Abstract
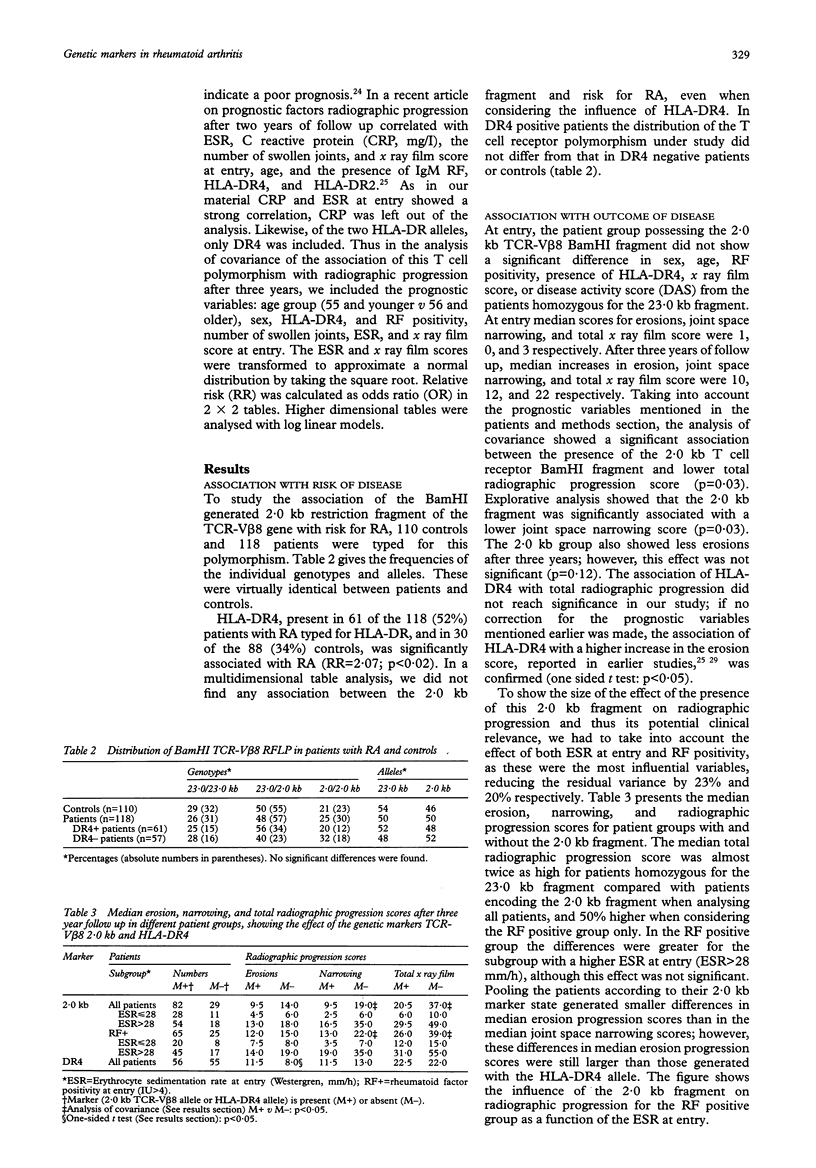
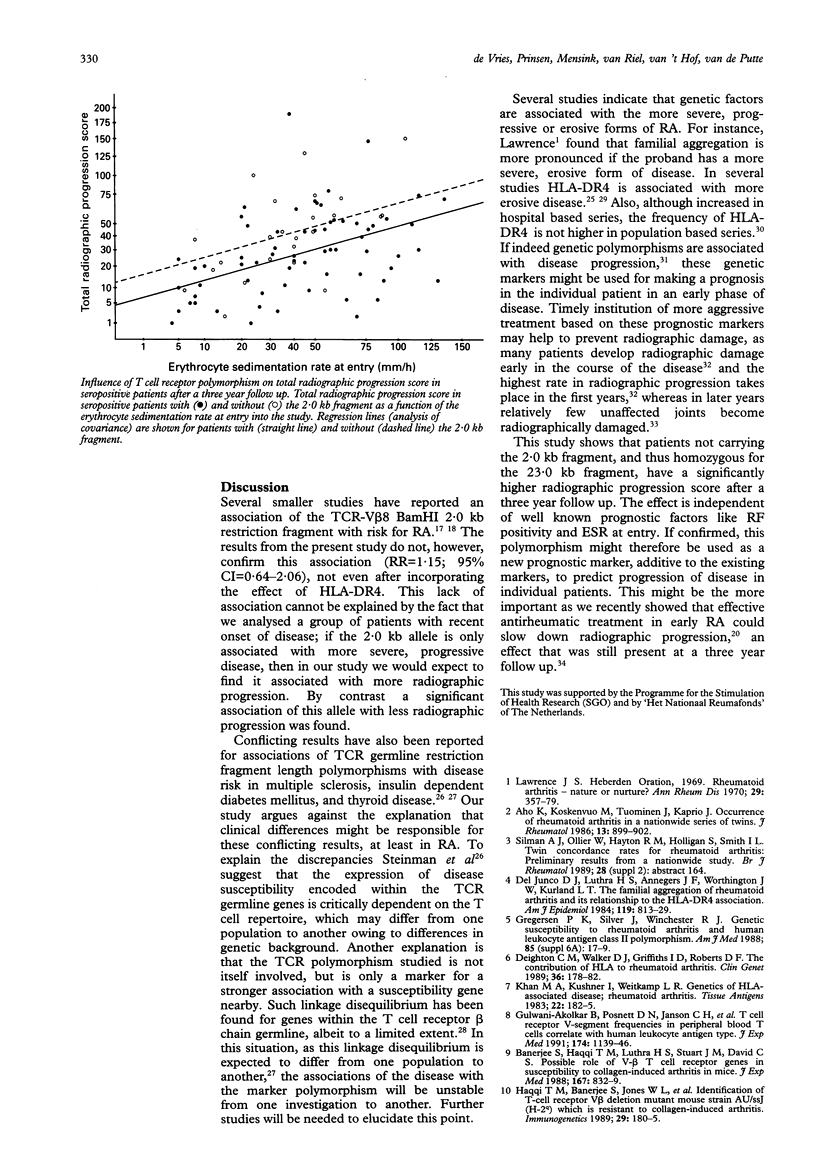
OBJECTIVE--In rheumatoid arthritis (RA) genetic factors influence susceptibility to disease and progression. Identifying these genetic factors may give more insight into the aetiology and pathogenesis of this disease. Furthermore, if these genetic markers can predict progression in an early stage of disease, timely institution of more aggressive treatment in patients with a bad prognosis may help to prevent joint damage. Several studies have shown that HLA-DRB1 alleles are associated with RA, whereas others have indicated that genes not linked to the HLA complex are also involved. Candidates for such genes are the T cell receptor (TCR) alpha/beta genes. METHODS--The association of a polymorphism in a TCR beta chain variable region gene (TCR-V beta 8) with both risk for RA and radiographic progression of joint disease was analysed after a three year follow up. A cohort of 118 white patients with a duration of disease shorter than one year at entry, and 110 white controls were typed for this (BamHI) TCR-V beta 8 polymorphism. RESULTS--The distribution of the two alleles, 2.0 and 23.0 kb, was identical in patients and controls. Radiographic progression (modified Sharp method) after a three year follow up, studied in 111 patients, was significantly less in the group possessing the 2.0 kb allele (p = 0.03). CONCLUSION--This does not confirm the reported association of the (BamHI) TCR-V beta 8 2.0 kb allele with RA. By contrast with previous findings in smaller studies, in the present study this 2.0 kb allele was protective against radiographic progression. Because well known prognostic variables in RA were corrected for, the findings indicate that the TCR-V beta 8 polymorphism studied is a new prognostic marker for this disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K., Koskenvuo M., Tuominen J., Kaprio J. Occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis in a nationwide series of twins. J Rheumatol. 1986 Oct;13(5):899–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S., Haqqi T. M., Luthra H. S., Stuart J. M., David C. S. Possible role of V beta T cell receptor genes in susceptibility to collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):832–839. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall S. S., Concannon P., Charmley P., McFarland H. F., Gatti R. A., Hood L. E., McFarlin D. E., Biddison W. E. The germline repertoire of T cell receptor beta-chain genes in patients with chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jan;21(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook A., Corbett M. Radiographic changes in early rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Feb;36(1):71–73. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charmley P., Chao A., Concannon P., Hood L., Gatti R. A. Haplotyping the human T-cell receptor beta-chain gene complex by use of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4823–4827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deighton C. M., Walker D. J., Griffiths I. D., Roberts D. F. The contribution of HLA to rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Genet. 1989 Sep;36(3):178–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaine A. G., Vaughan R. W., Taube D. H., Welsh K. I. Association of membranous nephropathy with T-cell receptor constant beta chain and immunoglobulin heavy chain switch region polymorphisms. Immunogenetics. 1988;27(1):19–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00404439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funkhouser S. W., Concannon P., Charmley P., Vredevoe D. L., Hood L. Differences in T cell receptor restriction fragment length polymorphisms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Apr;35(4):465–471. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghatak S., Sainis K., Owen F. L., Datta S. K. T-cell-receptor beta- and I-A beta-chain genes of normal SWR mice are linked with the development of lupus nephritis in NZB x SWR crosses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6850–6853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giphart M. J., Verduijn W. The Eurotransplant HLA-DRB oligonucleotide typing set. Eur J Immunogenet. 1991 Feb-Apr;18(1-2):57–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1991.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulwani-Akolkar B., Posnett D. N., Janson C. H., Grunewald J., Wigzell H., Akolkar P., Gregersen P. K., Silver J. T cell receptor V-segment frequencies in peripheral blood T cells correlate with human leukocyte antigen type. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1139–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haqqi T. M., Banerjee S., Jones W. L., Anderson G., Behlke M. A., Loh D. Y., Luthra H. S., David C. S. Identification of T-cell receptor V beta deletion mutant mouse strain AU/ssJ (H-2q) which is resistant to collagen-induced arthritis. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(3):180–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00373643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillert J., Olerup O. Germ-line polymorphism of TCR genes and disease susceptibility--fact or hypothesis? Immunol Today. 1992 Feb;13(2):47–49. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90132-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Tanimoto M., Kamura H., Yoneda M., Morishima Y., Yamauchi K., Itatsu T., Takatsuki K., Saito H. Association of HLA antigen and restriction fragment length polymorphism of T cell receptor beta-chain gene with Graves' disease and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Jul;69(1):100–104. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-1-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. A., Kushner I., Weitkamp L. R. Genetics of HLA-associated disease; rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Antigens. 1983 Sep;22(3):182–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1983.tb01189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. S. Heberden Oration, 1969. Rheumatoid arthritis--nature or nurture? Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Jul;29(4):357–379. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.4.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra N. K., Verduijn W., Taneja V., Drabbels J., Singh S. P., Giphart M. J. Analysis of HLA-DR2-associated polymorphisms by oligonucleotide hybridization in an Asian Indian population. Hum Immunol. 1991 Dec;32(4):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(91)90087-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward B. A., Welsh K. I., Leslie R. D., Pyke D. A., Demaine A. G. T cell receptor beta chain polymorphisms are associated with insulin-dependent diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Oct;70(1):152–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seboun E., Robinson M. A., Doolittle T. H., Ciulla T. A., Kindt T. J., Hauser S. L. A susceptibility locus for multiple sclerosis is linked to the T cell receptor beta chain complex. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1095–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu G., Clark S. P., Yoshikai Y., Malissen M., Yanagi Y., Strauss E., Mak T. W., Hood L. The human T cell antigen receptor is encoded by variable, diversity, and joining gene segments that rearrange to generate a complete V gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L., Oksenberg J. R., Bernard C. C. Association of susceptibility to multiple sclerosis with TCR genes. Immunol Today. 