Abstract
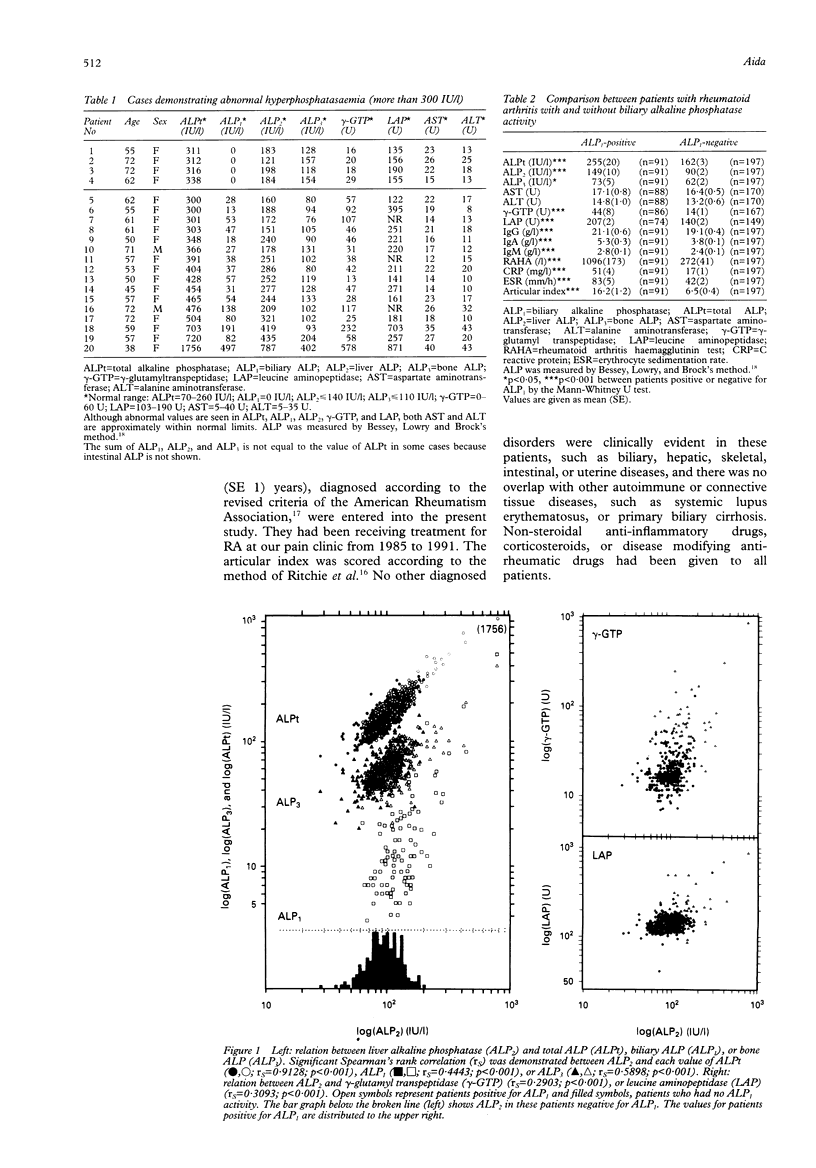
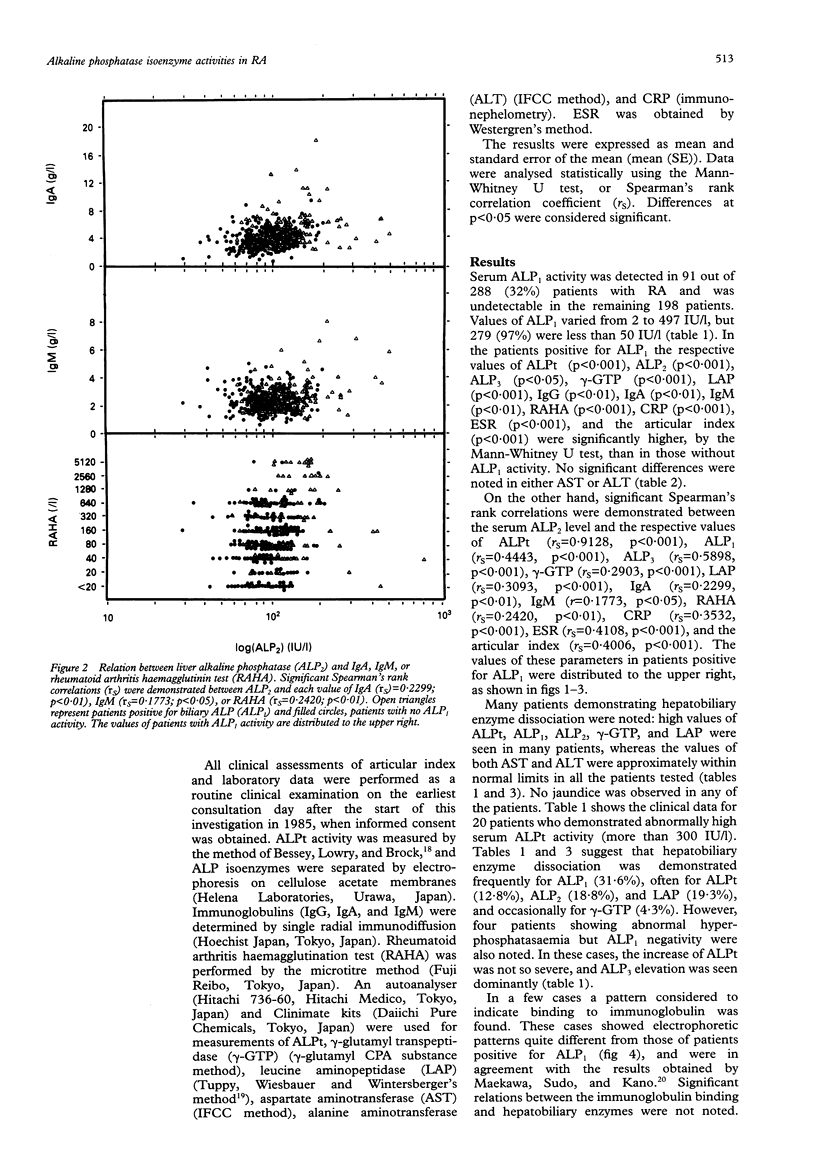
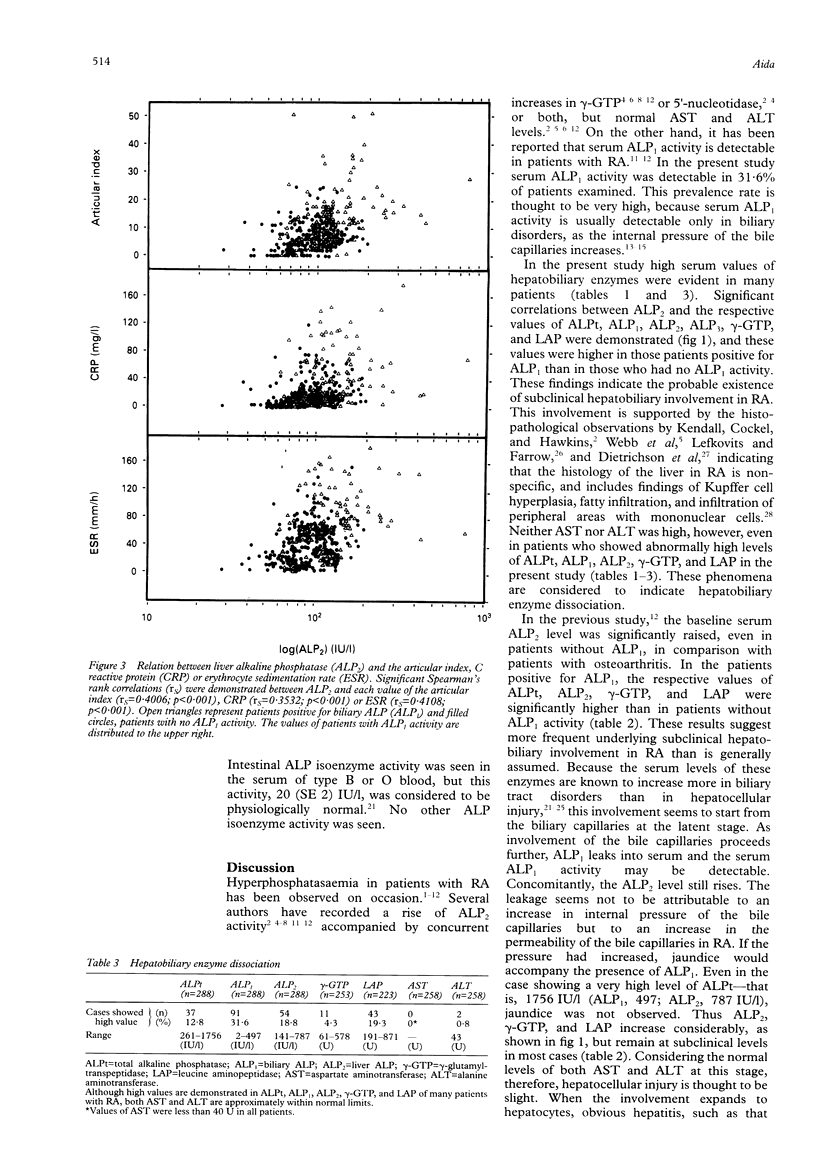
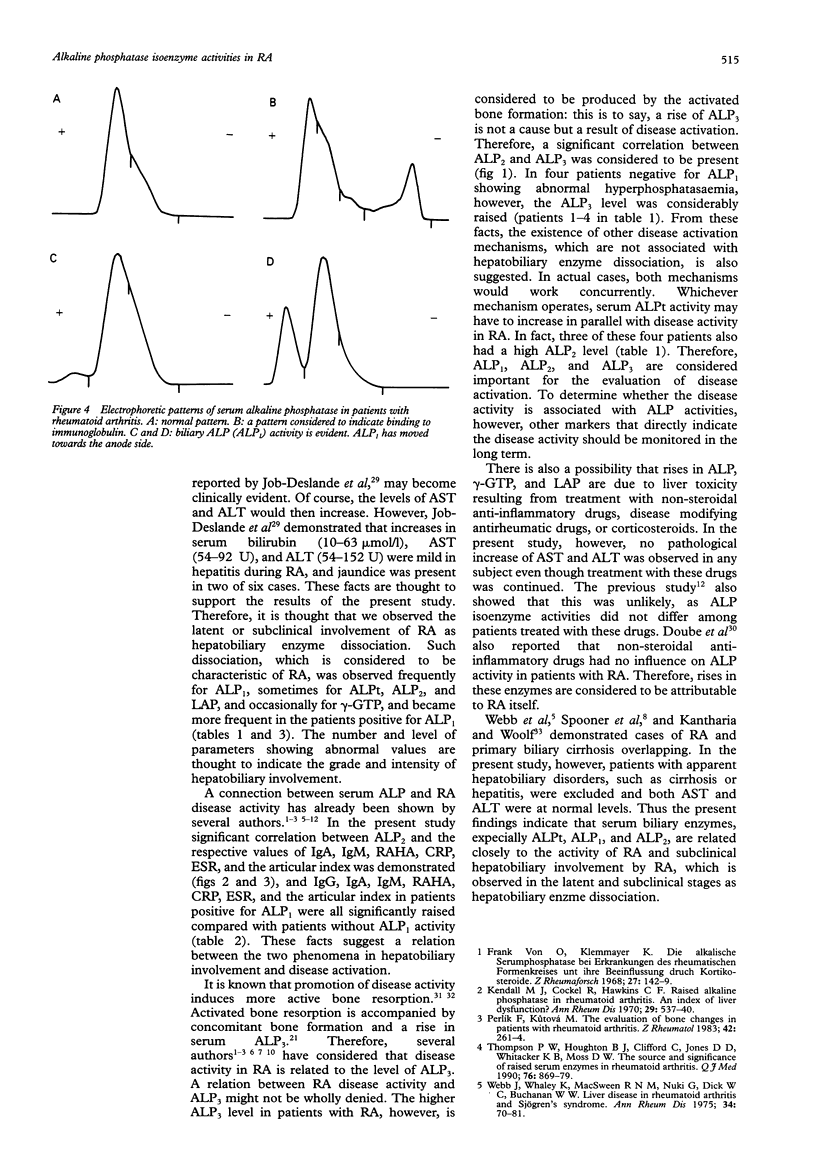
OBJECTIVES--Hyperphosphatasaemia has been observed occasionally in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and it has been suggested that the serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) level is related to the activity of the disease. Therefore, the relationship between serum ALP and RA was studied. METHODS--The serum activities of hepatobiliary enzymes (ALP isoenzymes, gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (GTP), leucine aminopeptidase (LAP), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT)), immunoglobulins, RA haemagglutinin test (RAHA), C reactive protein (CRP), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) were observed in 288 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. RESULTS--Serum biliary ALP (ALP1) activity was detected in 31.6% of the patients. In patients positive for ALP1 the respective values of total ALP (ALPt) (p < 0.001), liver ALP (ALP2) (p < 0.001), bone ALP (ALP3) (p < 0.05), gamma-GTP (p < 0.001), LAP (p < 0.001), immunoglobulins IgG (p < 0.01), IgA (p < 0.01), and IgM (p < 0.01), RAHA (p < 0.001), CRP (p < 0.001), ESR (p < 0.001), and articular index (p < 0.001) were significantly higher than in patients who did not have ALP1. Significant Spearman's rank correlations (rs) were demonstrated between serum ALP2 level and the respective values of ALPt (rs = 0.9128, p < 0.001), ALP1 (rs = 0.4443, p < 0.001), ALP3 (rs = 0.5898, p < 0.001), gamma-GTP (rs = 0.2903, p < 0.001), LAP (rs = 0.3093, p < 0.001), IgA (rs = 0.2299, p < 0.01), IgM (rs = 0.1773, p < 0.05), RAHA (rs = 0.2420, p < 0.01), CRP (rs = 0.3532, p < 0.001), ESR (rs = 0.4006, p < 0.001). the articular index (rs = 0.4006, p < 0.001). However, no significant difference or correlation was noted for either AST or ALT. In