse, requirement for further courses, and merits relative to other second generation bisphosphonates remain to be established.
Full text
PDF
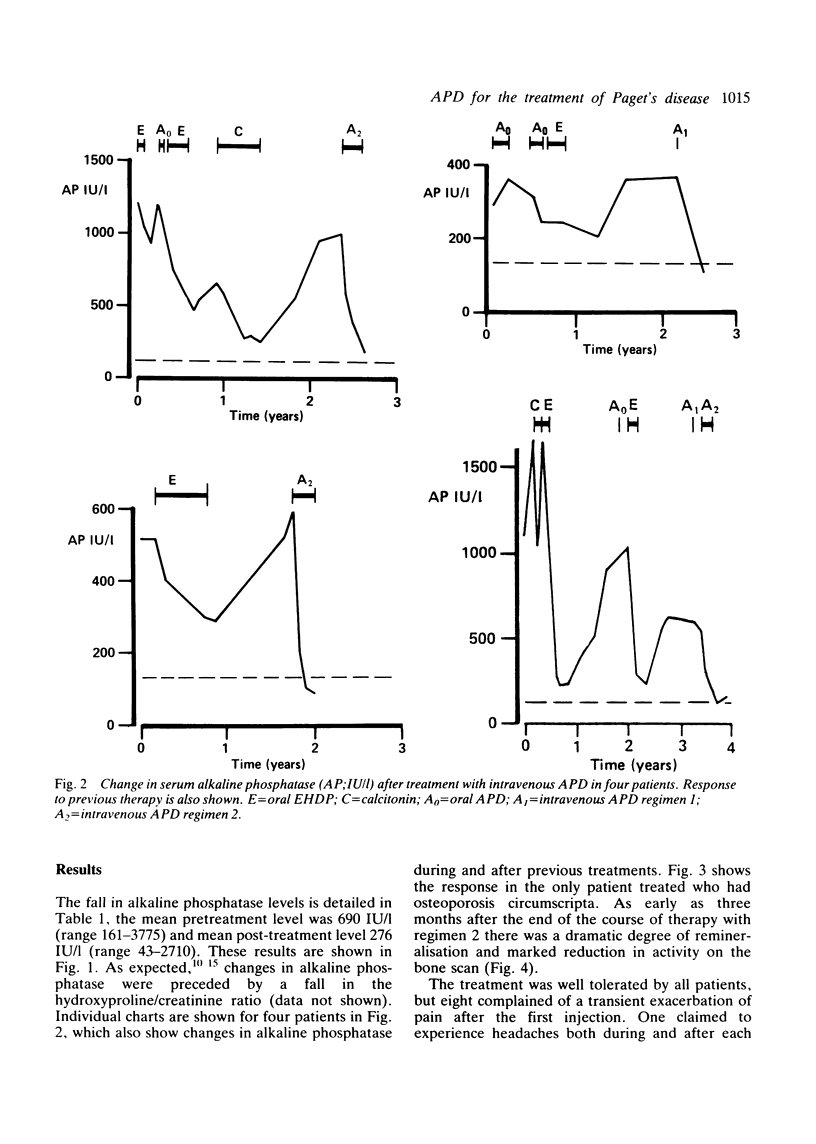
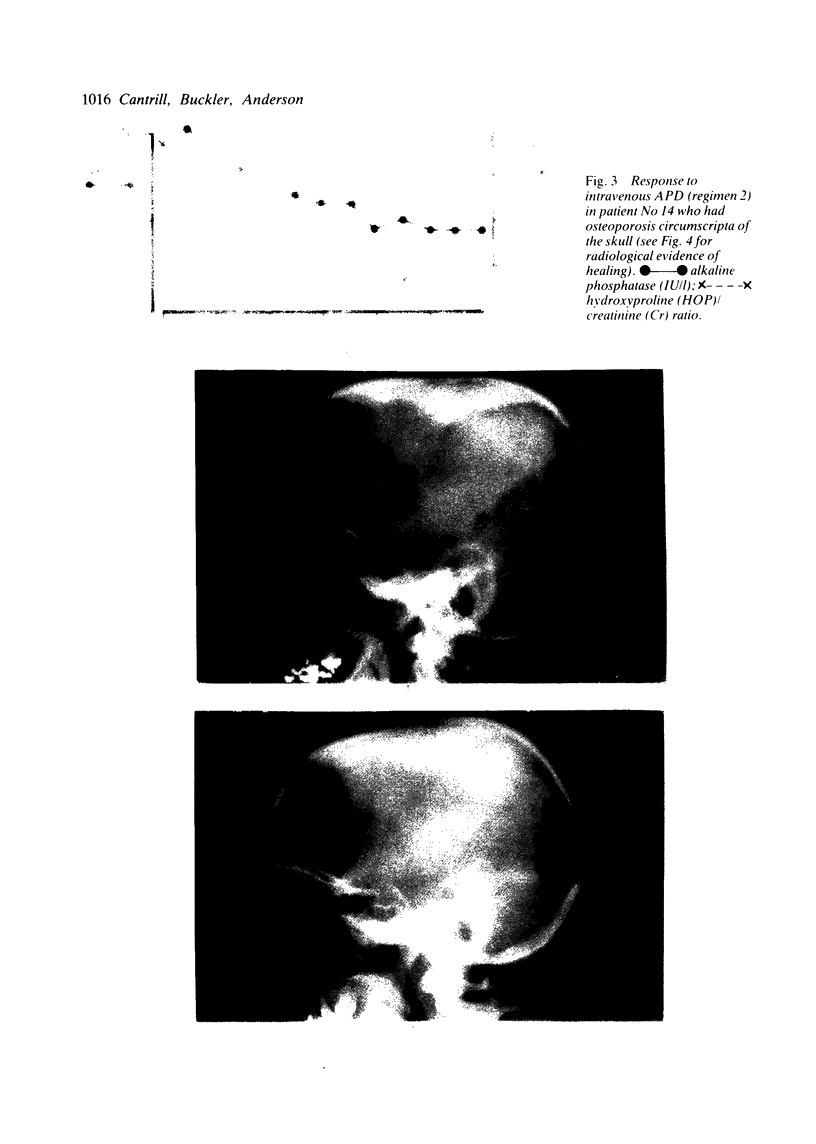


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avramides A., Flores A., DeRose J., Wallach S. Paget's disease of the bone: observations after cessation of long-term synthetic salmon calcitonin treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Mar;42(3):459–463. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-3-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce B. F., Smith L., Fogelman I., Johnston E., Ralston S., Boyle I. T. Focal osteomalacia due to low-dose diphosphonate therapy in Paget's disease. Lancet. 1984 Apr 14;1(8381):821–824. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92272-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield R., Rosner W., Skinner J., McWhorter J., Resnick L., Feldman F., Kammerman S., Ryan K., Kunigonis M., Bohne W. Diphosphonate therapy of paget's disease of bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Jan;44(1):96–106. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-1-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewis P., Prasad B. K., Anderson D. C., Willets S. Clinical experience with the use of two diphosphonates in the treatment of Paget's disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Jan;44(1):34–38. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman I., Smith L., Mazess R., Wilson M. A., Bevan J. A. Absorption of oral diphosphonate in normal subjects. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1986 Jan;24(1):57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1986.tb03254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frijlink W. B., Bijvoet O. L., te Velde J., Heynen G. Treatment of Paget's disease with (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)-1, 1-bisphosphonate (A.P.D.). Lancet. 1979 Apr 14;1(8120):799–803. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91318-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein H. S., Clifton-Bligh P., Posen S. Paget's disease of bone: experiences with 100 patients treated with salmon calcitonin. Med J Aust. 1981 Sep 19;2(6):278–280. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1981.tb128316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heynen G., Delwaide P., Bijvoet O. L., Franchimont P. Clinical and biological effects of low doses of (3 amino-1 hydroxypropylidene)-1,1-bisphosphonate (APD) in Paget's disease of bone. Eur J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;12(1):29–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1982.tb00936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mautalen C. A., Casco C. A., Gonzalez D., Ghiringhelli G. R., Massironi C., Fromm G. A., Plantalech L. Side effects of disodium aminohydroxypropylidenediphosphonate (APD) during treatment of bone diseases. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Mar 17;288(6420):828–829. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6420.828-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier P. J., Chapuy M. C., Alexandre C., Bressot C., Edouard C., Vignon C., Mathieu L., Trechsel U. Effects of disodium dichloromethylene diphosphonate on Paget's disease of bone. Lancet. 1979 Sep 8;2(8141):489–492. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91551-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael W. R., King W. R., Wakim J. M. Metabolism of disodium ethane-1-hydroxy-1,1-diphosphonate (disodium etidronate) in the rat, rabbit, dog and monkey. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1972 Apr;21(4):503–515. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(72)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recker R. R., Saville P. D. Intestinal absorption of disodium ethane-1-hydroxy-1,1-diphosphonate (disodium etidronate) using a deconvolution technique. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1973 Apr;24(4):580–589. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(73)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleeboom H. P., Bijvoet O. L., van Oosterom A. T., Gleed J. H., O'Riordan J. L. Comparison of intravenous (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)-1, 1-bisphosphonate and volume repletion in tumour-induced hypercalcaemia. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):239–243. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vellenga C. J., Mulder J. D., Bijvoet O. L. Radiological demonstration of healing in Paget's disease of bone treated with APD. Br J Radiol. 1985 Sep;58(693):831–837. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-58-693-831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates A. J., Percival R. C., Gray R. E., Atkins R. M., Urwin G. H., Hamdy N. A., Preston C. J., Beneton M. N., Russell R. G., Kanis J. A. Intravenous clodronate in the treatment and retreatment of Paget's disease of bone. Lancet. 1985 Jun 29;1(8444):1474–1477. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92253-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]