Abstract
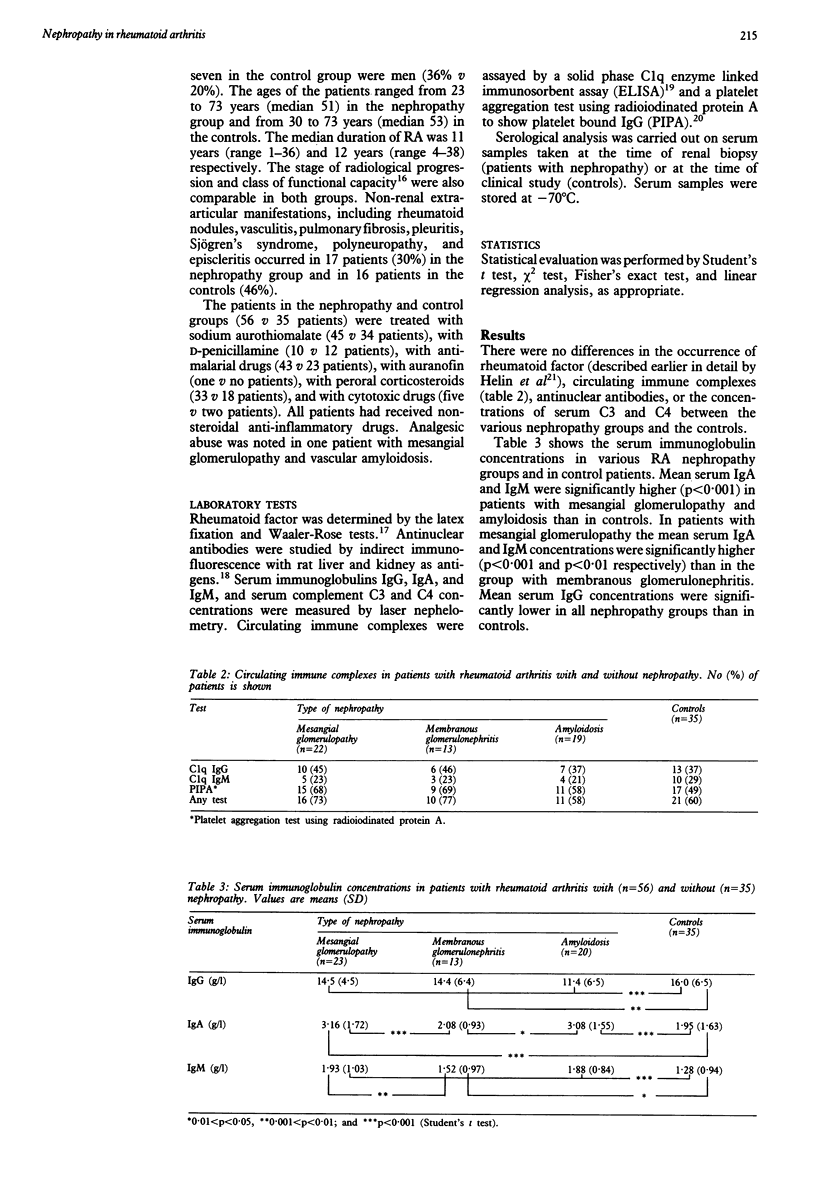
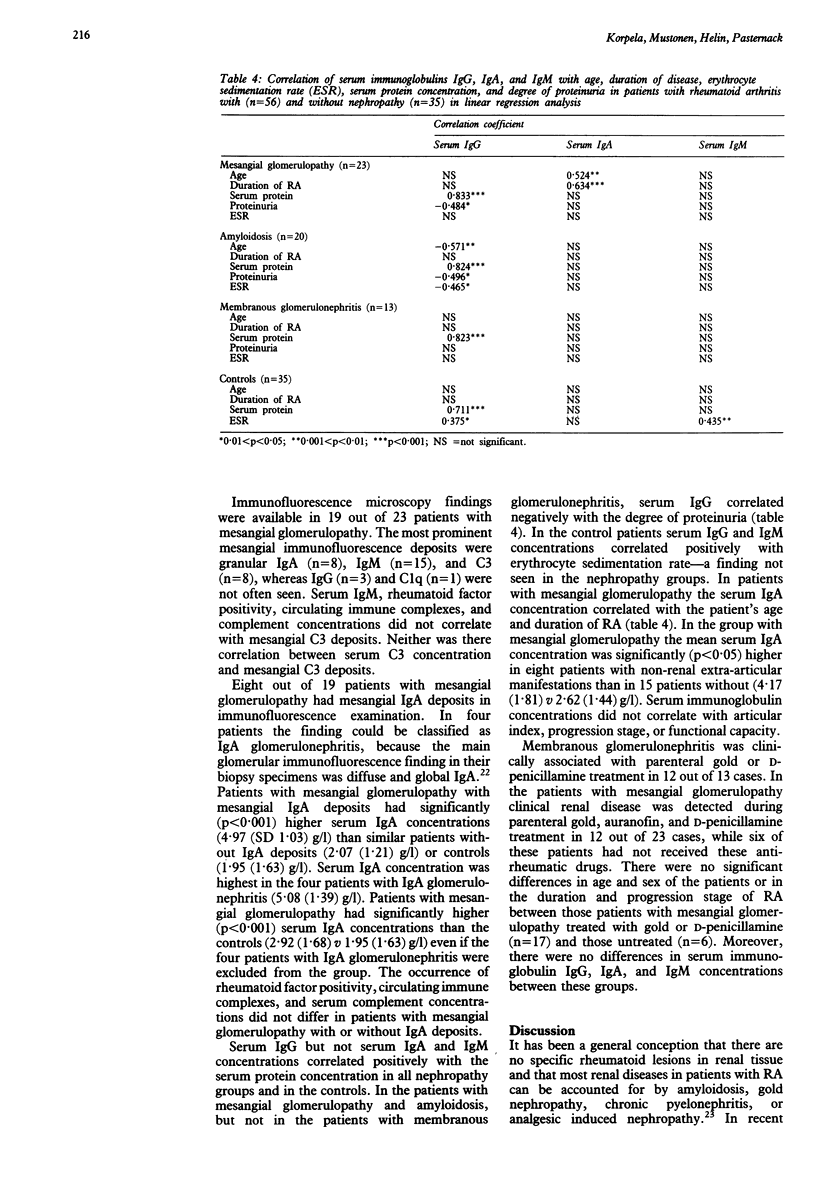
Serum immunoglobulins IgG, IgA, and IgM, serum complement components C3 and C4, circulating immune complexes, antinuclear antibodies, and rheumatoid factor were measured in 56 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and nephropathy (23 with mesangial glomerulopathy; 13 with membranous glomerulonephritis; and 20 with amyloidosis) and 35 patients with RA without nephropathy (controls). Renal immunofluorescence findings in patients with mesangial glomerulopathy were compared with the serologic data. There were no differences in the occurrence of rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibodies, and circulating immune complexes and the concentrations of serum complement C3 and C4 between various RA nephropathy groups and controls. Serum IgA and IgM concentrations were significantly higher in patients with mesangial glomerulopathy and amyloidosis than in controls. In patients with mesangial glomerulopathy glomerular IgM, IgA, and C3 were the most prominent findings in immunofluorescence examination. The serum IgA concentration was significantly higher in those patients with mesangial glomerulopathy with mesangial IgA deposits than in those without (4.97 (SD 1.03) g/l v 2.07 (1.21) g/l). The highest serum IgA concentrations (5.08 (1.39) g/l) were seen in the four patients with IgA glomerulonephritis. The prevalence of IgA glomerulonephritis in the renal biopsy material of the patients with RA was 5%, which possibly differs little from that seen in the general population. The results suggest that circulating immune complexes may not have any major role in the pathogenesis of various nephropathy types in patients with RA, contrary to their role in most extra-articular manifestations of RA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arden J., Mullinax F., Waller M. Immunoglobulin levels in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with rheumatoid factor titers, clinical stage and disease duration. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Jun;10(3):228–234. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman M., Adu D., Howie A. J., McConkey B., Michael J., Popert A. J. Rheumatoid arthritis and IgA nephropathy. Br J Rheumatol. 1987 Aug;26(4):299–302. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/26.4.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. S., Clark W. F. A role for insoluble antibody-antigen complexes in glomerulonephritis? Clin Nephrol. 1982 Aug;18(2):55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Salant D. J. In situ immune complex formation and glomerular injury. Kidney Int. 1980 Jan;17(1):1–13. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald O. M., Barnes L., Woods R., McHugh L., Barry C., O'Loughlin S. Direct immunofluorescence of normal skin in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1985 Nov;24(4):340–345. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/24.4.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco A. E., Schur P. H. Hypocomplementemia in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Mar-Apr;14(2):231–238. