Abstract
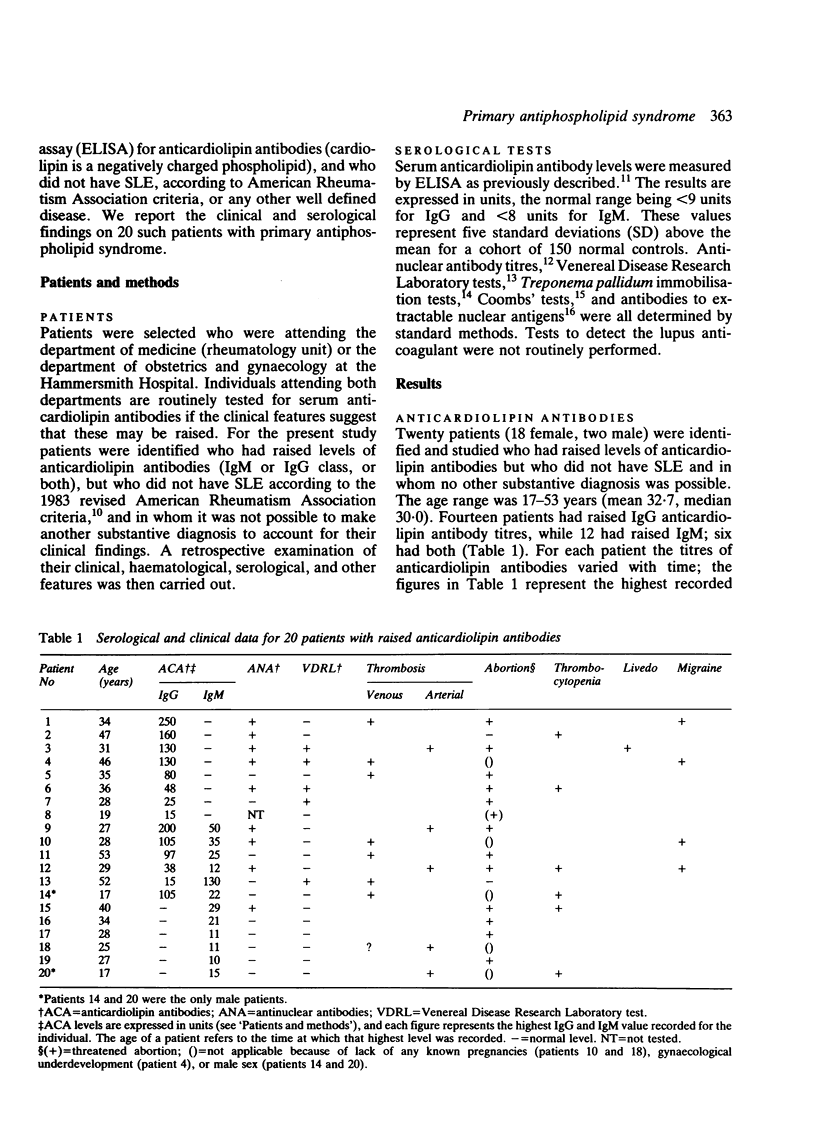
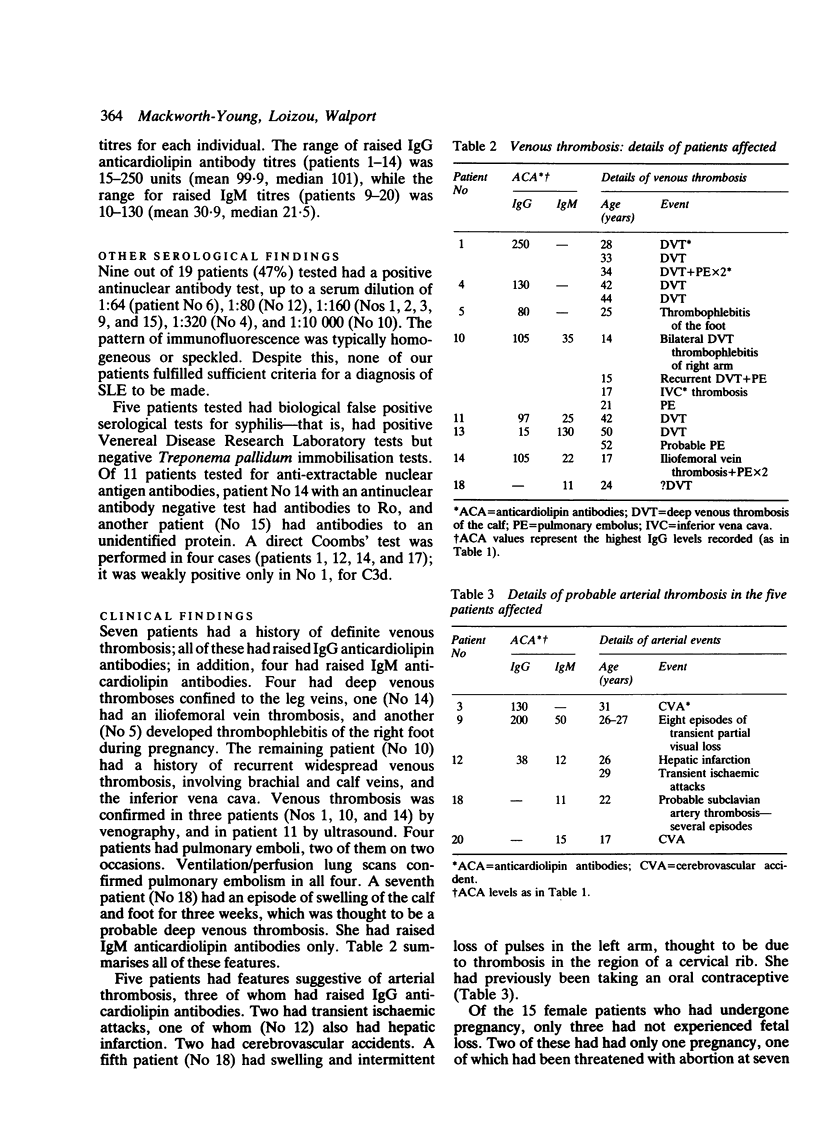
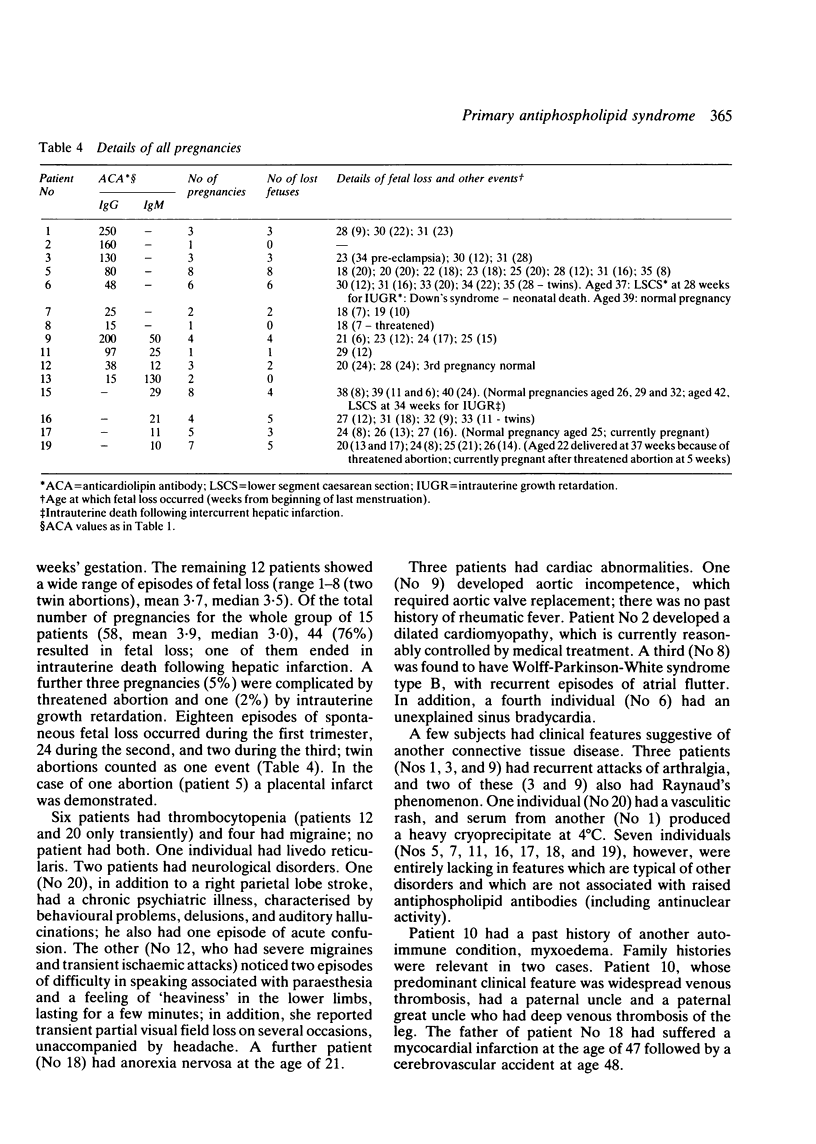
Raised levels of serum antiphospholipid antibodies have most commonly been reported in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). There remains, however, a group of patients with raised antiphospholipid antibody levels who do not have any other well defined disease, but do have clinical features associated with these raised antibodies. The clinical, haematological, and serological features of 20 such patients are reported. Antiphospholipid antibody levels were measured by a solid phase assay for anticardiolipin activity. Fourteen patients had raised IgG antiphospholipid antibodies, 12 had raised IgM, and six had both. Nine out of 19 had raised antinuclear antibody levels; however, non fulfilled criteria for the diagnosis of SLE. Seven patients had a history of venous thrombosis and five of definite or presumed arterial thrombosis-for example, stroke. Of the 15 female patients who underwent pregnancy, 12 experienced fetal loss with up to eight abortions each (mean 3.6). Six individuals had thrombocytopenia and four others had migraines. Other clinical features included livedo reticularis, cardiac and neuropsychiatric disorders, arthralgias, and Raynaud's phenomenon. These findings confirm that the clinical features of individuals with what may be called the 'primary antiphospholipid syndrome' are similar to those in patients with other diagnoses who have raised antiphospholipid antibodies. They indicate that the antiphospholipid syndrome may be related to SLE and other autoimmune diseases, but that, although it frequently overlaps with these disorders, it also exists as a distinct entity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein R. M., Steigerwald J. C., Tan E. M. Association of antinuclear and antinucleolar antibodies in progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):43–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn C. C., Gharavi A. E., Hughes G. R. Antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens in 173 patients with DNA-binding positive SLE: an association between antibodies to ribonucleoprotein and Sm antigens observed by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1982 May;8(1):13–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreras L. O., Vermylen J. G. "Lupus" anticoagulant and thrombosis--possible role of inhibition of prostacyclin formation. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Aug 24;48(1):38–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaço C. B., Male D. K. Anti-phospholipid antibodies in syphilis and a thrombotic subset of SLE: distinct profiles of epitope specificity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):449–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyssinet J. M., Cazenave J. P. Lupus-like anticoagulants, modulation of the protein C pathway and thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Aug 4;58(2):679–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Asherson R. A., Gharavi A. E., Morgan S. H., Derue G., Hughes G. R. Thrombocytopenia in SLE and related autoimmune disorders: association with anticardiolipin antibody. Br J Haematol. 1985 Feb;59(2):227–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb02988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Hughes G. R. Anti-phospholipid antibodies. Clin Rheum Dis. 1985 Dec;11(3):591–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G. R. The anticardiolipin syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1985 Oct-Dec;3(4):285–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. G., Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Tincani A., Asherson R. A., Valesini G., Denman A. M., Froude G., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: occurrence in Behçet's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Oct;43(5):746–748. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.5.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loizou S., McCrea J. D., Rudge A. C., Reynolds R., Boyle C. C., Harris E. N. Measurement of anti-cardiolipin antibodies by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): standardization and quantitation of results. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):738–745. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackworth-Young C. G., Harris E. N., Steere A. C., Rizvi F., Malawista S. E., Hughes G. R., Gharavi A. E. Anticardiolipin antibodies in Lyme disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Aug;31(8):1052–1056. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moysan J. F., Jouquan J., Gérard C., Pennec Y., Le Goff P., Youinou P. La cible des anticorps anti-cardiolipine est-elle la même au cours du syndrome de Gougerot-Sjögren et au cours du lupus érythémateux disséminé? Rev Med Interne. 1987 Mar-Apr;8(2):163–168. doi: 10.1016/s0248-8663(87)80165-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibold J. R., Knight P. J., Peter J. B. Anticardiolipin antibodies in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):1052–1053. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein C., Miller M. H., Axtens R., Buchanan R., Littlejohn G. O. Livedo reticularis associated with increased titers of anticardiolipin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol. 1987 May;123(5):596–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