1992 Feb;13(2):49–51. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90133-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. J., Griffiths M., Dewar P., Coates E., Dick W. C., Thompson M., Griffiths I. D. Association of MHC antigens with susceptibility to and severity of rheumatoid arthritis in multicase families. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Aug;44(8):519–525. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.8.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A., Jaraquemada D., Awad J., Festenstein H., Corbett M., Hay F. C., Roitt I. M. Association of HLA-DR4/Dw4 and DR2/Dw2 with radiologic changes in a prospective study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Preferential relationship with HLA-Dw rather than HLA-DR specificities. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Jan;27(1):20–25. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jongh B. M., van Romunde L. K., Valkenburg H. A., de Lange G. G., van Rood J. J. Epidemiological study of HLA and GM in rheumatoid arthritis and related symptoms in an open Dutch population. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Aug;43(4):613–619. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.4.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Junco D., Luthra H. S., Annegers J. F., Worthington J. W., Kurland L. T. The familial aggregation of rheumatoid arthritis and its relationship to the HLA-DR4 association. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 May;119(5):813–829. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van 't Hof M. A., van Riel P. L., Theunisse L. A., Lubberts E. W., van Leeuwen M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Judging disease activity in clinical practice in rheumatoid arthritis: first step in the development of a disease activity score. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Nov;49(11):916–920. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.11.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van Leeuwen M. A., van Riel P. L., Koster A. M., van 't Hof M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Biannual radiographic assessments of hands and feet in a three-year prospective followup of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jan;35(1):26–34. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van Riel P. L., Nuver-Zwart I. H., Gribnau F. W., vad de Putte L. B. Effects of hydroxychloroquine and sulphasalazine on progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1989 May 13;1(8646):1036–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van Riel P. L., Nuver-Zwart I. H., van de Putte L. B. Sulphasalazine versus hydroxychloroquine in rheumatoid arthritis: 3-year follow-up. Lancet. 1990 Mar 3;335(8688):539–539. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90771-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van Riel P. L., van Leeuwen M. A., van 't Hof M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Prognostic factors for radiographic damage and physical disability in early rheumatoid arthritis. A prospective follow-up study of 147 patients. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Aug;31(8):519–525. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.8.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van Riel P. L., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Influence of prognostic features on the final outcome in rheumatoid arthritis: a review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1988 May;17(4):284–292. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(88)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