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank O., Klemmayer K. Das Verhalten der Immunglobuline im Serum bei progredient chronischer Polyarthritis in Abhängigkeit von der Verlaufsform. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1971 Jul;142(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin H., Korpela M., Mustonen J., Pasternack A. Mild mesangial glomerulopathy--a frequent finding in rheumatoid arthritis patients with hematuria or proteinuria. Nephron. 1986;42(3):224–230. doi: 10.1159/000183671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin H., Korpela M., Mustonen J., Pasternack A. Rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis associated renal disease and in lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Jun;45(6):508–511. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.6.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin H., Mustonen J., Pasternack A., Antonen J. IgM-associated glomerulonephritis. Nephron. 1982;31(1):11–16. doi: 10.1159/000182598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiki Y., Kobayashi Y., Tateno S., Sada M., Kashiwagi N. Strong association of HLA-DR4 with benign IgA nephropathy. Nephron. 1982;32(3):222–226. doi: 10.1159/000182849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hordon L. D., Sellars L., Morley A. R., Wilkinson R., Thompson M., Griffiths I. D. Haematuria in rheumatoid arthritis: an association with mesangial glomerulonephritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Jun;43(3):440–443. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.3.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakle C., Feigal D. W., Robbins D. L., Shapiro R., Wiesner K. Serum IgG and IgM rheumatoid factors and complement activation in extraarticular rheumatoid disease. J Rheumatol. 1985 Apr;12(2):227–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jans H., Halberg P., Lorenzen I. Circulating immune complexes in rheumatoid arthritis with extra-articular manifestations. Scand J Rheumatol. 1983;12(3):215–218. doi: 10.3109/03009748309098536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwabara H., Shishido H., Tomura S., Tuchida H., Miyajima T. Strong association between IgA nephropathy and HLA-DR4 antigen. Kidney Int. 1982 Oct;22(4):377–382. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekomäki R., Penttinen K. Platelets and 125I-labelled staphylococcal protein A in the detection of immune complexes in serum. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1979 Feb;1(4):305–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustonen J., Pasternack A., Helin H., Nikkilä M. Clinicopathologic correlations in a series of 143 patients with IgA glomerulonephritis. Am J Nephrol. 1985;5(3):150–157. doi: 10.1159/000166925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayi G. S., Wooley P., Batchelor J. R. Genetic basis of rheumatoid disease: HLA antigens, disease manifestations, and toxic reactions to drugs. Br Med J. 1978 Nov 11;2(6148):1326–1328. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6148.