Abstract
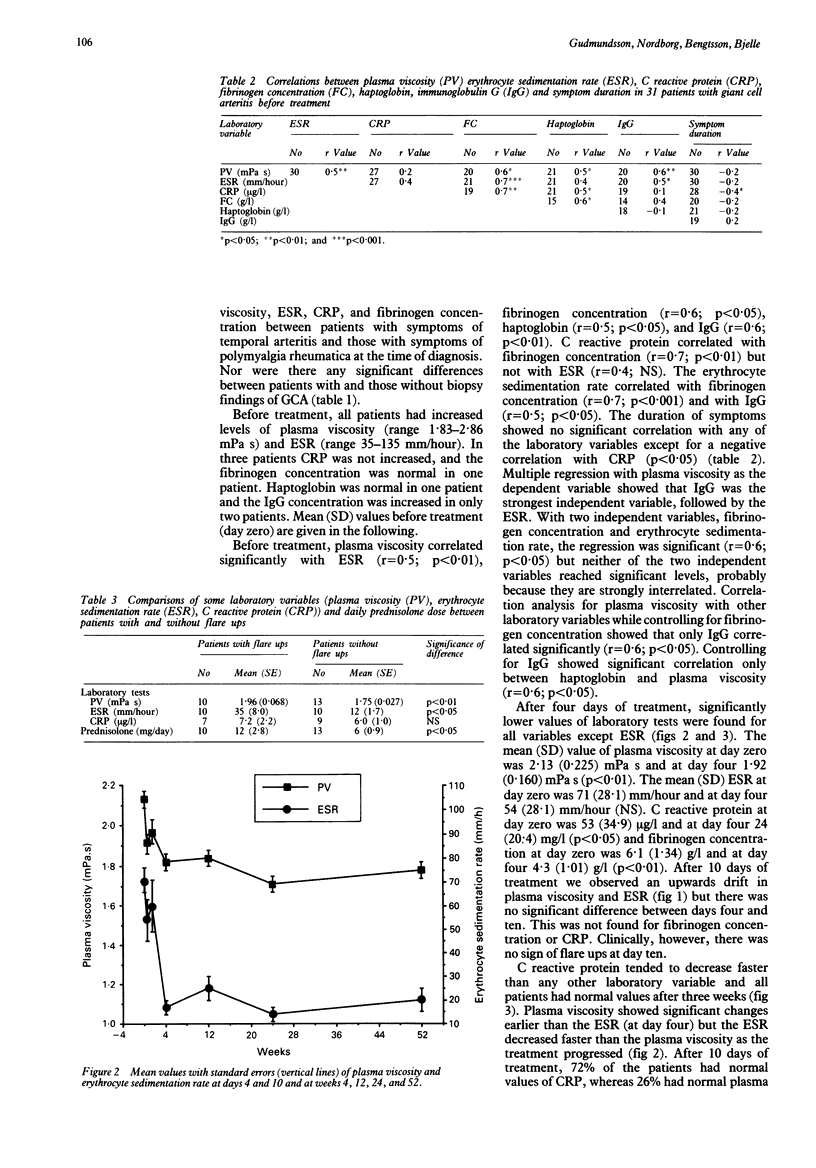
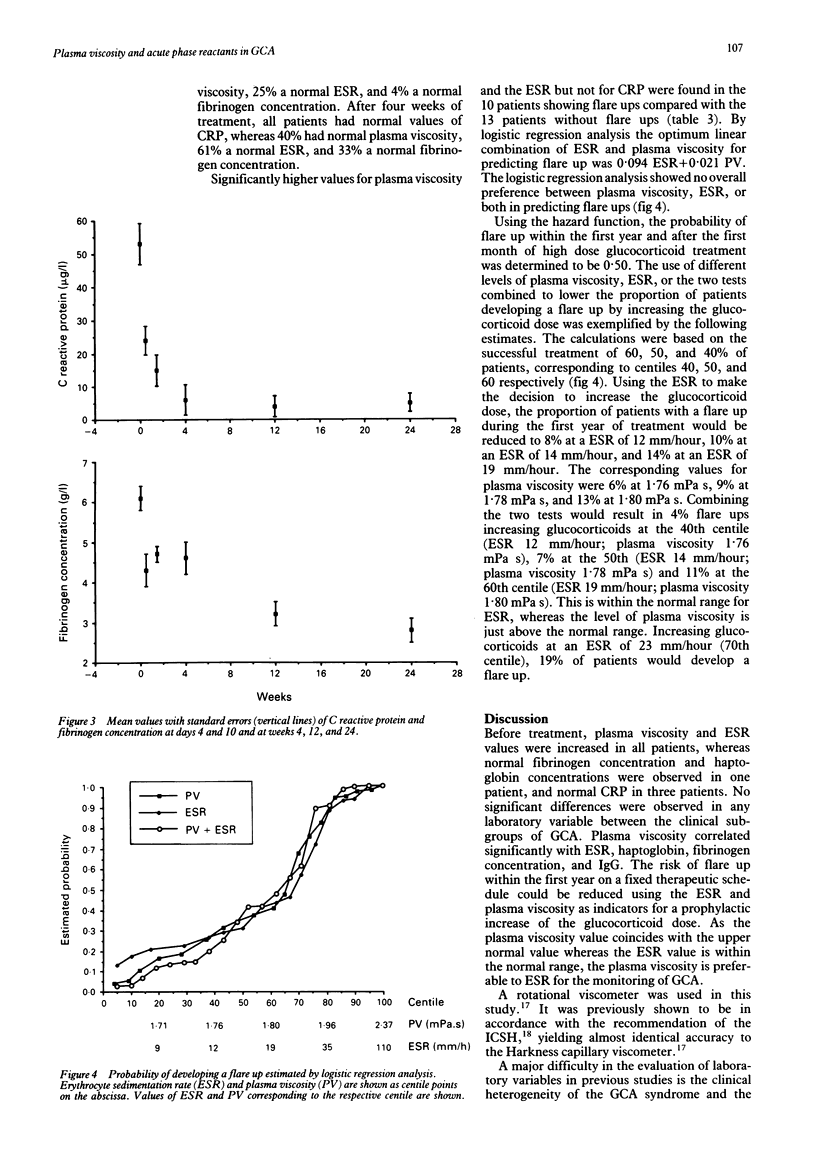
Thirty one patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA) receiving standardised prednisolone treatment were followed up for one year with analyses of plasma viscosity, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C reactive protein (CRP), and fibrinogen concentration. On the day of diagnosis all patients had an increased plasma viscosity and ESR, whereas the concentration of CRP was normal in three patients and fibrinogen concentration and haptoglobin values were normal in one patient. IgG levels were increased in two patients. Plasma viscosity correlated significantly with the ESR, IgG level, and fibrinogen concentration. Laboratory variables in subgroups of patients with GCA proved by biopsy were not different from the whole group of patients with GCA. The follow up showed that CRP normalised faster than the ESR, plasma viscosity, and fibrinogen concentration. Plasma viscosity and the ESR paralleled clinical findings more closely and predicted flare ups better than the other variables. Plasma viscosity had advantages over the ESR for predicting flare ups and in the clinical monitoring of treatment with glucocorticoids.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison M. C., Gough K. R. Steroid sensitive systemic disease with anaemia in the elderly: a manifestation of giant cell arteritis? Postgrad Med J. 1985 Jun;61(716):501–503. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.61.716.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson R., Malmvall B. E., Bengtsson B. A. Acute phase reactants in the initial phase of giant cell arteritis. Acta Med Scand. 1986;220(4):365–367. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1986.tb02779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson B. A., Malmvall B. E. The epidemiology of giant cell arteritis including temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Incidences of different clinical presentations and eye complications. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Jul;24(7):899–904. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttiger L. E., Svedberg C. A. Normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate and age. Br Med J. 1967 Apr 8;2(5544):85–87. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5544.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dare B., Byrne E. Giant cell arteritis. A five-year review of biopsy-proven cases in a teaching hospital. Med J Aust. 1980 Apr 19;1(8):372–373. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1980.tb134927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta B., Panayi G. S. Interleukin-6 in serum of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1990 Dec;29(6):456–458. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/29.6.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M. E., Ralston S. The ESR in the diagnosis and management of the polymyalgia rheumatica/giant cell arteritis syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Apr;42(2):168–170. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esselinckx W., Bucknall R. C., Dixon A. S. Polymyalgia rheumatica. Assessment of disease activity using erythrocyte sedimentation rate and plasma viscosity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Dec;36(6):560–562. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.6.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esselinckx W., Doherty S. M., Dixon A. S. Polymyalgia rheumatica. Abrupt and gradual withdrawal of prednisolone treatment, clinical and laboratory observations. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Jun;36(3):219–224. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.3.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley J. A., McNeil B. J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology. 1982 Apr;143(1):29–36. doi: 10.1148/radiology.143.1.7063747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness J. The viscosity of human blood plasma; its measurement in health and disease. Biorheology. 1971 Dec;8(3):171–193. doi: 10.3233/bir-1971-83-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. G., Hazleman B. L. Prognosis and management of polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Feb;40(1):1–5. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle V., Cawston T. E., Hazleman B. L. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C reactive protein in the assessment of polymyalgia rheumatica/giant cell arteritis on presentation and during follow up. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Aug;48(8):667–671. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.8.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallya R. K., Hind C. R., Berry H., Pepys M. B. Serum C-reactive protein in polymyalgia rheumatica. A prospective serial study. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Apr;28(4):383–387. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miehle W. Polymyalgia arteriitica (rheumatica). Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1983 Dec 23;95(24):855–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myles A. B., Perera T., Ridley M. G. Prevention of blindness in giant cell arteritis by corticosteroid treatment. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Feb;31(2):103–105. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordborg E., Andersson R., Tengborn L., Edén S., Bengtsson B. A. von Willebrand factor antigen and plasminogen activator inhibitor in giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 May;50(5):316–320. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.5.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordborg E., Bengtsson B. A. Death rates and causes of death in 284 consecutive patients with giant cell arteritis confirmed by biopsy. BMJ. 1989 Aug 26;299(6698):549–550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6698.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordborg E., Bengtsson B. A., Nordborg C. Temporal artery morphology and morphometry in giant cell arteritis. APMIS. 1991 Nov;99(11):1013–1023. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1991.tb01294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordborg E., Nordborg C., Bengtsson B. A. Giant cell arteritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1992 Feb;4(1):23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. R., Jones J. G., Hazleman B. L. Relationship of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate to acute phase proteins in polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Oct;40(5):493–495. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen S., Iversen T. O. Rheumatic polymyalgia. Long-term treatment with steroids. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1971;17(3):165–168. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1971.17.issue-1-4.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recommendation for a selected method for the measurement of plasma viscosity. International Committee for Standardization in Haematology. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Oct;37(10):1147–1152. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.10.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen S., Lorenzen I. Giant-cell arteritis, temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. A retrospective study of 63 patients. Acta Med Scand. 1977;201(3):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1977.tb15683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiek J., Krause M., Wiederholt M., Hansen L. L. Hämorheologische Parameter bei Patienten mit Riesenzellarteriitis vor und nach der Behandlung mit Steroiden. Fortschr Ophthalmol. 1990;87(6):671–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise C. M., Agudelo C. A., Chmelewski W. L., McKnight K. M. Temporal arteritis with low erythrocyte sedimentation rate: a review of five cases. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Dec;34(12):1571–1574. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


