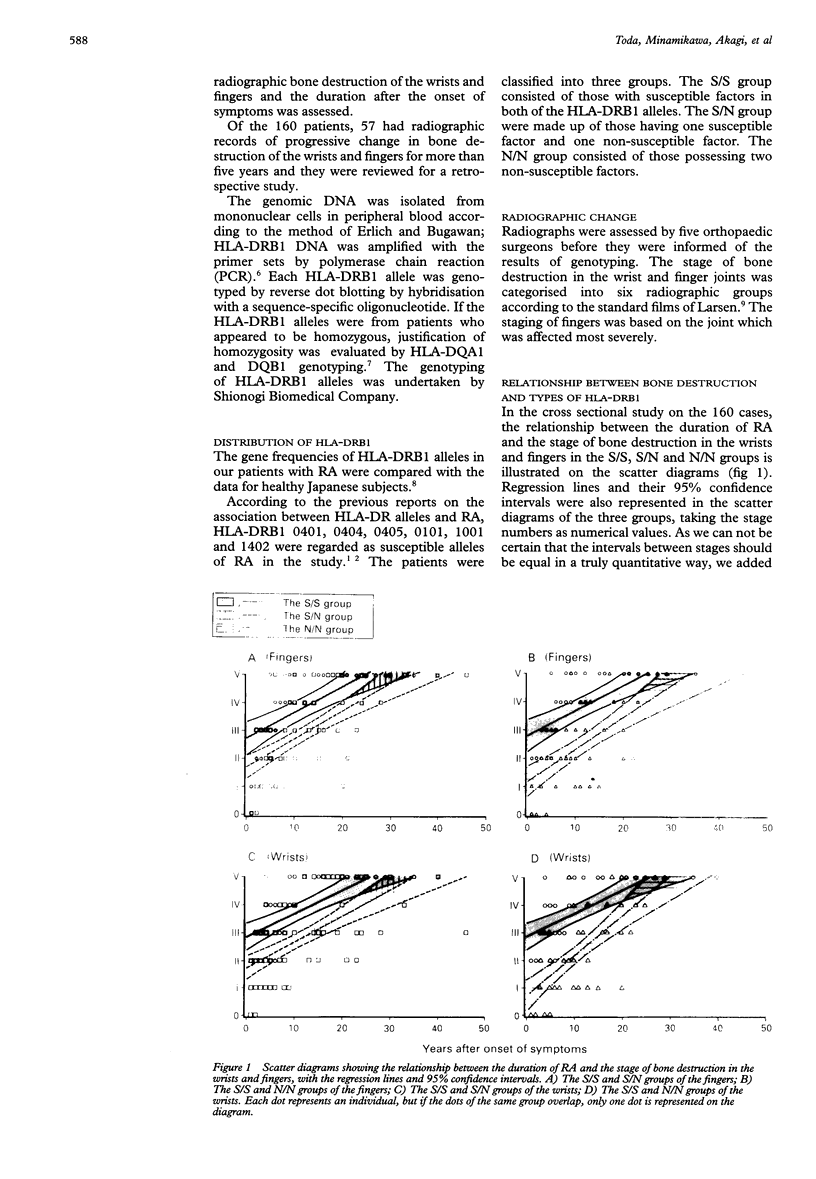
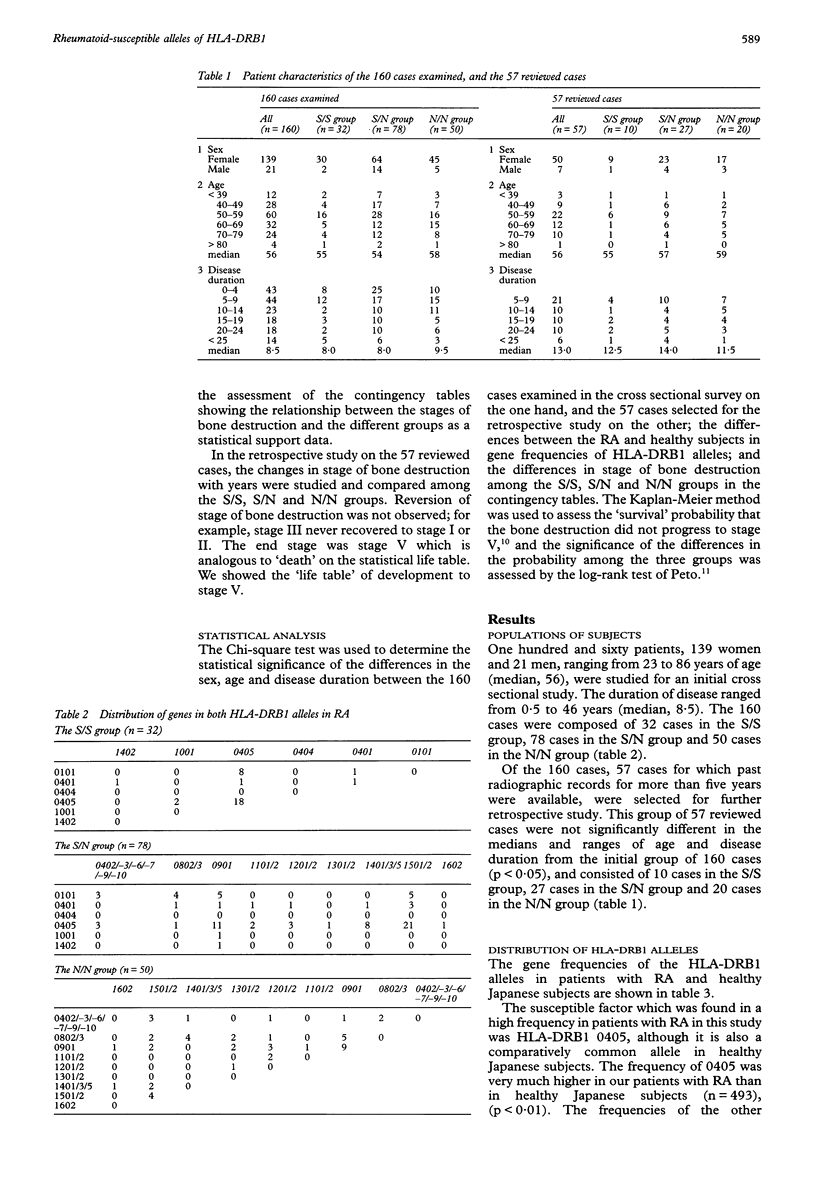
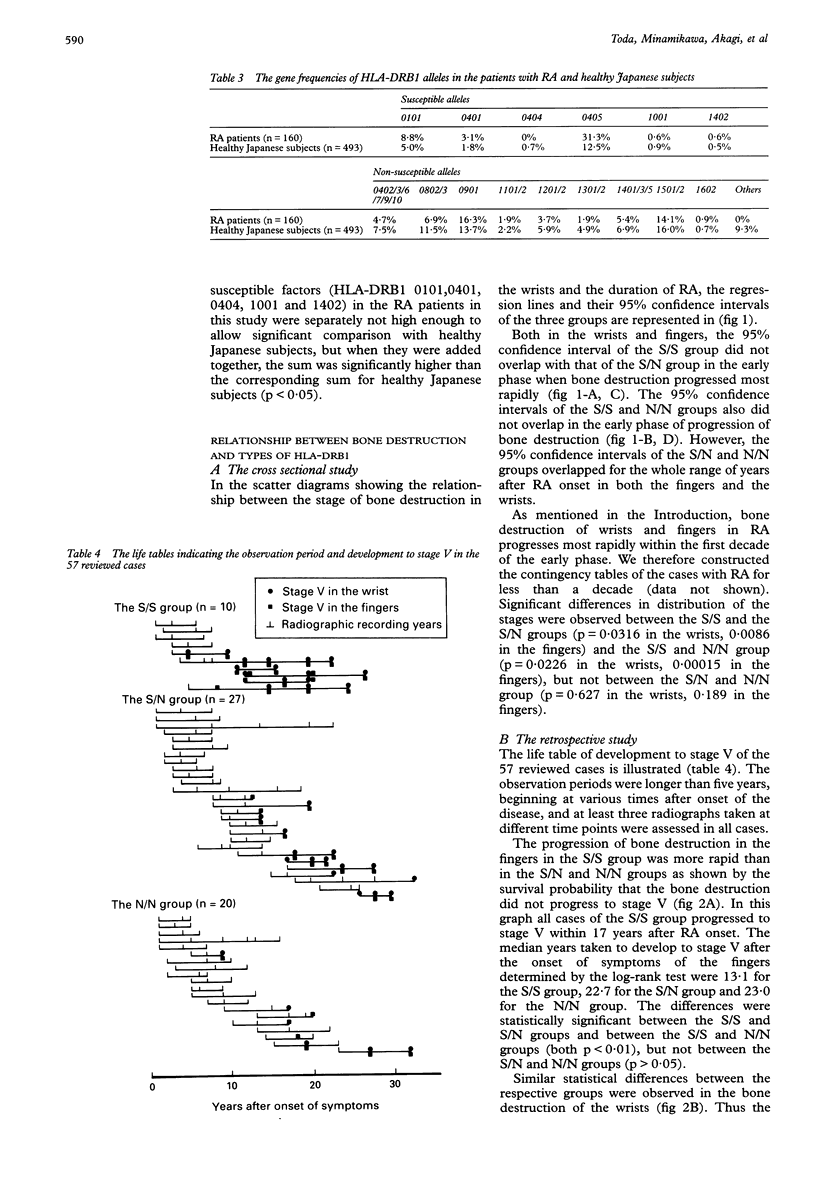
Abstract
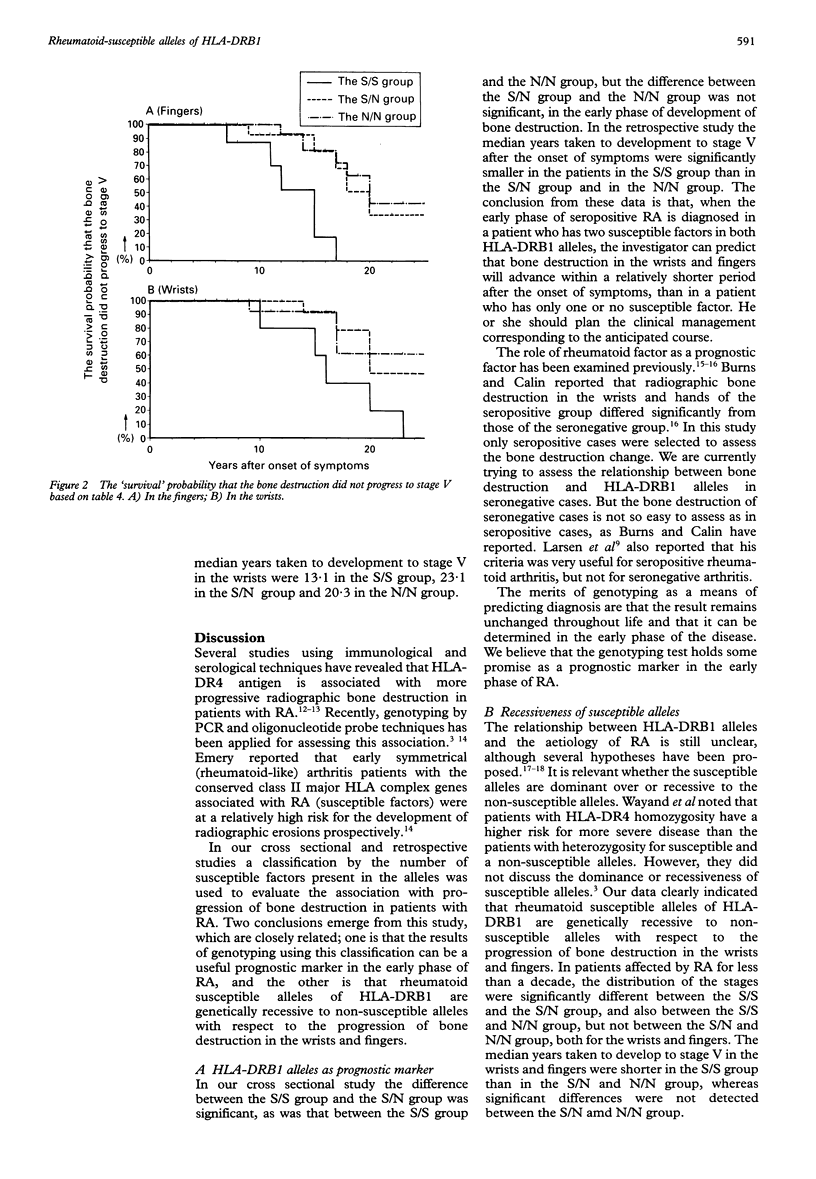
OBJECTIVE--To assess the relationship between HLA-DRB1 genotypes and the progression of bone destruction in Japanese patients with RA. METHODS--The HLA-DRB1 alleles were determined by polymerase chain reaction and allele specific oligonucleotide probe techniques in 160 Japanese patients with RA. HLA-DR 0101, 0401, 0404, 0405, 1001 and 1402 were regarded as susceptible alleles of RA according to previous reports. Patients were classified into three groups (S/S, S/N and N/N group), based on the possession of two, one or no susceptible factor. The grading of radio-graphic changes in the wrists and fingers were evaluated by Larsen's criteria. The radiographic grades were first compared with the results of genotyping in the 160 cross sectional cases. A retrospective study was then conducted on a subgroup consisting of 57 cases