Abstract
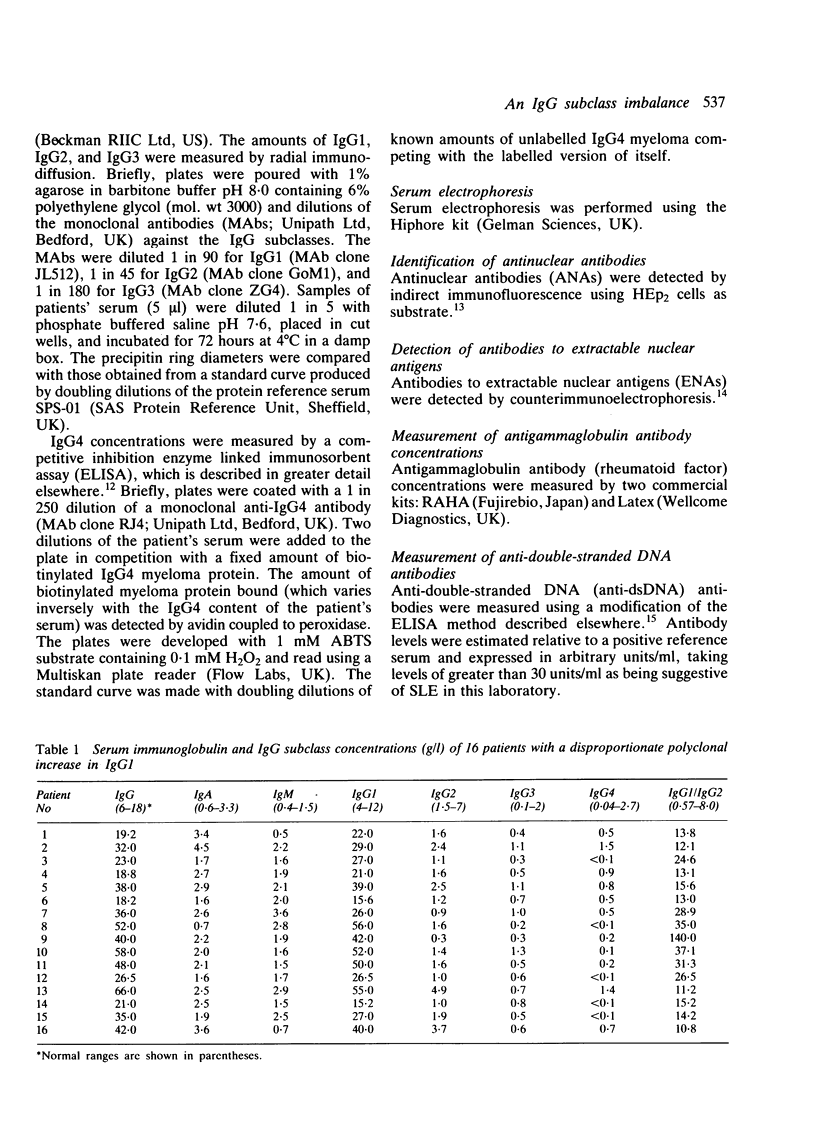
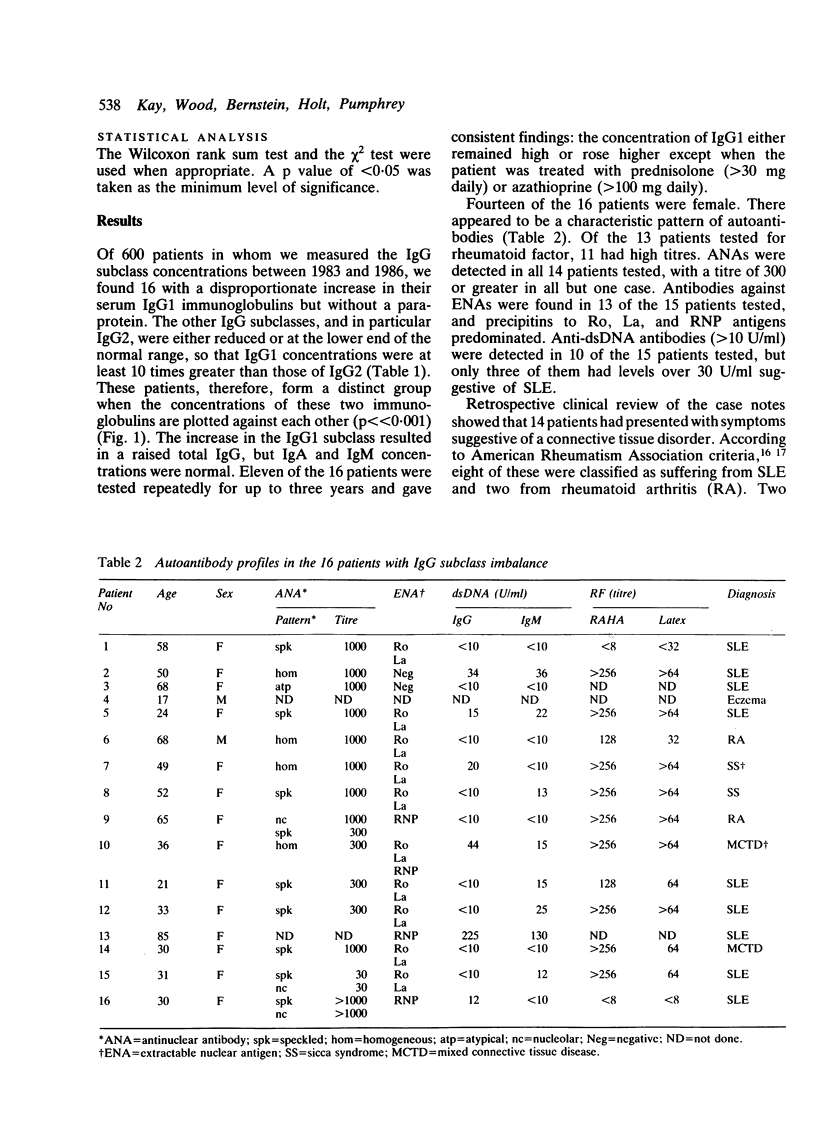
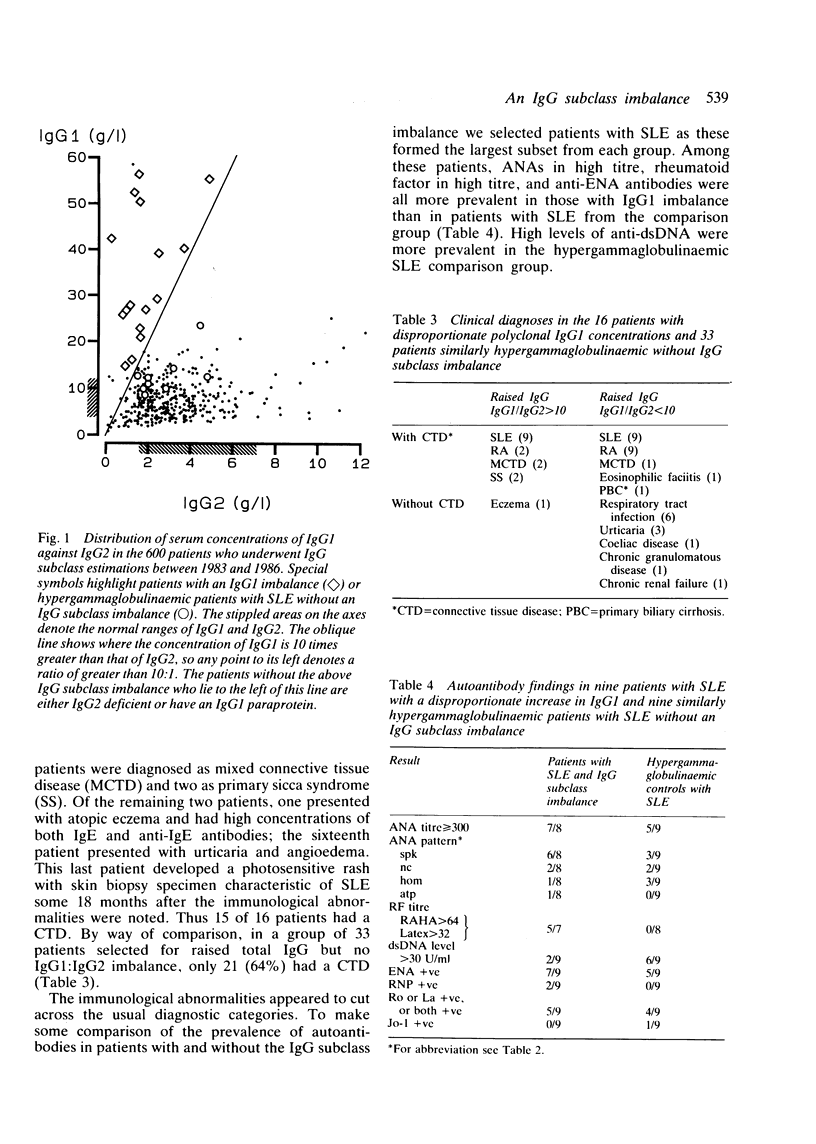
A group of 16 patients with a disproportionate polyclonal increase in their serum IgG1, resulting in raised concentrations of total IgG immunoglobulin, has been discovered. The other IgG subclasses in these patients are either normal or slightly reduced, resulting in an IgG1:IgG2 ratio of at least 10:1. Most cases are marked by the presence of anti-extractable nuclear antigen (anti-ENA) antibodies and high titres of rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibody. All but one patient has a connective tissue disease, nearly twice the prevalence found in similarly hypergammaglobulinaemic patients without this IgG subclass imbalance. Among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), those with the IgG1 disorder have a higher prevalence of high titre rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibody, but a lower prevalence of anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies above 30 U/ml. It is suggested that this immunoglobulin abnormality may reflect a unique immunoregulatory dysfunction in these patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Sagawa A., Pascual E., Hebert J., Sadeghee S. Suppressor T-cell abnormality in idiopathic systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Sep;6(2):192–199. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando D. G., Sercarz E. E., Hahn B. H. Mechanisms of T and B cell collaboration in the in vitro production of anti-DNA antibodies in the NZB/NZW F1 murine SLE model. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3185–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Bunn C. C., Hughes G. R. Identification of antibodies to acidic antigens by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Oct;41(5):554–555. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.5.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Steigerwald J. C., Tan E. M. Association of antinuclear and antinucleolar antibodies in progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):43–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi A. T., Hooijkaas H., Benner R., Tees R., Nordin A. A., Schreier M. H. Clones of helper T cells mediate antigen-specific, H-2-restricted DTH. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):62–63. doi: 10.1038/290062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Jasin H. E. Suppressor function of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in normal individuals and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):106–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI108607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., McVay-Boudreau L., Hugenberger J., Naidorf K., Shen F. W., Gershon R. K. Immunoregulatory circuits among T-cell sets. II. Physiologic role of feedback inhibition in vivo: absence in NZB mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1116–1125. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Dyer K., Craven S. Y., Fuller C. R., Yount W. J. Subclass restriction and polyclonality of the systemic lupus erythematosus marker antibody anti-Sm. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1270–1277. doi: 10.1172/JCI111826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. Immunoregulation in autoimmunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980 Jul;66(1):5–17. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(80)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golds E. E., Stephen I. B., Esdaile J. M., Strawczynski H., Poole A. R. Lymphocyte transformation to connective tissue antigens in adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and a nonarthritic control population. Cell Immunol. 1983 Nov;82(1):196–209. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Smith C. I. IgG subclasses in bacterial infections. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:122–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda M., Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Kotani H., Tsunematsu T., Moriyama K., Fukase M. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: antibodies to desialized, rather than intact, T cells preferentially bind to and eliminate suppressor effector T cells. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):940–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI110533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isakson P. C., Puré E., Vitetta E. S., Krammer P. H. T cell-derived B cell differentiation factor(s). Effect on the isotype switch of murine B cells. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):734–748. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz J. L., Minami R. M., Teplitz R. L. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies to native and denatured DNA. J Immunol Methods. 1979;29(2):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manny N., Datta S. K., Schwartz R. S. Synthesis of IgM by cells of NZB and SWR mice and their crosses. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1220–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Posnett D. N., Kunkel H. G. Human malignant T cells capable of inducing an immunoglobulin class switch. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):134–144. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milon G., Marchal G., Seman M., Truffa-Bachi P., Zilberfarb V. Is the delayed-type hypersensitivity observed after a low dose of antigen mediated by helper T cells? J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1103–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutsopoulos H. M., Boehm-Truitt M., Kassan S. S., Chused T. M. Demonstration of activation of B lymphocytes in New Zealand black mice at birth by an immunoradiometric assay for murine IgM. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1639–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce D. C., Yount W. J., Eisenberg R. A. Subclass restriction of anti-SS-B (La) autoantibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jan;38(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumphrey R. S. Automated filing and reporting in a regional immunology service laboratory using a PET computer. Med Inform (Lond) 1981 Oct-Dec;6(4):279–283. doi: 10.3109/14639238109010693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Arguelles A., Alarcón-Segovia D., Llorente L., Del Giudice-Knipping J. A. Heterogeneity of the spontaneously expanded and mitogen-induced generation of suppressor cell function of T cells on B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Sep;23(9):1004–1009. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagawa A., Abdou N. I. Suppressor-cell antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. Possible mechanism for suppressor-cell dysfunction. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):536–539. doi: 10.1172/JCI109333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Reeves J. P., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Complement-dependent immunoglobulin M anti-thymus-derived cell antibodies preferentially inactivate suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):954–965. doi: 10.1172/JCI109396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Reeves J. P., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. T-cell subsets and antibodies to T-cell subsets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1260–1269. doi: 10.1172/JCI109581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Monroe M., Rothfield N. The gammaG subclass of antinuclear and antinucleic acid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Mar-Apr;15(2):174–182. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakib F., Stanworth D. R. Antigammaglobulin (rheumatoid factor) activity of human IgG subclasses. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Feb;37(1):12–17. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideras P., Bergstedt-Lindqvist S., MacDonald H. R., Severinson E. Secretion of IgG1 induction factor by T cell clones and hybridomas. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jun;15(6):586–593. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideras P., Bergstedt-Lindqvist S., Severinson E. Partial biochemical characterization of IgG1-inducing factor. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jun;15(6):593–598. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Abe T., Kiyotaki M., Toguchi T., Koide J., Morimoto C., Homma M. In vitro immune response of SLE lymphocytes. The mechanism involved in B-cell activation. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Nov;16(5):369–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Shawler D. L., Eisenberg R. A., Dixon F. J. Splenic immunoglobulin-secreting cells and their regulation in autoimmune mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):446–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos G. C., Balow J. E. Cellular immune responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Prog Allergy. 1984;35:93–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. B., Wood K. J., Doré P., Swainson J. A., Brenchley P. E., Pumphrey R. S. Investigation of IgG4 levels in atopic patients using a competitive inhibition assay employing biotinylated IgG4 myeloma and avidin peroxidase. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Feb 27;87(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90344-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