many patients who showed abnormal hyperphosphatasaemia, hepatobiliary enzyme dissociation was observed: levels of ALPt (in 12.8%), ALP1 (in 31.6%), ALP2 (18.8%), gamma-GTP (in 4.3%), and LAP (in 19.3%) were abnormally high, but both AST and ALT were within normal limits. CONCLUSION--These findings are considered to be characteristic of RA, and suggest the existence of latent or subclinical hepatobiliary involvement and an association between the expansion of hepatobiliary involvement and the mechanism of disease activation. Thus measurement of the serum levels of ALP and its isoenzymes in RA is considered to be important.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artur Y., Wellman-Bednawska M., Jacquier A., Siest G. Associations between serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and apolipoproteins: relationships with hepatobiliary diseases. Clin Chem. 1984 Aug;30(8):1318–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst D., Lathe G. H., Aparicio S. R. Serum alkaline phosphatase, nucleotide pyrophosphatase, 5'-nucleotide and lipoprotein-X in cholestasis. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Mar 15;67(3):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimmino M. A., Accardo S. Changes in the isoenzyme pattern of alkaline phosphatase in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chem. 1990 Jul;36(7):1376–1377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimmino M. A., Buffrini L., Barisone G., Bruzzone M., Accardo S. Alkaline phosphatase activity in the serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Z Rheumatol. 1990 May-Jun;49(3):143–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofton P. M., Smith A. F. High-molecular-mass alkaline phosphatase in serum and bile: physical properties and relationship with other high-molecular-mass enzymes. Clin Chem. 1981 Jun;27(6):860–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrichson O., From A., Christoffersen