Abstract
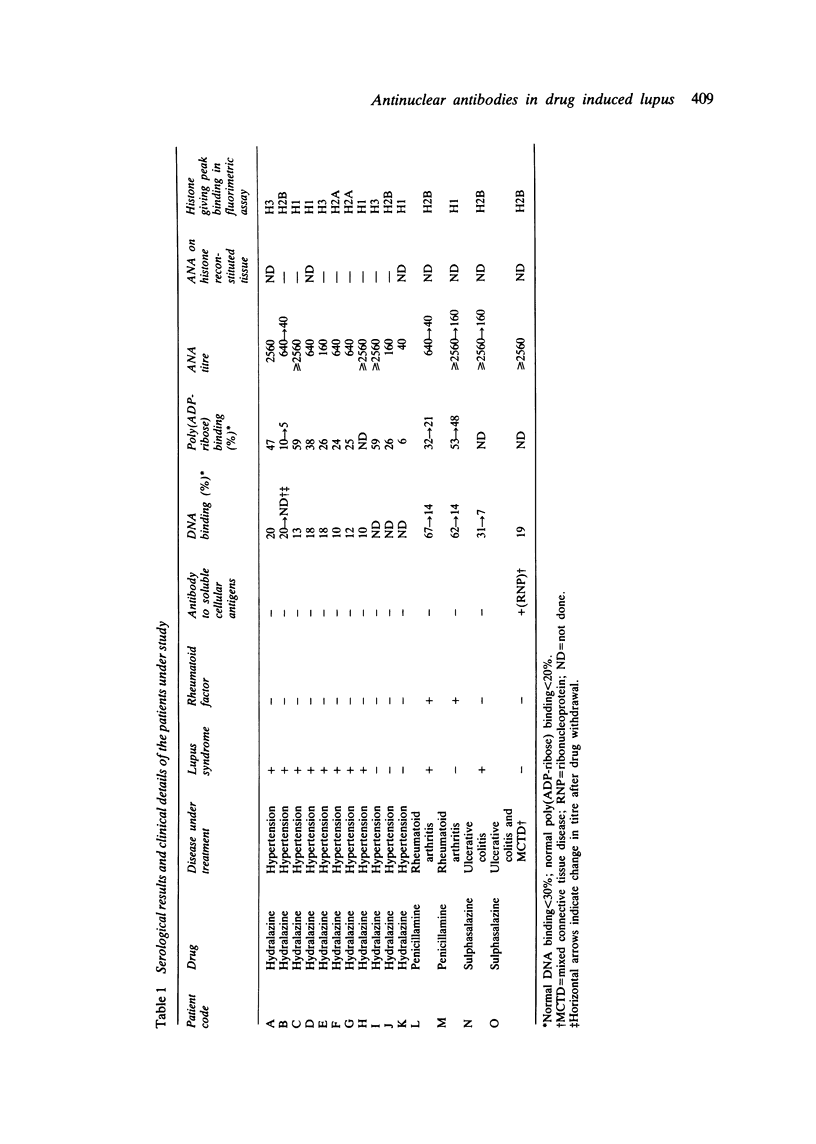
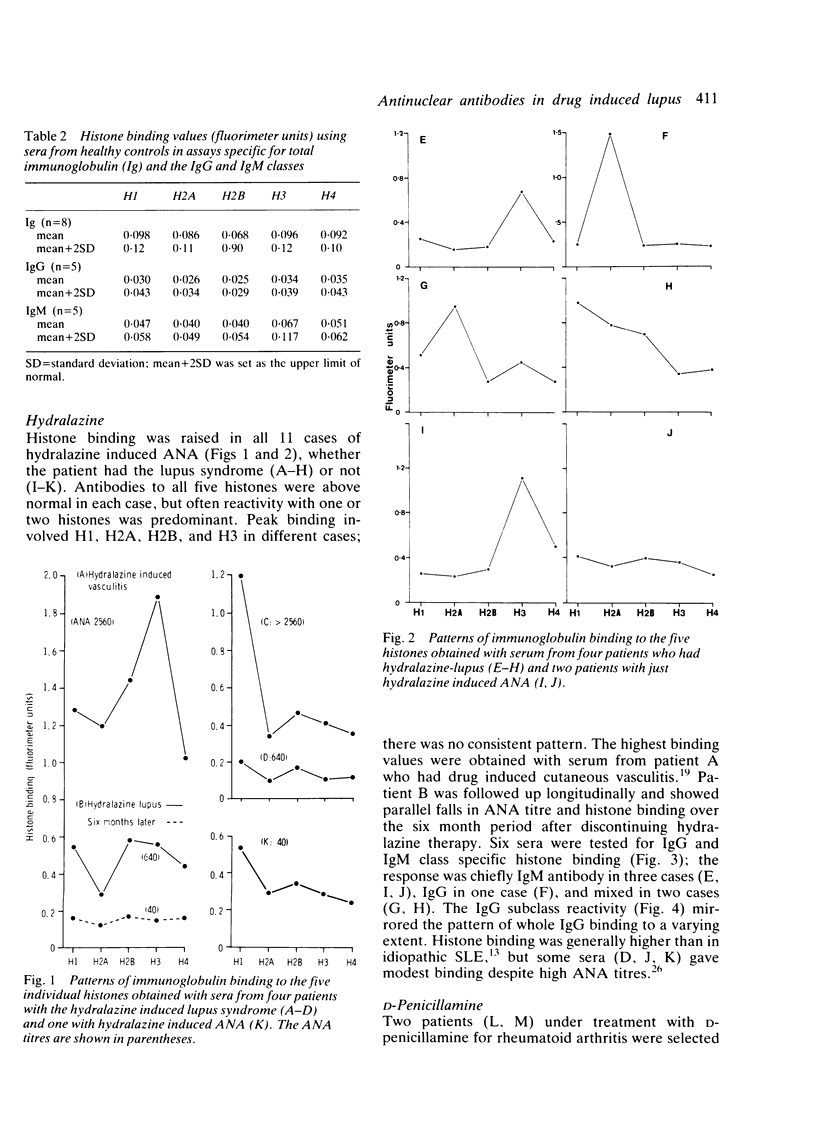
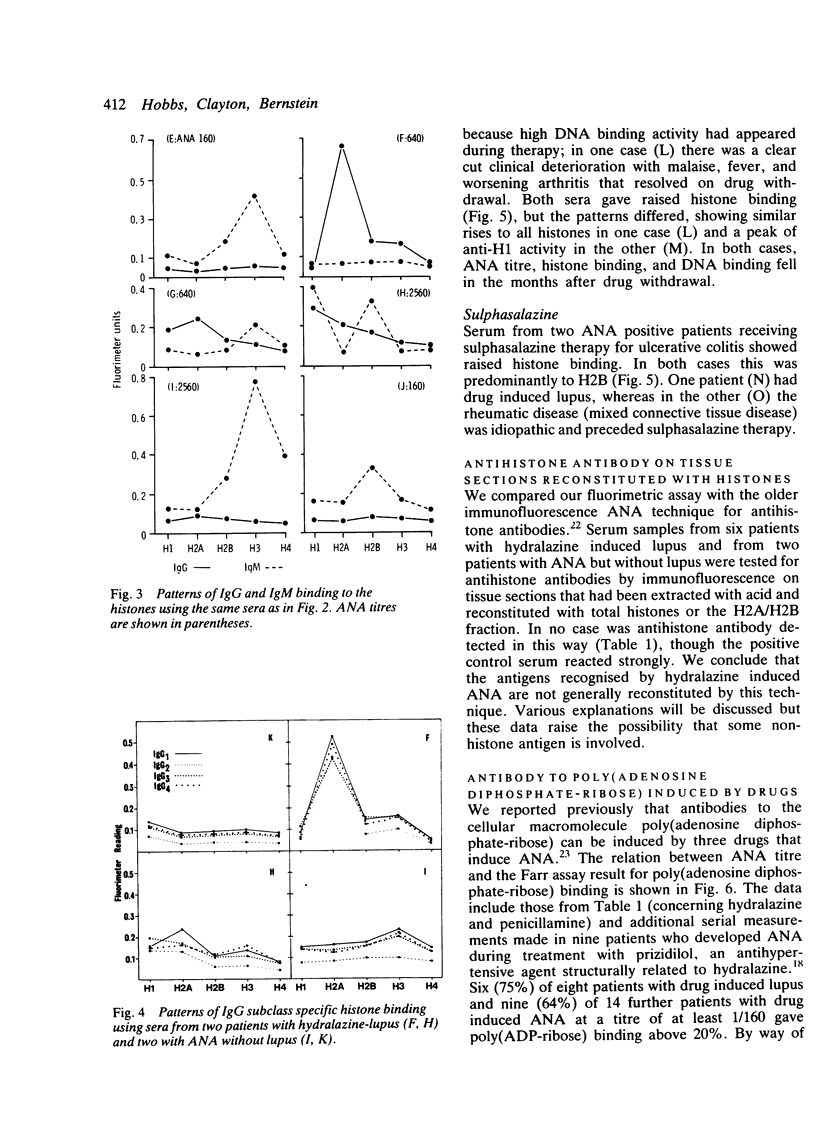
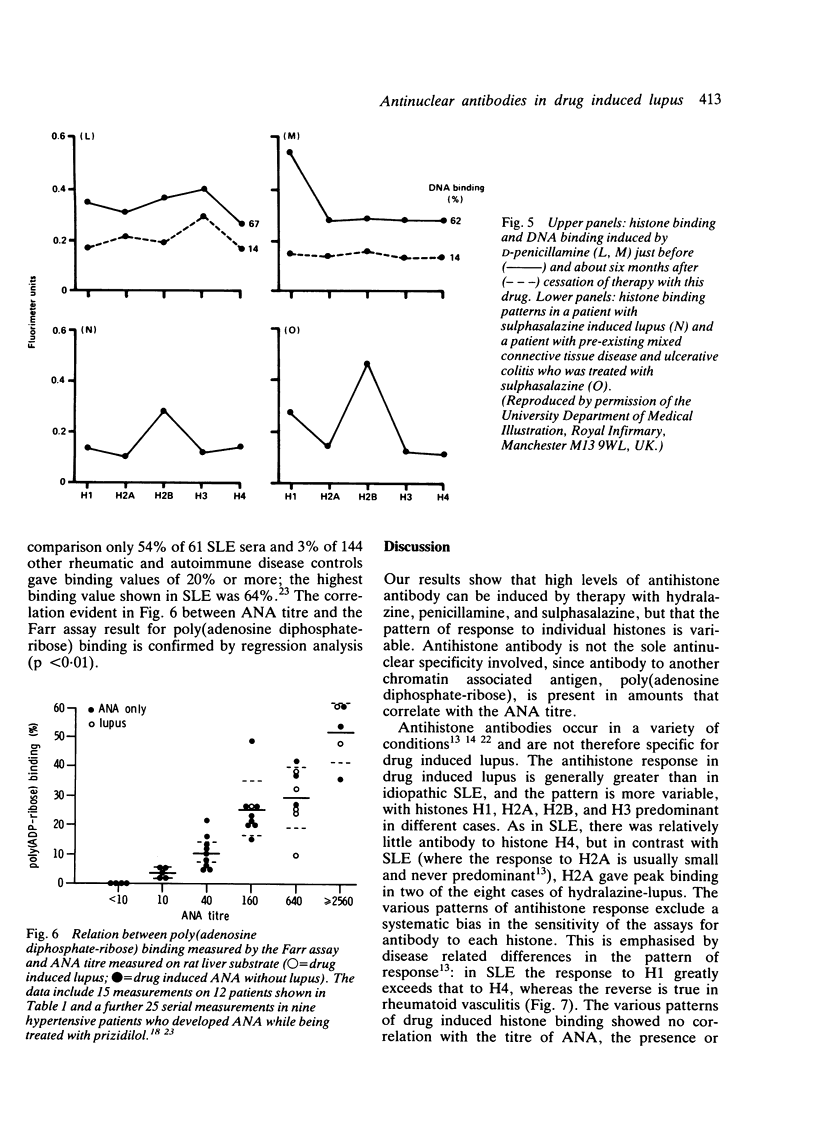
Certain drugs are a frequent source of antinuclear antibody (ANA) induction, and ANA is invariably present in the few patients who progress to the drug induced lupus syndrome. This report concerns the fine specificity of the ANA response to hydralazine, penicillamine, and sulphasalazine therapy. Using highly purified individual histones in fluorimetric assays, antihistone antibodies are always detectable, often in large amounts, but the pattern of response to individual histones is variable and not drug specific. In addition to the response to the three histones H1, H2B, and H3 reminiscent of idiopathic systemic lupus erythematosus, antibody to histone H2A predominates in some drug induced cases. Contrary to previous thought, histones are not the sole target of the antinuclear response: we also demonstrate a significant correlation between ANA titre and antibody to poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose). Like the histones, this is a macromolecule that can bind to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). It is proposed that drug induced damage to chromatin leads to ANA production, while drug induced impairment of complement activity may then enable these autoantibodies to mediate the lupus syndrome.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batchelor J. R., Welsh K. I., Tinoco R. M., Dollery C. T., Hughes G. R., Bernstein R., Ryan P., Naish P. F., Aber G. M., Bing R. F. Hydralazine-induced systemic lupus erythematosus: influence of HLA-DR and sex on susceptibility. Lancet. 1980 May 24;1(8178):1107–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91554-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Bunn C. C., Hughes G. R. Identification of antibodies to acidic antigens by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Oct;41(5):554–555. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.5.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Egerton-Vernon J., Webster J. Hydrallazine-induced cutaneous vasculitis. Br Med J. 1980 Jan 19;280(6208):156–157. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6208.156-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestein H. G., Zvaifler N. J., Weisman M. H., Shapiro R. F. Lymphocyte alteration by procainamide: relation to drug-induced lupus erythematosus syndrome. Lancet. 1979 Oct 20;2(8147):816–819. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron H. A., Ramsay L. E. The lupus syndrome induced by hydralazine: a common complication with low dose treatment. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Aug 18;289(6442):410–412. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6442.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubroff L. M., Reid R. J., Jr Hydralazine-pyrimidine interactions may explain hydralazine-induced lupus erythematosus. Science. 1980 Apr 25;208(4442):404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.7367866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A., Barland P. The diagnostic value of antihistone antibodies in drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Feb;28(2):158–162. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielder A. H., Walport M. J., Batchelor J. R., Rynes R. I., Black C. M., Dodi I. A., Hughes G. R. Family study of the major histocompatibility complex in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: importance of null alleles of C4A and C4B in determining disease susceptibility. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Feb 5;286(6363):425–428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6363.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzler M. J., Tan E. M. Antibodies to histones in drug-induced and idiopathic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):560–567. doi: 10.1172/JCI109161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths I. D., Kane S. P. Sulphasalazine-induced lupus syndrome in ulcerative colitis. Br Med J. 1977 Nov 5;2(6096):1188–1189. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6096.1188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman L., Barland P. Histone reactivity of drug-induced antinuclear antibodies. A comparison of symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Jul;24(7):927–931. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. A., Thomas J. O. Antibodies to histones in systemic lupus erythematosus: localization of prominent autoantigens on histones H1 and H2B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs R. N., Lea D. J., Phua K. K., Johnson P. M. Binding of isolated rheumatoid factors to histone proteins and basic polycations. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Aug;42(4):435–438. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.4.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs R. N., Lea D. J., Ward D. J. A fluorimetric assay for human antibodies to all the histones. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G. R., Rynes R. I., Gharavi A., Ryan P. F., Sewell J., Mansilla R. The heterogeneity of serologic findings and predisposing host factors in drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Aug;24(8):1070–1073. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg I. Histones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:159–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. W. The isolation and purification of histones. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:183–203. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Tanuma S., Sugimura T. Immunofluorescent staining of poly(ADP-ribose) in situ in HeLa cell chromosomes in the M phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2801–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson R., Karlberg B. E., Norlander B., Wirsén A. Prizidilol, an antihypertensive with precapillary vasodilator and beta-adrenoceptor blocking actions, in primary hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 May;29(5):588–593. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Honda B. M., Mills A. D., Finch J. T. Nucleosomes are assembled by an acidic protein which binds histones and transfers them to DNA. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):416–420. doi: 10.1038/275416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansilla-Tinoco R., Harland S. J., Ryan P. J., Bernstein R. M., Dollery C. T., Hughes G. R., Bulpitt C. J., Morgan A., Jones J. M. Hydralazine, antinuclear antibodies, and the lupus syndrome. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Mar 27;284(6320):936–939. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6320.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okolie E. E., Shall S. The significance of antibodies to poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Apr;36(1):151–164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish J. A., Chylack L. T., Jr, Woehler M. E., Cheng H. M., Pathak M. A., Morison W. L., Krugler J., Nelson W. F. Dermatological and ocular examinations in rabbits chronically photosensitized with methoxsalen. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Sep;73(3):250–255. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12514338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry H. M., Jr Late toxicity to hydralazine resembling systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1973 Jan;54(1):58–72. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Schur P. H., Rose J. A., Decker J. L., Talal N. Measurement of serum DNA-binding activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 25;281(13):701–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909252811304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portanova J. P., Rubin R. L., Joslin F. G., Agnello V. D., Tan E. M. Reactivity of anti-histone antibodies induced by procainamide and hydralazine. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Oct;25(1):67–79. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekvig O. P., Hannestad K. Human autoantibodies that react with both cell nuclei and plasma membranes display specificity for the octamer of histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 in high salt. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1720–1733. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., McNally E. M., Nusinow S. R., Robinson C. A., Tan E. M. IgG antibodies to the histone complex H2A-H2B characterize procainamide-induced lupus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Jul;36(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan P. F., Hughes G. R., Bernstein R., Mansilla R., Dollery C. T. Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in hydralazine-induced lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1979 Dec 8;2(8154):1248–1249. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92371-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Ng Y. C., Peters D. K. The role of complement and its receptor in the elimination of immune complexes. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 21;315(8):488–495. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608213150805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim E., Gill E. W., Sim R. B. Drugs that induce systemic lupus erythematosus inhibit complement component C4. Lancet. 1984 Aug 25;2(8400):422–424. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92905-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D., Ward M. Rabbit antibodies to histone fractions as specific reagents for preparative and comparative studies. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 25;245(6):1261–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walshe J. M. Penicillamine and the SLE syndrome. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1981 Jan-Feb;7:155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O. Analysis of autoimmunity through experimental models of thyroiditis and allergic encephalomyelitis. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:159–273. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi Y., Litwin A., Adams L., Zimmer H., Hess E. V. Induction of antibodies to nuclear antigens in rabbits by immunization with hydralazine-human serum albumin conjugates. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):958–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI108176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


