Abstract
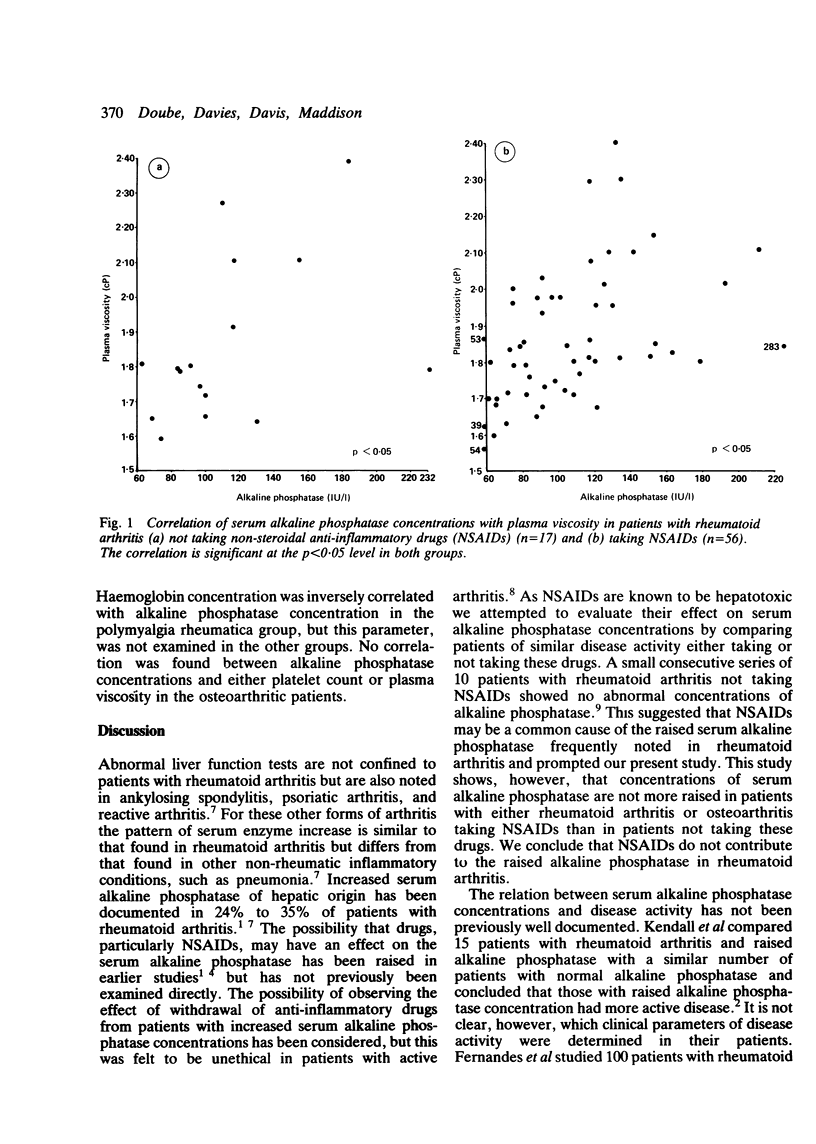
The influence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and of disease activity on the serum alkaline phosphatase concentration was examined in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and polymyalgia rheumatica. Concentrations of serum alkaline phosphatase were similar both in patients with rheumatoid arthritis taking NSAIDs and in those not taking NSAIDs. In patients with osteoarthritis NSAID use was not associated with a significant increase in serum alkaline phosphatase. In rheumatoid arthritis no correlation was found between clinical indices of disease activity and serum alkaline phosphatase concentrations. There was significant correlation with plasma viscosity in rheumatoid arthritis, both in those taking and not taking NSAIDs, and in polymyalgia rheumatica. Serum alkaline phosphatase concentrations are not influenced by NSAIDs. Concentrations correlate with laboratory parameters, but not clinical indices of disease activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akesson A., Berglund K., Karlsson M. Liver function in some common rheumatic disorders. Scand J Rheumatol. 1980;9(2):81–88. doi: 10.3109/03009748009098135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doube A. Liver function tests and NSAIDs in rheumatoid arthritis. N Z Med J. 1987 Feb 25;100(818):120–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes L., Sullivan S., McFarlane I. G., Wojcicka B. M., Warnes T. W., Eddleston A. L., Hamilton E. B., Williams R. Studies on the frequency and pathogenesis of liver involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979 Dec;38(6):501–506. doi: 10.1136/ard.38.6.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall M. J., Cockel R., Becker J., Hawkins C. F. Raised serum alkaline phosphatase in rheumatoid disease. An index of liver dysfunction? Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Sep;29(5):537–540. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.5.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J. R., Pickup M. E., Dixon J. S., Leatham P. A., Rhind V. M., Wright V., Downie W. W. Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase levels in arthritis: a correlation with clinical and laboratory indices of disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Oct;37(5):428–431. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.5.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills P. R., MacSween R. N., Dick W. C., More I. A., Watkinson G. Liver disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Scott Med J. 1980 Jan;25(1):18–22. doi: 10.1177/003693308002500104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thould A. K. Constrictive pericarditis in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Feb;45(2):89–94. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.2.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J., Whaley K., MacSween R. N., Nuki G., Dick W. C., Buchanan W. W. Liver disease in rheumatoid arthritis and Sjøgren's syndrome. Prospective study using biochemical and serological markers of hepatic dysfunction. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Feb;34(1):70–81. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


