Abstract
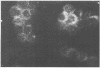
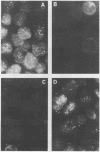
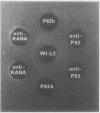
Antibodies to rheumatoid arthritis nuclear antigen (RANA) are detected by immunodiffusion (ID) and immunofluorescence (IF), though reports of the identity of the antigen(s) have been conflicting. In this study it is shown conclusively that ID and IF anti-RANA react with epitopes on Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA-1) and that the major epitope detected by immunofluorescence is represented by a synthetic peptide, P62, corresponding to part of EBNA-1. In an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) anti-P62 antibodies in 35 rheumatoid arthritis sera were threefold higher than those of 35 age and sex matched controls, with the highest levels occurring in young patients with active joint disease.
Full text
PDF


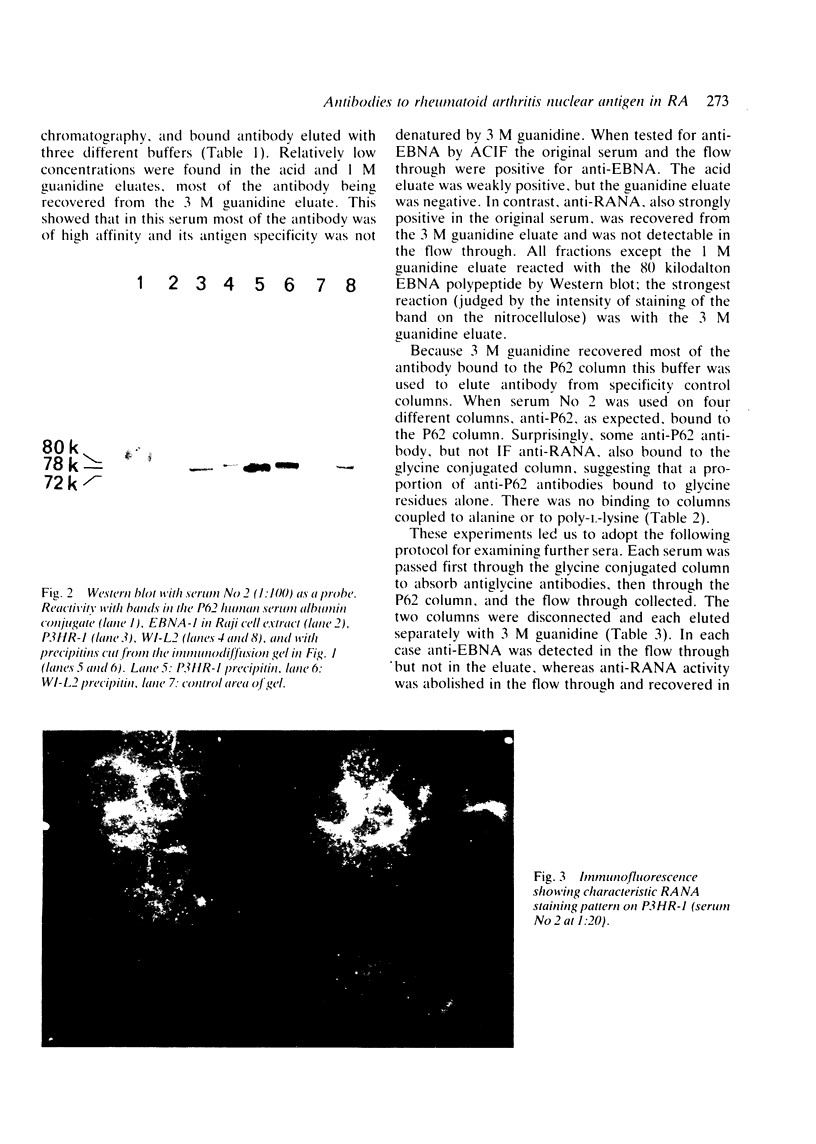
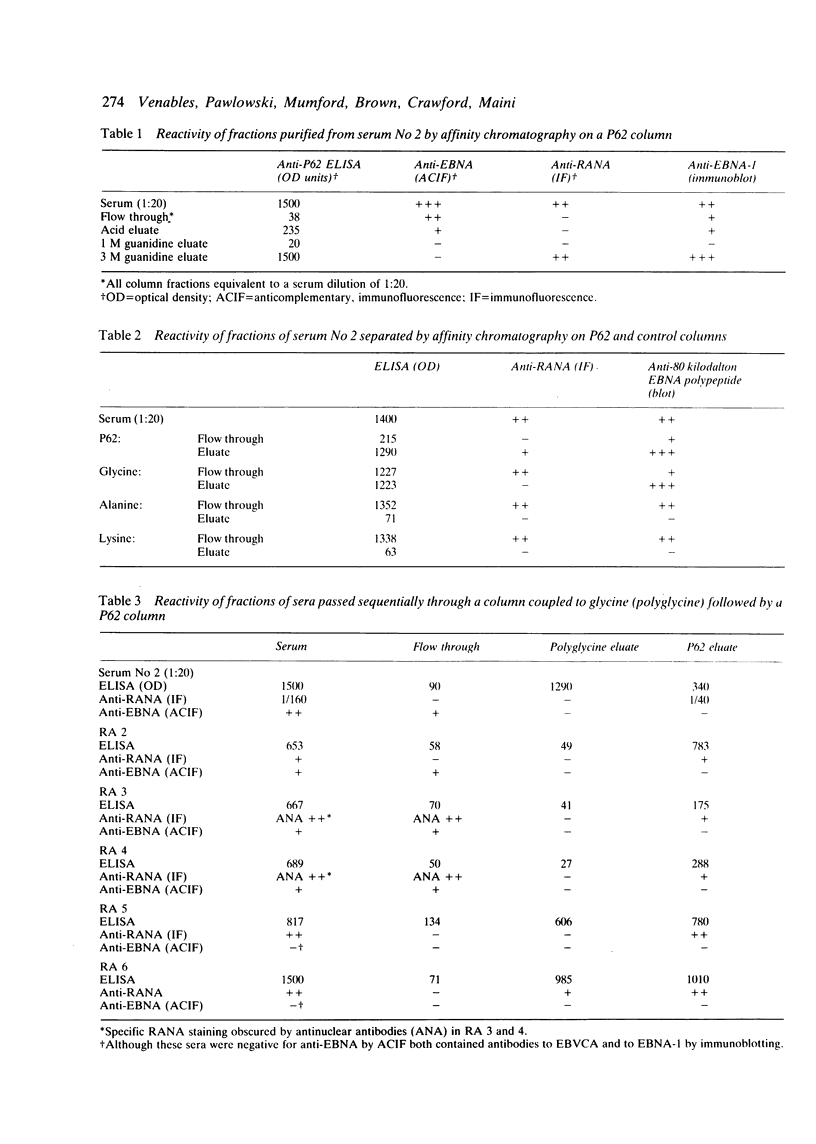
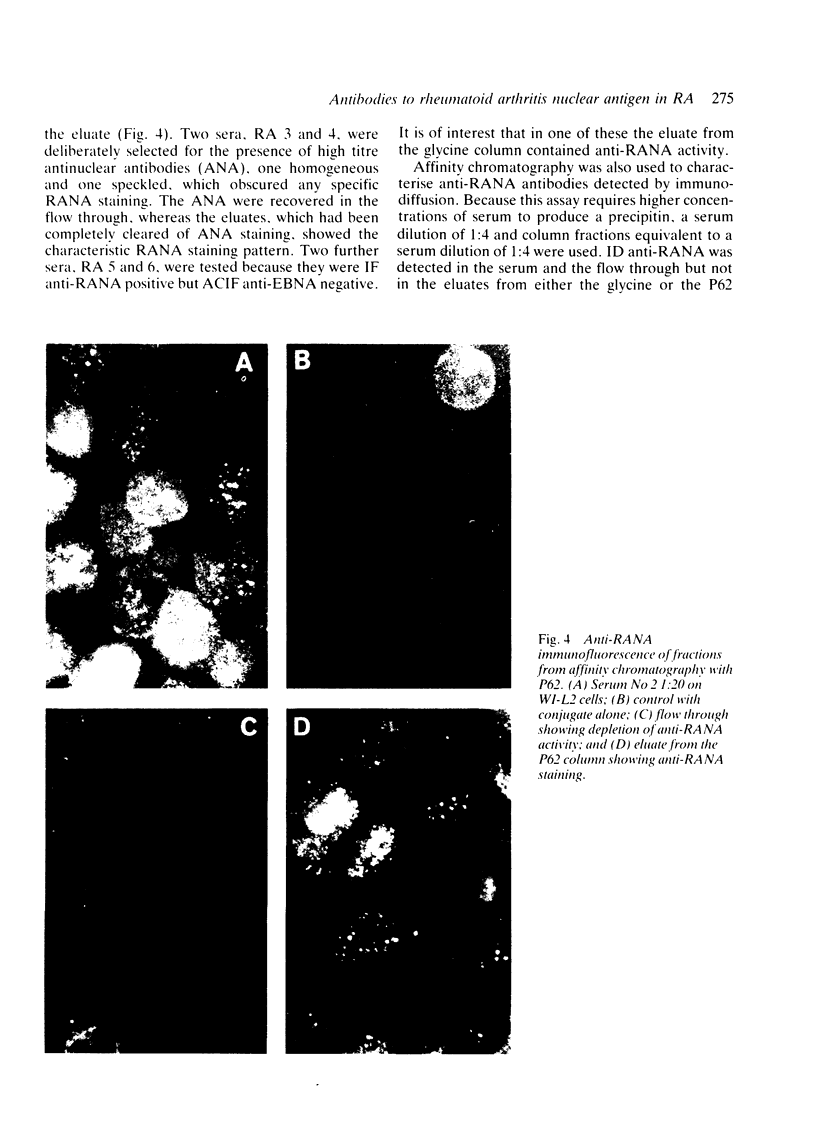

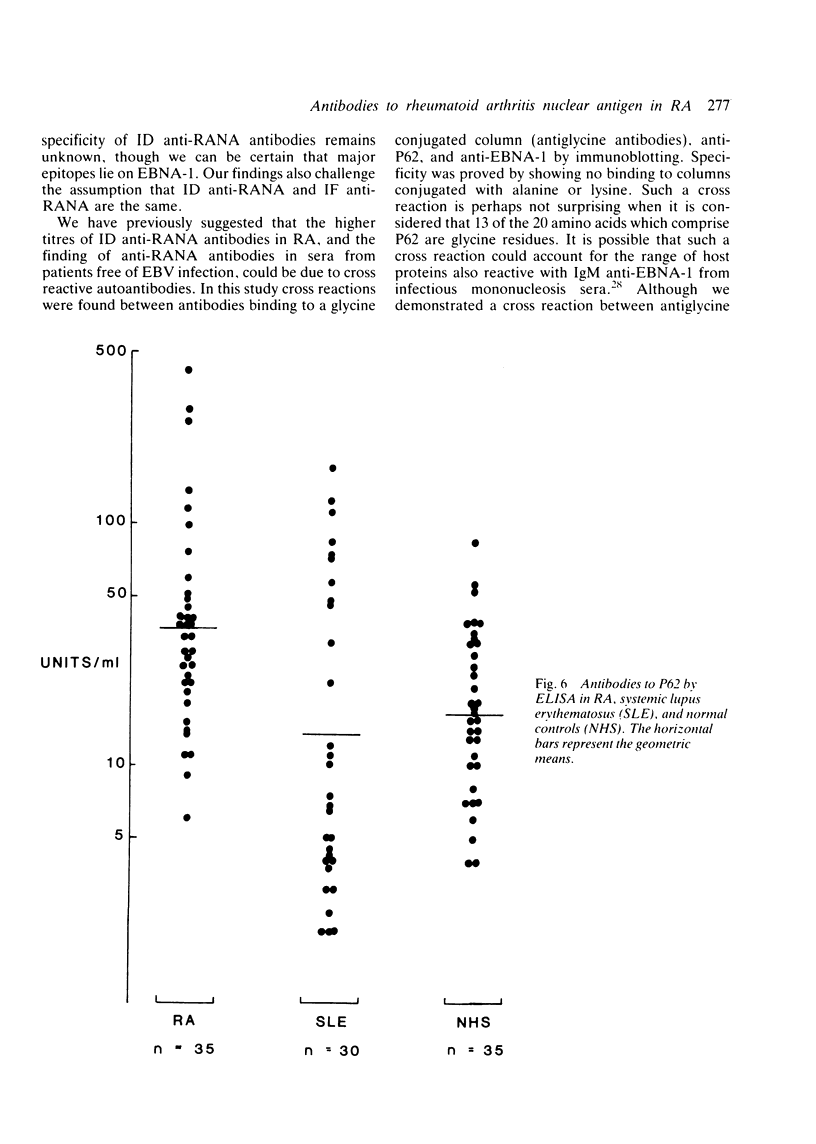


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alspaugh M. A., Shoji H., Nonoyama M. A search for rheumatoid arthritis-associated nuclear antigen and Epstein-Barr virus specific antigens or genomes in tissues and cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jun;26(6):712–720. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano M. A., Carson D. A., Niederman J. C., Feorino P., Vaughan J. H. Antibody to the rheumatoid arthritis nuclear antigen. Its relationship to in vivo Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1238–1242. doi: 10.1172/JCI109779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. J., Crawford D. H., Bucknall R. C., Allen C., Thompson J. L., Epstein M. A., Hall N. D., Bacon P. A. Infection with E.B. virus and rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1979 Jan;1(8107):105–105. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernberg I., Kallin B., Dillner J., Falk K., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Hammarskjöld M. L., Klein G. Lymphoblastoid cell lines and Burkitt-lymphoma-derived cell lines differ in the expression of a second Epstein-Barr virus encoded nuclear antigen. Int J Cancer. 1986 Nov 15;38(5):729–737. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R., Sportsman R., Rhodes G., Luka J., Pearson G., Vaughan J. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane contains a 62,000-molecular-weight protein that shares an antigenic epitope with the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded associated nuclear antigen. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1539–1547. doi: 10.1172/JCI112469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Hanukoglu I. Unraveling the structure of the intermediate filaments. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):332–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90367-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataaha P. K., Mortazavi-Milani S. M., Russell G., Holborow E. J. Anti-intermediate filament antibodies, antikeratin antibody, and antiperinuclear factor in rheumatoid arthritis and infectious mononucleosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Jul;44(7):446–449. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.7.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K. C., Brown K. A., Perry J. D., Holborow E. J. Anti-RANA antibody: a marker for seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1980 Mar 1;1(8166):447–449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90997-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes G., Carson D. A., Valbracht J., Houghten R., Vaughan J. H. Human immune responses to synthetic peptides from the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculley T. B., Pope J. H., Hazelton R. A. Correlation between the presence of antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen type 2 and antibodies to the rheumatoid arthritis nuclear antigen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):964–970. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculley T. B., Walker P. J., Moss D. J., Pope J. H. Identification of multiple Epstein-Barr virus-induced nuclear antigens with sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):88–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.88-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter L., Carson D. A., Jensen F. C., Holbrook T. L., Vaughan J. H. In vitro effects of Epstein-Barr virus on peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and normal subjects. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1429–1434. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables P. J., Roffe L. M., Erhardt C. C., Maini R. N., Edwards J. M., Porter A. D. Titers of antibodies to RANA in rheumatoid arthritis and normal sera. Relationship to Epstein-Barr virus infection. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Dec;24(12):1459–1468. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Stocks M. R., Charles P. J., Maini R. N. Antibodies to La, Jo-1, nRNP and Sm detected by multi-track immunoblotting using a novel filter holder: a comparative study with counterimmunoelectrophoresis and immunodiffusion using sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren's syndrome. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jul 11;91(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]