P., Juhl E. Morphological changes in liver biopsies from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1976;5(2):65–69. doi: 10.3109/03009747609099892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doube A., Davies J., Davis M., Maddison P. J. Influence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and disease activity on serum alkaline phosphatase concentrations in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 May;48(5):368–371. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.5.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes L., Sullivan S., McFarlane I. G., Wojcicka B. M., Warnes T. W., Eddleston A. L., Hamilton E. B., Williams R. Studies on the frequency and pathogenesis of liver involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979 Dec;38(6):501–506. doi: 10.1136/ard.38.6.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank O., Klemmayer K. Die alkalische Serumphosphatase bei Erkrankungen des rheumatischen Formenkreises und ihre Beeinflussung durch Kortikosteroide. Z Rheumaforsch. 1968 Apr;27(3):142–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job-Deslandre C., Feldmann J. L., Djian Y., Menkes C. J. Chronic hepatitis during rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1991 Sep-Oct;9(5):507–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantharia B. K., Woolf A. D. Raised alkaline phosphatase in rheumatoid arthritis: primary biliary cirrhosis? Br J Rheumatol. 1987 Aug;26(4):313–314. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/26.4.313-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall M. J., Cockel R., Becker J., Hawkins C. F. Raised serum alkaline phosphatase in rheumatoid disease. An index of liver dysfunction? Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Sep;29(5):537–540. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.5.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEFKOVITS A. M., FARROW I. J. The liver in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1955 Jun;14(2):162–169. doi: 10.1136/ard.14.2.