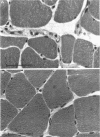
Abstract
OBJECTIVES--To investigate the incidence and significance of Type II fibre atrophy, vessel wall thickening, lymphocytic vasculitis and myositis in needle quadriceps muscle biopsies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and their correlations with clinical and laboratory parameters. METHODS--Needle quadriceps muscle biopsies from 55 patients with SLE and 26 controls were prospectively examined. Clinical and laboratory parameters recorded at the time of muscle biopsy included arthralgia, arthritis, myalgia, proximal weakness, vasculitic rashes, Schirmer test, ENA antibodies, ESR, serum creatine kinase (CK) and plasma C3 degradation products. RESULTS--Abnormal muscle biopsies were significantly more frequent in patients with SLE compared with controls (P < 0.005). None of the controls had lymphocytic vasculitis and/or myositis. The difference in incidence between patients with SLE and controls for lymphocytic vasculitis was significant at P < 0.005. Due to the small number of SLE patients with myositis, the difference in incidence for this abnormal finding reached only P = 0.09. In the SLE patient group, lymphocytic vasculitis was associated with significantly higher ESR values (P = 0.007) and higher incidence of arthritis (P = 0.01); and appears to characterise a subset of patients with positive Schirmer tests, anti-Ro and/or anti-La antibodies. Raised serum CK was found to correspond with underlying myositis in patients with SLE and these patients also had an increased incidence of symptoms of proximal weakness and/or anti-RNP antibodies. In contrast, both Type II fibre atrophy and vessel wall thickening failed to correlate with any of the clinical and laboratory parameters studied and appear to be non-specific findings. CONCLUSIONS--Abnormal muscle biopsies are common in patients with SLE and the presence of lymphocytic vasculitis and/or myositis signify pathology in these patients. Histopathological abnormalities in needle quadriceps muscle biopsies are further valuable parameters in the assessment of patients with SLE.
Full text
PDF
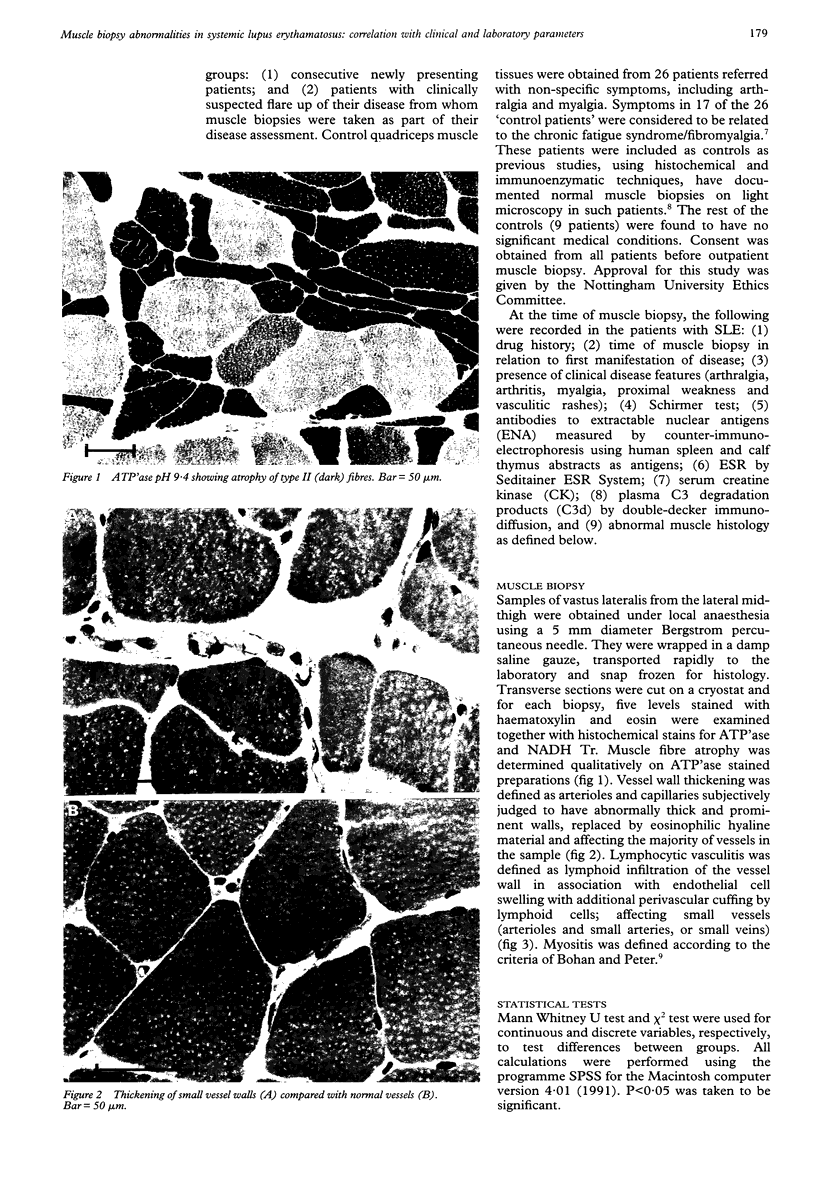
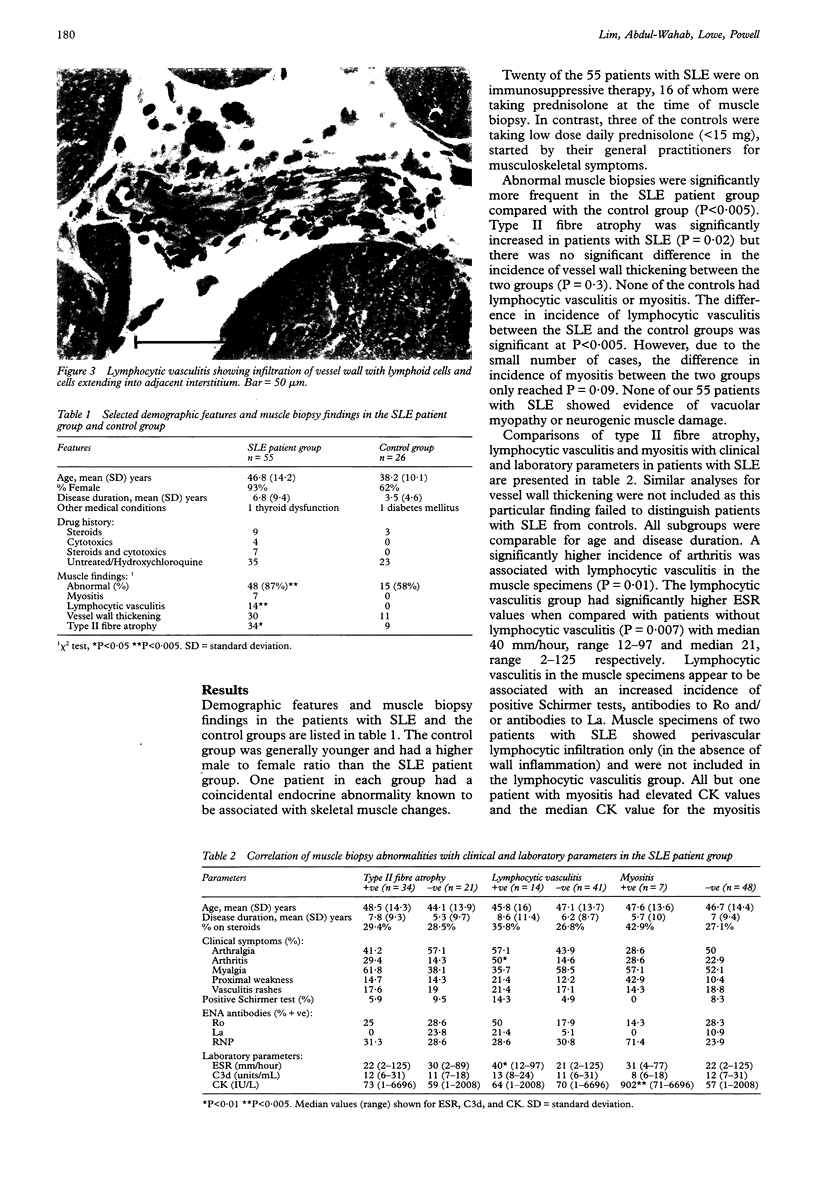


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedell S. E., Bush B. T. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. From folklore to facts. Am J Med. 1985 Jun;78(6 Pt 1):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohan A., Peter J. B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 13;292(7):344–347. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502132920706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS E. L., TUFFANELLI D. L. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS. COMPUTER ANALYSIS OF 520 CASES. JAMA. 1964 Oct 12;190:104–111. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070150014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewes A. M., Andreasen A., Schrøder H. D., Høgsaa B., Jennum P. Pathology of skeletal muscle in fibromyalgia: a histo-immuno-chemical and ultrastructural study. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Jun;32(6):479–483. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.6.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. A., Hopkinson N. D., Kinnear W. J., Watson L., Powell R. J., Johnston I. D. Respiratory disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: correlation with results of laboratory tests and histological appearance of muscle biopsy specimens. Thorax. 