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillemer S. R., Reynolds W. J., Yoon S. J., Perera M., Newkirk M., Klein M. IgA related disorders in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1987 Oct;14(5):880–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon M. I., Gallo G., Poon T. P., Goldblat M. V., Tchertkoff V. The kidney in rheumatoid arthritis. A study based on renal biopsies. Nephron. 1974;12(4):297–310. doi: 10.1159/000180342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Kojima H., Koshikawa S. IgA nephropathy in rheumatoid arthritis. Nephron. 1988;48(2):169–170. doi: 10.1159/000184903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellars L., Siamopoulos K., Wilkinson R., Leohapand T., Morley A. R. Renal biopsy appearances in rheumatoid disease. Clin Nephrol. 1983 Sep;20(3):114–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serov V. V., Tareeva I. E., Borisov I. A., Varshavskii V. A. Revmatoidnaia nefropatiia. Sov Med. 1972 Mar;35(3):14–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinniah R. Occurrence of mesangial IgA and IgM deposits in a control necropsy population. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Mar;36(3):276–279. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.3.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrifvars B. Immunofluorescence study of renal biopsies in chronic rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1979;8(4):241–247. doi: 10.3109/03009747909114630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P. Association of the B-cell alloantigen DRw4 with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 20;298(16):869–871. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804202981602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tönroth T., Skrifvars B. Gold nephropathy prototype of membranous glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1974 Jun;75(3):573–590. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman S., Høier-Madsen M., Halberg P., Jans H., Sylvest J. Deposits of immunoglobulins and complement in skin of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Influence of anti-rheumatic treatment. Scand J Rheumatol. 1979;8(2):119–123. doi: 10.3109/03009747909105349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Riel P. L., van de Putte L. B., Gribnau F. W., de Waal R. M. Serum IgA and gold-induced toxic effects in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Intern Med. 1984 Jul;144(7):1401–1403. doi: 10.1001/archinte.144.7.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziola B., Salmi A., Penttinen K. Porcine C1q and the solid-phase immunoassay of human immune complexes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Mar 26;49(3):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Nydegger U., Perrin L. H., Fehr K., McCormick J., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Circulating and intra-articular immune complexes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of 125I-Clq binding activity with clinical and biological features of the disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1308–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI108399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


