Abstract
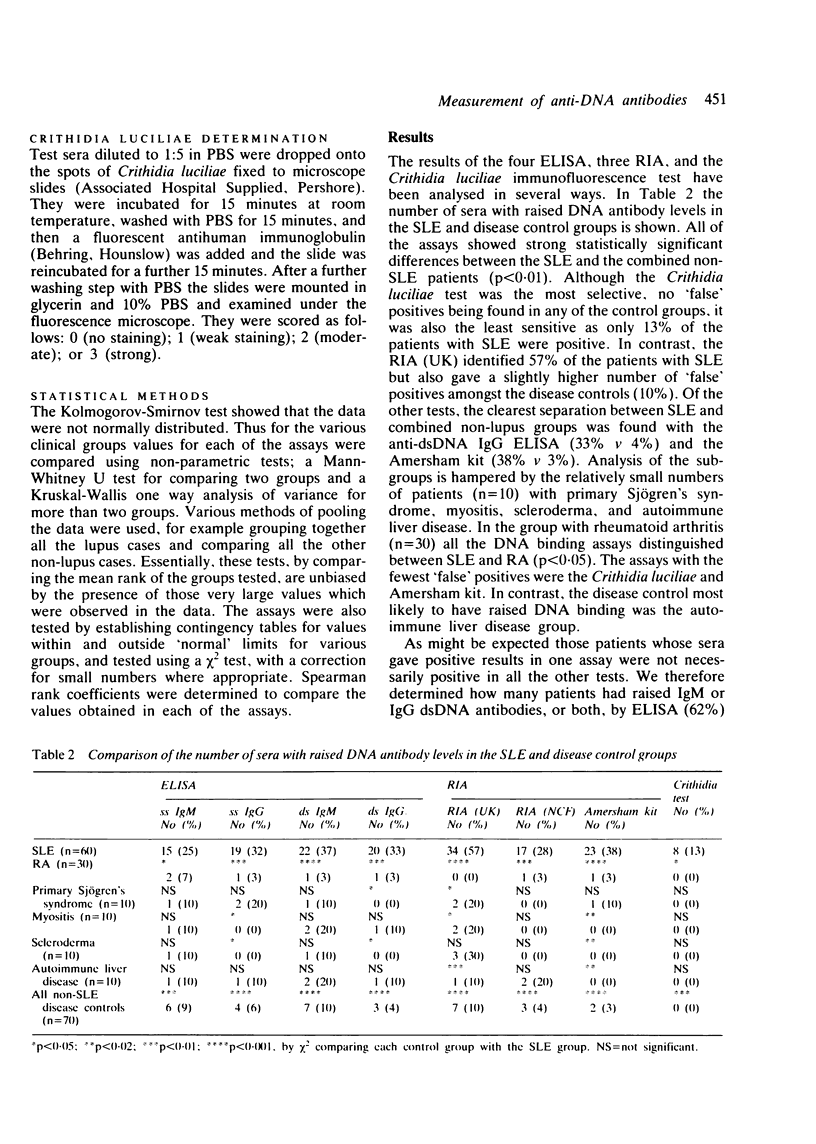
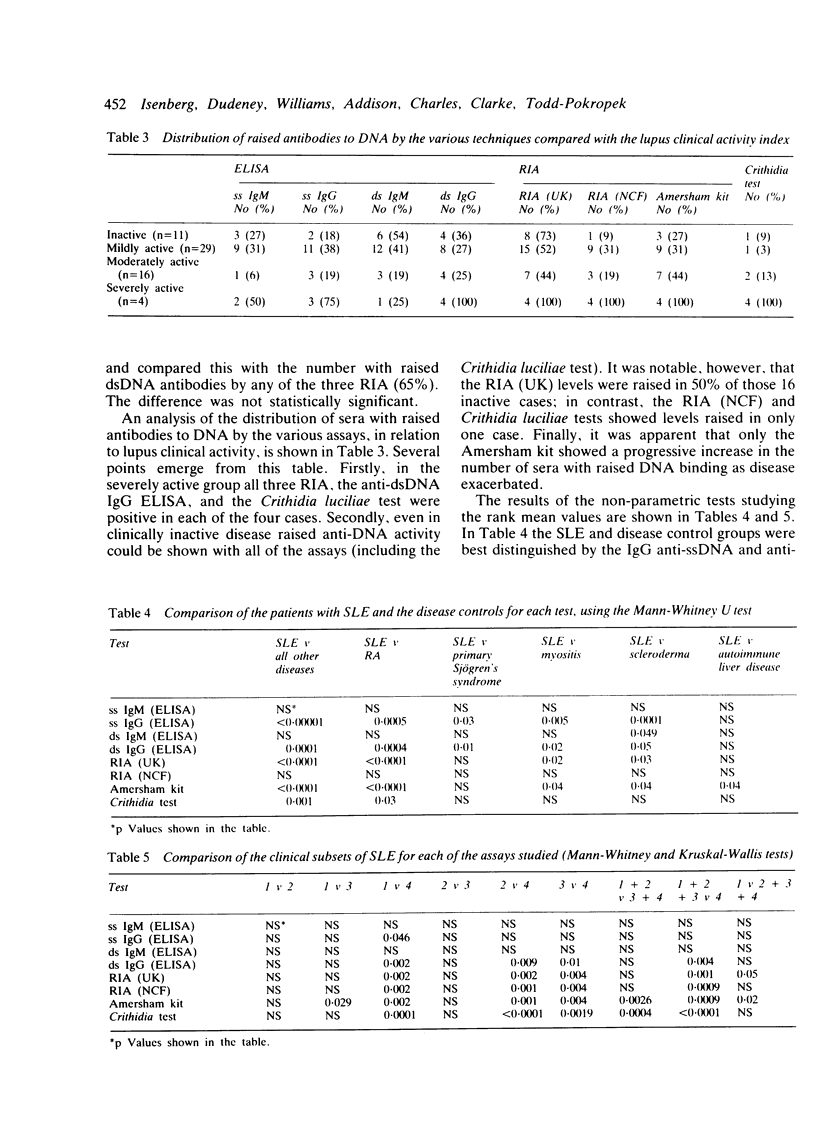
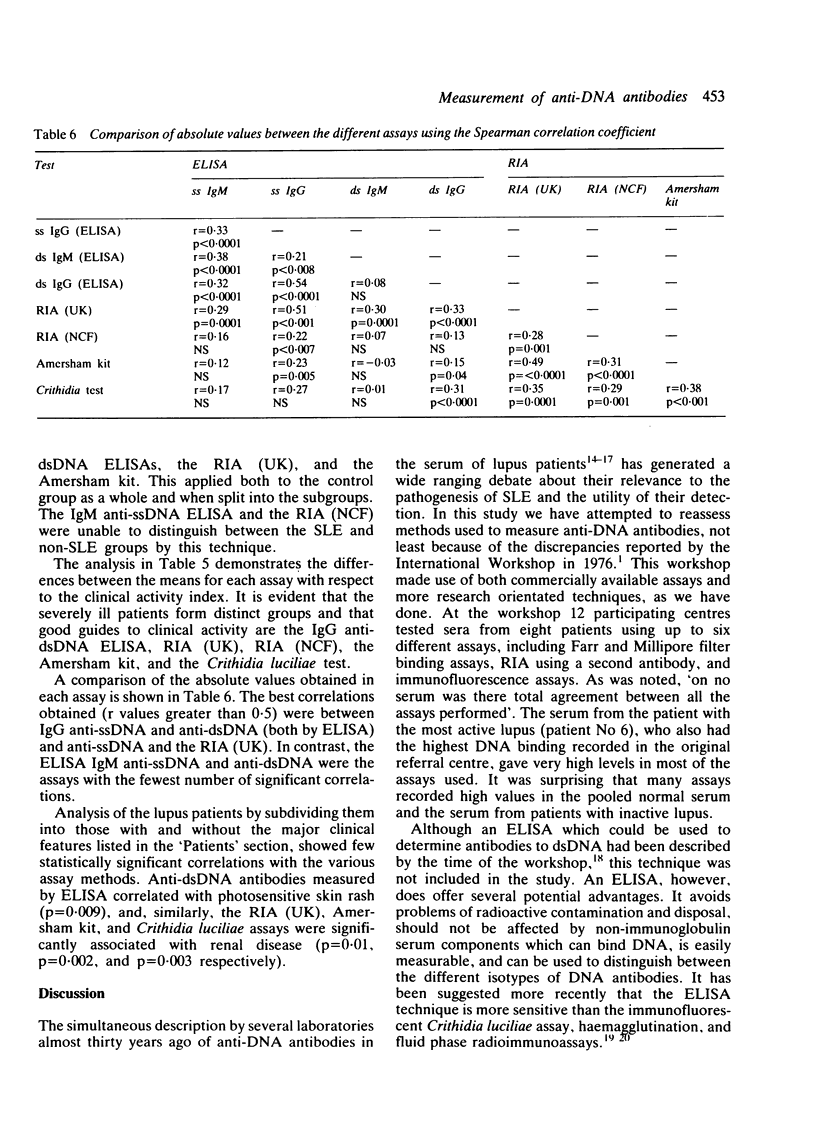
One hundred and thirty coded sera, 60 from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and 70 from patients with other autoimmune rheumatic diseases were tested for deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) binding activity by five different types of assay. These were enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (distinguishing IgG and IgM anti-ssDNA and anti-dsDNA), Crithidia luciliae, a nitrocellulose filter assay, the Amersham kit, and another modified Farr assay, the radioimmunoassay (RIA) (UK). The Crithidia test was the most specific, none of the controls was positive, but the least sensitive (13% positive only). The RIA (UK) was the most sensitive (57% positive). In most of the assays 3-9% of the controls were positive. When the SLE sera were analysed according to disease activity the IgG anti-dsDNA ELISA, all three RIA values, and the Crithidia test values were raised in all the patients with severely active disease. Some patients with inactive disease, however, were positive in each of the tests. The best interassay correlations (r less than 0.49) were found between RIA (UK), and ss IgG and the Amersham kit; and between ds IgG and ss IgG. In the main, however, it was clear that different assays are dependent upon distinctive properties of DNA antibodies. It seems inevitable that most major rheumatology units will require more than one anti-DNA antibody assay.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballou S. P., Kushner I. Immunochemical characteristics of antibodies to DNA in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):58–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu A., Quismorio F. P., Jr, Friou G. J., Vayuvegula B., Mirick G. IgG antibodies to double-stranded DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus sera. Independent variation of complement fixing activity and total antibody content. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jun;22(6):565–570. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu A., Quismorio F. P., Jr, kitridou R. C., Friou G. J. Complement fixing antibodies to DS-DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus: a study using the immunofluorescent Crithidia luciliae method. J Rheumatol. 1979 Jul-Aug;6(4):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohan A., Peter J. B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 13;292(7):344–347. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502132920706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEPPELLINI R., POLLI E., CELADA F. A DNA-reacting factor in serum of a patient with lupus erythematosus diffusus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Dec;96(3):572–574. doi: 10.3181/00379727-96-23544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casperson G. F., Voss E. W., Jr Colicin E1 plasmid as a probe for detection and study of anti-dna activity in SLE sera. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):293–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. B., Schnneider G., Schur P. H. Enzyme immunoassay for antibodies to native DNA. Specificity and quality of antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jan;26(1):52–62. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D. Anti-DNA antibodies: problems in their study and interpretation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Aug;65(2):215–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza R. H., Swaak T., Aarden L., Smeenk R. Complement-fixing antibodies to dsDNA detected by the immunofluorescence technique on Crithidia luciliae. A critical appraisal. J Rheumatol. 1985 Dec;12(6):1109–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg B., Keiser H. A Millipore filter assay for antibodies to native DNA in sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Mar-Apr;16(2):199–207. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Karsh J., Anken M. Studies on autoantibodies to deoxyribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleoprotein with enzyme-immunoassay (ELISA). J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jan;97(1):97–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Rowe D., Tookman A., Hopp A., Griffiths M., Paice E., Stewart J., Beverley P. C. An immunohistological study of secondary Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Jun;43(3):470–476. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Shoenfeld Y., Schwartz R. S. Multiple serologic reactions and their relationship to clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Feb;27(2):132–138. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Shoenfeld Y., Schwartz R. S. The use of hybridomas to analyse autoimmunity. Br Med Bull. 1984 Jul;40(3):262–266. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIEVITS J. H., SCHUIT H. R. A simple indirect LE-cell test with increased sensitivity. Vox Sang. 1957 Sep;2(4):288–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1957.tb03705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kredich N. M., Skyler J. S., Foote L. J. Antibodies to native DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. A technique of rapid and quantitative determination. Arch Intern Med. 1973 May;131(5):639–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIESCHER P., STRASSLE R. New serological methods for the detection of the L.E. factor. Vox Sang. 1957 Sep;2(4):283–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1957.tb03704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackworth-Young C. G., Chan J. K., Bunn C. C., Hughes G. R., Gharavi A. E. Complement fixation by anti-dsDNA antibodies in SLE: measurement by radioimmunoassay and relationship with disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Apr;45(4):314–318. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.4.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Lahita R. G., Zarro V. J., MacWilliam J., Koffler D. Clinical significance of anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies detected by a solid phase enzyme immunoassay. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Apr;24(4):602–610. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow W. J., Isenberg D. A., Todd-Pokropek A., Parry H. F., Snaith M. L. Useful laboratory measurements in the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Q J Med. 1982 Spring;51(202):125–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Schur P. H., Rose J. A., Decker J. L., Talal N. Measurement of serum DNA-binding activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 25;281(13):701–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909252811304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Bull Rheum Dis. 1981;31(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS W. C., HOLMAN H. R., DEICHER H., KUNKEL H. G. Complement fixation with cell nuclei and DNA in lupus erythematosus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Dec;96(3):575–579. doi: 10.3181/00379727-96-23545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeenk R., van der Lelij G., Aarden L. Avidity of antibodies to dsDNA: comparison of IFT on Crithidia luciliae, Farr assay, and PEG assay. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):73–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerfield S. D., Roberts M. W., Booth R. J. Double-stranded DNA antibodies: a comparison of four methods of detection. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Sep;34(9):1032–1035. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.9.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer R. D., Gilliam J. N. DNA antibody class, subclass, and complement fixation in systemic lupus erythematosus with and without nephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Aug;10(4):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak A. J., Aarden L. A., Statius van Eps L. W., Feltkamp T. E. Anti-dsDNA and complement profiles as prognostic guides in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Mar;22(3):226–235. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak A. J., Groenwold J., Aarden L. A., Feltkamp T. E. Detection of anti-dsDNA as diagnostic tool. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Feb;40(1):45–49. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold R. T., Young F. E., Tan E. M., Farr R. S. Deoxyribonucleic acid antibody: a method to detect its primary interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):806–807. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