1992 Nov;47(11):957–960. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.11.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald O., Soden M., Yanni G., Robinson R., Bresnihan B. Morphometric analysis of blood vessels in synovial membranes obtained from clinically affected and unaffected knee joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Nov;50(11):792–796. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.11.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenber D. A., Snaith M. L. Muscle Disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a study of its nature, frequency and cause. J Rheumatol. 1981 Nov-Dec;8(6):917–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lexell J., Henriksson-Larsén K., Winblad B., Sjöström M. Distribution of different fiber types in human skeletal muscles: effects of aging studied in whole muscle cross sections. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Oct;6(8):588–595. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lexell J., Taylor C. C., Sjöström M. What is the cause of the ageing atrophy? Total number, size and proportion of different fiber types studied in whole vastus lateralis muscle from 15- to 83-year-old men. J Neurol Sci. 1988 Apr;84(2-3):275–294. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(88)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. L. Comparison of the microangiopathy of systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleroderma, and diabetes mellitus. Lab Invest. 1970 Apr;22(4):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. L., Hurd E. R., Lewis D. C., Ziff M. Evidence of microvascular injury in scleroderma and systemic lupus erythematosus: quantitative study of the microvascular bed. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jun;71(6):919–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'LEARY P. A., LAMBERT E. H., SAYRE G. P. Muscie studies in cutaneous disease. J Invest Dermatol. 1955 Mar;24(3):301–310. doi: 10.1038/jid.1955.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxenhandler R., Hart M. N., Bickel J., Scearce D., Durham J., Irvin W. Pathologic features of muscle in systemic lupus erythematosus: a biopsy series with comparative clinical and immunopathologic observations. Hum Pathol. 1982 Aug;13(8):745–757. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(82)80298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M., YAMAZAKI J. N. Vacuolar myopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958 May;29(5):455–463. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/29.5.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. B., Nakane P. K. Basement membranes. Synthesis and deposition in response to cellular injury. Lab Invest. 1969 Jul;21(1):27–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M., Van Venrooij W. J. Autoantibodies to the URNP particles: relationship to clinical diagnosis and nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Feb;83(2):286–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05629.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos G. C., Moutsopoulos H. M., Steinberg A. D. Muscle involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. JAMA. 1981 Aug 14;246(7):766–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]