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINEDA E. P., GOLDBARG J. A., BANKS B. M., RUTENBURG A. M. Serum leucine aminopeptidase in pancreatic and hepatobiliary diseases. Gastroenterology. 1960 May;38:698–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlík F., Kůtová M. The evaluation of bone changes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Z Rheumatol. 1983 Sep-Oct;42(5):261–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posen S. Alkaline phosphatase. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jul;67(1):183–203. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-1-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. P., Sammons H. G. The nature of the serum alkaline phosphatases in liver diseases. J Clin Pathol. 1974 May;27(5):392–398. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.5.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUTTENBURG A. M., GOLDBARG J. A., PINEDA E. P. SERUM GAMMA-GLUTAMYL TRANSPEPTIDASE ACTIVITY IN HEPATOBILIARY PANCREATIC DISEASE. Gastroenterology. 1963 Jul;45:43–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rico H., Hernandez E. R., Gomez-Castresana F., Yague M., Cabranes J. A., Valor R. Osteopenia in rheumatoid arthritis: a biochemical, hormonal and histomorphometric study. Clin Rheumatol. 1990 Mar;9(1):63–68. doi: 10.1007/BF02030244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosalki S. B., Foo A. Y., Tanner P. A. Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and alkaline phosphatase in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Dec;35(12):1395–1395. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.12.1395-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook P. N., Ansell B. M., Foster S., Gumpel J. M., Hesp R., Reeve J., Zanelli J. M. Bone turnover in early rheumatoid arthritis. 1. Biochemical and kinetic indexes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Sep;44(9):575–579. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.9.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siede W. H., Seiffert U. B., Merle S., Goll H. G., Oremek G. Alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes in rheumatic diseases. Clin Biochem. 1989 Apr;22(2):121–124. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(89)80009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner R. J., Smith D. H., Bedford D., Beck P. R. Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and alkaline phosphatase in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jun;35(6):638–641. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.6.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUPPY H., WIESBAUER U., WINTERSBERGER E. [Amino acid-p-nitroanilide as a substrate for aminopeptidases and other proteolytic enzymes]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1962 Nov 15;329:278–288. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1962.329.1.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. W., Houghton B. J., Clifford C., Jones D. D., Whitaker K. B., Moss D. W. The source and significance of raised serum enzymes in rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1990 Aug;76(280):869–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J., Whaley K., MacSween R. N., Nuki G., Dick W. C., Buchanan W. W. Liver disease in rheumatoid arthritis and Sjøgren's syndrome. Prospective study using biochemical and serological markers of hepatic dysfunction. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Feb;34(1):70–81. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinblatt M. E., Tesser J. R., Gilliam J. H., 3rd The liver in rheumatic diseases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1982 May;11(4):399–405. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(82)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


