Abstract
Identification of several autoantibodies in serum samples from patients with ankylosing spondylitis or suspected ankylosing spondylitis is reported. Five antibodies associated with ankylosing spondylitis were identified by applying cytoimmunofluorescence and immunoblotting techniques to antigen pools from insect tissue. At least one of these antibodies was found in 82% of serum samples from patients with ankylosing spondylitis. A 36 kD drosophila antigen, which showed the most common and most dominant reaction, was further purified and isolated. Thirty two (34%) of the serum samples from 95 patients with definite ankylosing spondylitis and 12 (28%) of the serum samples from 43 patients with suspected ankylosing spondylitis reacted with this antigen. Antibodies purified from the 36 kD antigen reacted specifically with a 69 kD antigen present in separations of total protein preparations from human lymphocytes and HeLa cells. The 36 kD antibody was not found in 29 patients with rheumatoid arthritis nor in 38 apparently healthy controls. The prevalence of the 36 kD antibody was comparable in HLA-B27 positive and negative patients. In addition, the same immunoreaction was found in patients with so called 'seronegative' spondylarthropathies, particularly of the ankylosing spondylitis-type, suggesting that this antibody is specific for ankylosing spondylitis or other 'seronegative' spondylarthropathies with the typical clinical and radiological changes of ankylosing spondylitis.
Full text
PDF

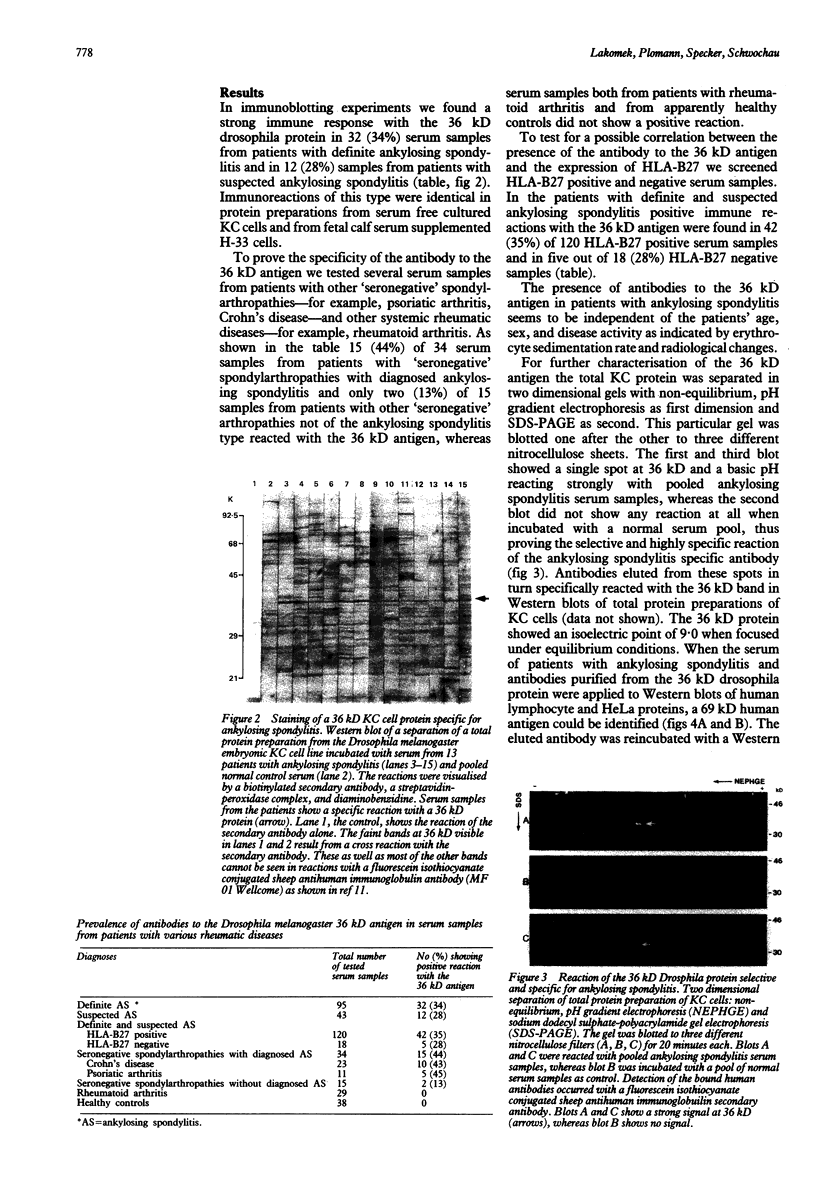
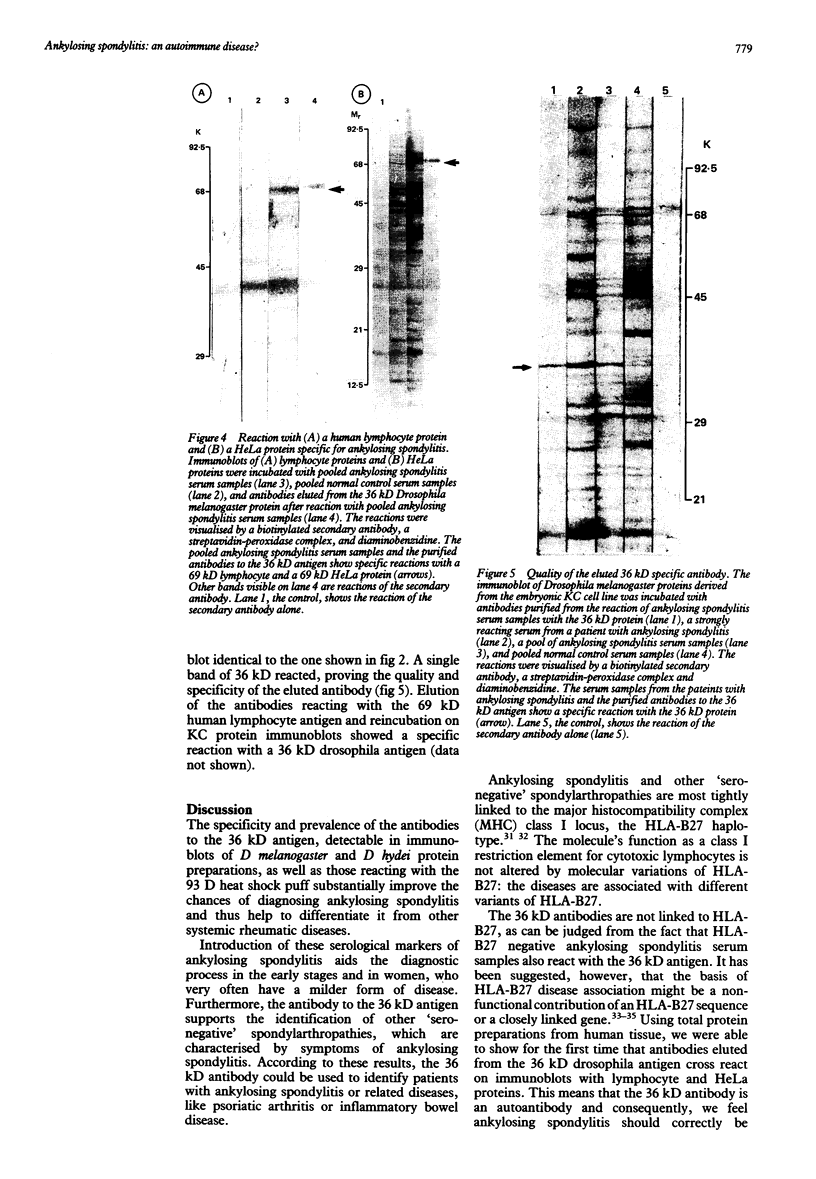


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C. Seronegative spondylarthropathies. Bull Rheum Dis. 1987;37(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYUM A. SEPARATION OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS. Nature. 1964 Nov 21;204:793–794. doi: 10.1038/204793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. I., Todd J. A., McDevitt H. O. The molecular basis of HLA-disease association. Adv Hum Genet. 1989;18:1–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewerton D. A., Hart F. D., Nicholls A., Caffrey M., James D. C., Sturrock R. D. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet. 1973 Apr 28;1(7809):904–907. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calin A., Fries J. F. Striking prevalence of ankylosing spondylitis in "healthy" w27 positive males and females. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 23;293(17):835–839. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510232931701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppin H. L., McDevitt H. O. Absence of polymorphism between HLA-B27 genomic exon sequences isolated from normal donors and ankylosing spondylitis patients. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2168–2172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G. II. Established diploid cell lines of Drosophila melanogaster as potential material for the study of genetics of somatic cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1971;55:220–227. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65224-0_36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. In vitro culture of Drosophila melanogaster embryonic cells. In Vitro. 1970 Nov-Dec;6(3):162–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02617759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eghtedari A. A., Davis P., Bacon P. A. Immunological reactivity in ankylosing spondylitis. Circulating immunoblasts, autoantibodies, and immunoglobulins. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Apr;35(2):155–157. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.2.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson V., Kornreich H. Systemic rheumatic disorders ("collagen disease") in childhood: lupus erythematosus, anaphylactoid purpura, dermatomyositis, and scleroderma. I. Bull Rheum Dis. 1967 Jan;17(5):435–contd. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr R. W., Hahn Y., Schwartz B. D. Structural identity of human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen-B27 molecules from patients with ankylosing spondylitis and normal individuals. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):443–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI110468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella T. D. Correlative studies of lymphocyte transformation and plasma protein levels in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1979 Nov-Dec;6(6):621–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella T. D., Espinoza L., Vasey F. B. Serum complement and immunoglobulin levels in sporadic and familial ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1975 Sep;2(3):308–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakomek H. J., Schwochau M., Decken K., Juli E., Will H., Krüskemper H. L. Attempts towards a serological diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol. 1987 Sep;6 (Suppl 2):67–72. doi: 10.1007/BF02203387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakomek H. J., Will H., Zech M., Krüskemper H. L. A new serologic marker in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Sep;27(9):961–967. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll J. M. Pathogenic mechanism of B27 related seronegative polyarthritis: interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1987;5 (Suppl 1):S7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll J. M., Wright V. New York clinical criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A statistical evaluation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jul;32(4):354–363. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.4.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. M., Groppi V. E., Jr, Browning E. T. Resolution of basic cellular proteins including histone variants by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: evaluation of lysine to arginine ratios and phosphorylation. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 15;103(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosstein L., Terasaki P. I., Bluestone R., Pearson C. M. High association of an HL-A antigen, W27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 5;288(14):704–706. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304052881403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwimmbeck P. L., Yu D. T., Oldstone M. B. Autoantibodies to HLA B27 in the sera of HLA B27 patients with ankylosing spondylitis and Reiter's syndrome. Molecular mimicry with Klebsiella pneumoniae as potential mechanism of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):173–181. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondermeijer P. J., Derksen J. W., Lubsen N. H. New cell line: established cell lines of Drosophila hydei. In Vitro. 1980 Nov;16(11):913–914. doi: 10.1007/BF02619327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de BLECOURT J., POLMAN A., de BLECOURT-MEINDERSMA Hereditary factors in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1961 Sep;20:215–220. doi: 10.1136/ard.20.3.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]