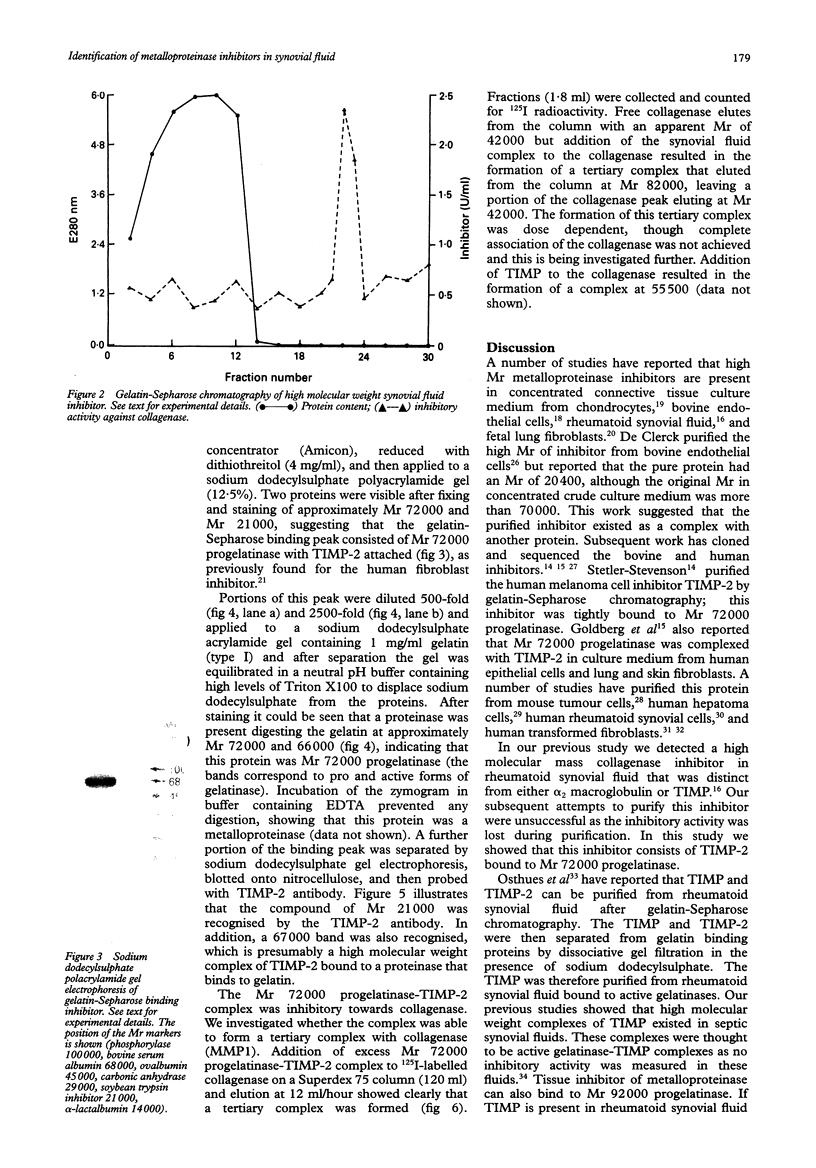
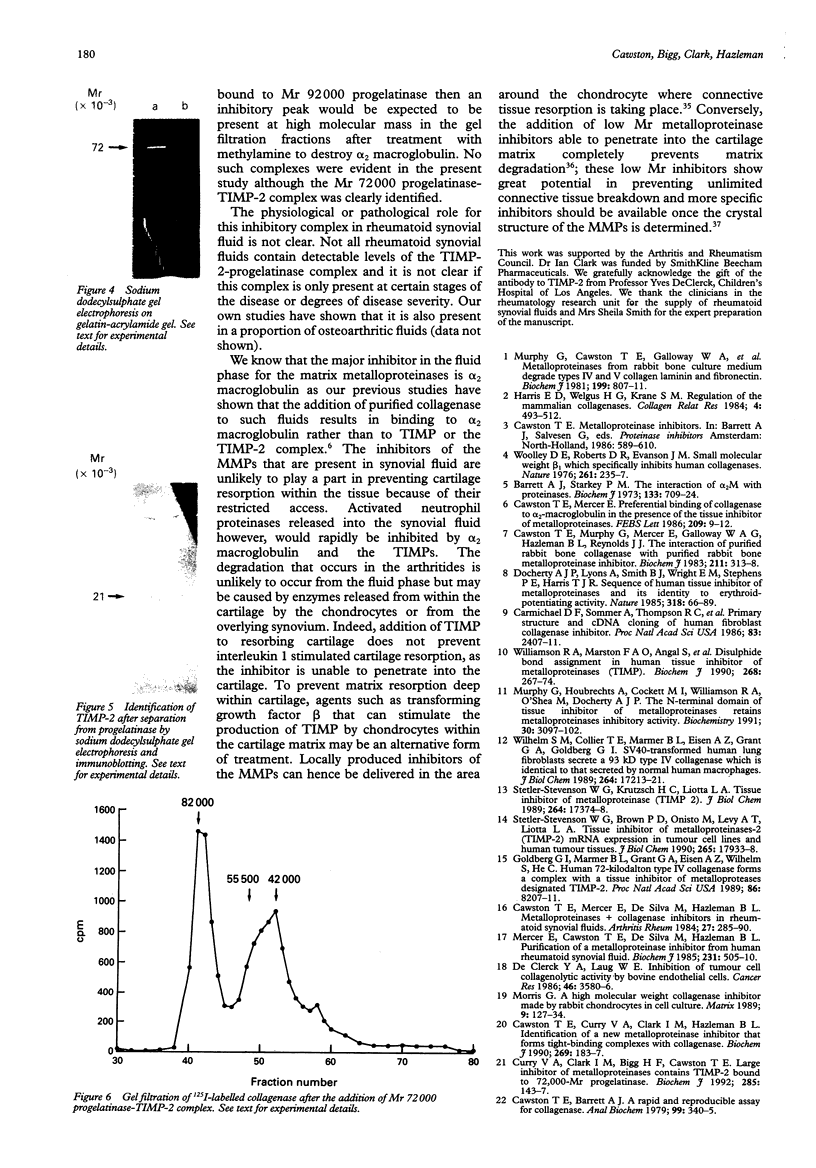
Abstract
The metalloproteinases are a family of enzymes that can degrade all the components of the extracellular matrix. These potent enzymes are often found in proenzyme forms and require activation before the substrate can be digested. To prevent unlimited connective tissue destruction a number of inhibitors exist to limit their activity. In a previous study it was found that metalloproteinases in proenzyme form and metalloproteinase inhibitors were often present in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Two of these inhibitors were identified in rheumatoid synovial fluid as alpha 2 macroglobulin and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP), the specific metalloproteinase inhibitor. A third inhibitory peak was unidentified. In the study reported here it was shown that this third inhibitor can be purified using gelatin-Sepharose chromatography and consists of TIMP-2 bound to progelatinase (relative molecular weight 72,000) in a similar way to that found in concentrated connective tissue culture medium. The importance of these proteinase inhibitors in synovial fluid is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews H. J., Edwards T. A., Cawston T. E., Hazleman B. L. Transforming growth factor-beta causes partial inhibition of interleukin 1-stimulated cartilage degradation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):144–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91974-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews H. J., Plumpton T. A., Harper G. P., Cawston T. E. A synthetic peptide metalloproteinase inhibitor, but not TIMP, prevents the breakdown of proteoglycan within articular cartilage in vitro. Agents Actions. 1992 Sep;37(1-2):147–154. doi: 10.1007/BF01987904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone T. C., Johnson M. J., De Clerck Y. A., Langley K. E. cDNA cloning and expression of a metalloproteinase inhibitor related to tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael D. F., Sommer A., Thompson R. C., Anderson D. C., Smith C. G., Welgus H. G., Stricklin G. P. Primary structure and cDNA cloning of human fibroblast collagenase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2407–2411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Barrett A. J. A rapid and reproducible assay for collagenase using [1-14C]acetylated collagen. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):340–345. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Curry V. A., Clark I. M., Hazleman B. L. Identification of a new metalloproteinase inhibitor that forms tight-binding complexes with collagenase. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):183–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2690183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., McLaughlin P., Hazleman B. L. Paired serum and synovial fluid values of alpha 2-macroglobulin and TIMP in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1987 Oct;26(5):354–358. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/26.5.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Mercer E. Preferential binding of collagenase to alpha 2-macroglobulin in the presence of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 1;209(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Mercer E., de Silva M., Hazleman B. L. Metalloproteinases and collagenase inhibitors in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Mar;27(3):285–290. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Murphy G., Mercer E., Galloway W. A., Hazleman B. L., Reynolds J. J. The interaction of purified rabbit bone collagenase with purified rabbit bone metalloproteinase inhibitor. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):313–318. doi: 10.1042/bj2110313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Tyler J. A. Purification of pig synovial collagenase to high specific activity. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):647–656. doi: 10.1042/bj1830647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. M., Cawston T. E. Fragments of human fibroblast collagenase. Purification and characterization. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 1;263(1):201–206. doi: 10.1042/bj2630201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
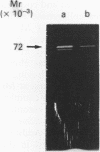
- Curry V. A., Clark I. M., Bigg H., Cawston T. E. Large inhibitor of metalloproteinases (LIMP) contains tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP)-2 bound to 72,000-M(r) progelatinase. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 1;285(Pt 1):143–147. doi: 10.1042/bj2850143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clerck Y. A., Yean T. D., Ratzkin B. J., Lu H. S., Langley K. E. Purification and characterization of two related but distinct metalloproteinase inhibitors secreted by bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17445–17453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClerck Y. A., Laug W. E. Inhibition of tumor cell collagenolytic activity by bovine endothelial cells. Cancer Res. 1986 Jul;46(7):3580–3586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Wilhelm S., He C. S. Human 72-kilodalton type IV collagenase forms a complex with a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteases designated TIMP-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8207–8211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Welgus H. G., Krane S. M. Regulation of the mammalian collagenases. Coll Relat Res. 1984 Dec;4(6):493–512. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. W., Bullen E. C., Banda M. J. Preferential inhibition of 72- and 92-kDa gelatinases by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13070–13075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. W., Bullen E. C., Banda M. J. Regulation of the autoactivation of human 72-kDa progelatinase by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13064–13069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi J., Ogawa K., Yamamoto S., Hayakawa T. Purification and characterization of a new tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP-2) from mouse colon 26 tumor cells. Matrix. 1991 Feb;11(1):10–16. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(11)80222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolkenbrock H., Orgel D., Hecker-Kia A., Noack W., Ulbrich N. The complex between a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP-2) and 72-kDa progelatinase is a metalloproteinase inhibitor. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jun 15;198(3):775–781. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer E., Cawston T. E., de Silva M., Hazleman B. L. Purification of a metalloproteinase inhibitor from human rheumatoid synovial fluid. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):505–510. doi: 10.1042/bj2310505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. M. A high molecular weight collagenase inhibitor made by rabbit chondrocytes in cell culture. Matrix. 1989 Mar;9(2):127–134. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(89)80030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osthues A., Knäuper V., Oberhoff R., Reinke H., Tschesche H. Isolation and characterization of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-1 and TIMP-2) from human rheumatoid synovial fluid. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jan 13;296(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80393-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Krutzsch H. C., Liotta L. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP-2). A new member of the metalloproteinase inhibitor family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17374–17378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umenishi F., Umeda M., Miyazaki K. Efficient purification of TIMP-2 from culture medium conditioned by human hepatoma cell line, and its inhibitory effects on metalloproteinases and in vitro tumor invasion. J Biochem. 1991 Aug;110(2):189–195. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm S. M., Collier I. E., Marmer B. L., Eisen A. Z., Grant G. A., Goldberg G. I. SV40-transformed human lung fibroblasts secrete a 92-kDa type IV collagenase which is identical to that secreted by normal human macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17213–17221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]