Abstract
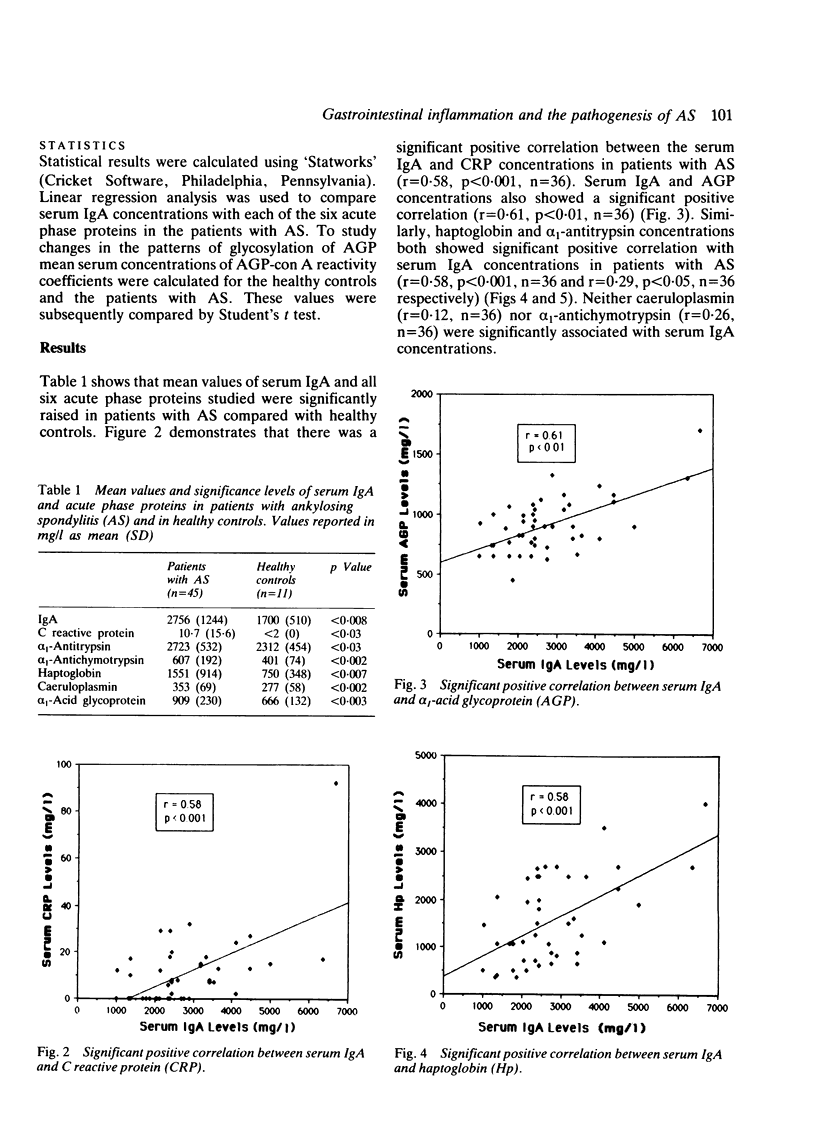
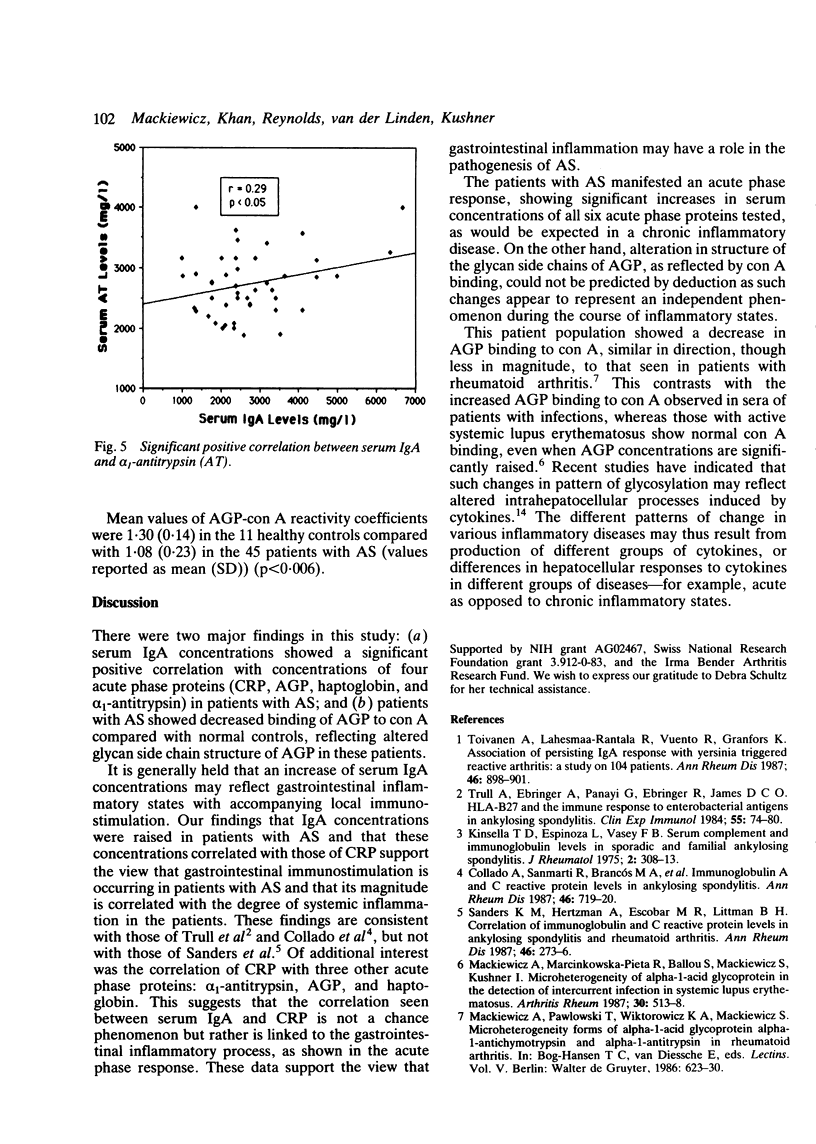
Several investigators have suggested that gastrointestinal inflammation has a role in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. To test this hypothesis markers of gastrointestinal immunostimulation, as manifested by serum IgA concentrations, were compared with serum markers of inflammation, as manifested by acute phase proteins. Serum samples from 45 unrelated Caucasian patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) were tested for correlation of serum IgA and six acute phase proteins: C reactive protein (CRP), alpha 1-antitrypsin, alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, caeruloplasmin, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (AGP), and haptoglobin. Serum IgA was shown to be significantly positively correlated with four of these six acute phase proteins: CRP (r = 0.58, p less than 0.001), alpha 1-antitrypsin (r = 0.29, p less than 0.05), AGP (r = 0.61, p less than 0.01), and haptoglobin (r = 0.58, p less than 0.001), suggesting that gastrointestinal immunostimulation does have a role in the pathogenesis of inflammation in AS. In addition, the microheterogeneity of the pattern of glycosylation of AGP, expressed as reactivity coefficients, was examined. The AGP reactivity coefficient has been shown to increase in infection, remain the same in systemic lupus erythematosus, and decrease in rheumatoid arthritis. It was found that the AGP reactivity coefficient was significantly decreased in patients with AS as compared with healthy controls (p less than 0.006). As recent studies have indicated that patterns of glycosylation reflect intrahepatocellular biosynthetic processes induced by cytokines our data suggest that cytokine-hepatocellular mechanisms in AS may be similar to those occurring in rheumatoid arthritis, but different from those in systemic lupus erythematosus or infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bog-Hansen T. C. Crossed immuno-affinoelectrophoresis. An analytical method to predict the result of affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):480–488. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collado A., Sanmarti R., Brancós M. A., Kanterewicz E., Gallart T., Rotés-Querol J., Cobos A. Immunoglobulin A and C reactive protein levels in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Sep;46(9):719–720. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.9.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella T. D., Espinoza L., Vasey F. B. Serum complement and immunoglobulin levels in sporadic and familial ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1975 Sep;2(3):308–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackiewicz A., Ganapathi M. K., Schultz D., Kushner I. Monokines regulate glycosylation of acute-phase proteins. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):253–258. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackiewicz A., Mackiewicz S. Determination of lectin-sugar dissociation constants by agarose affinity electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):481–488. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackiewicz A., Marcinkowska-Pieta R., Ballou S., Mackiewicz S., Kushner I. Microheterogeneity of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein in the detection of intercurrent infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;30(5):513–518. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackiewicz A., Wiktorowicz K., Mackiewicz S. Comparison of three immunoassays for C-reactive protein determination. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1985;33(5):693–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M., Hertzman A., Escobar M. R., Littman B. H. Correlation of immunoglobulin and C reactive protein levels in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Apr;46(4):273–276. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.4.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen A., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Vuento R., Granfors K. Association of persisting IgA response with yersinia triggered reactive arthritis: a study on 104 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Dec;46(12):898–901. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.12.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trull A., Ebringer A., Panayi G., Ebringer R., James D. C. HLA-B27 and the immune response to enterobacterial antigens in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jan;55(1):74–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Linden S., Valkenburg H. A., Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Apr;27(4):361–368. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