taken from the 160 cases used for the cross sectional study. RESULTS--In the scatter diagram of the 160 cross sectional cases expressing the relationship between the stage of bone destruction and duration of RA, the regression line and the 95% confidence intervals separated the S/S group from the S/N and N/N groups in the early phase of development of bone destruction. In the retrospective study on the 57 cases the median years taken to development to stage V in the wrists after the onset of symptoms were 13.1 in the patients in the S/S group, 22.7 in the S/N group and 23.0 in the N/N group. The difference observed between the S/S and S/N group, and between the S/S and N/N group were statistically significant (p < 0.01), but that between the S/N and N/N groups was not. Thus the bone destruction in the wrists and fingers progressed more rapidly in the S/S group than in the S/N and N/N groups; and the rheumatoid susceptible alleles of HLA-DRB1 can be considered to be genetically recessive to the non-susceptible alleles in the progression of bone destructions in the wrists and fingers. CONCLUSION--Genotyping of HLA-DRB1 can be a useful prognostic marker in the early phase of RA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook A., Corbett M. Radiographic changes in early rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Feb;36(1):71–73. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns T. M., Calin A. The hand radiograph as a diagnostic discriminant between seropositive and seronegative 'rheumatoid arthritis': a controlled study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Dec;42(6):605–612. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.6.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch R., Hill C. M., Hayball J. D., Lamb J. R., Rothbard J. B. Effect of natural polymorphism at residue 86 of the HLA-DR beta chain on peptide binding. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1292–1298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cats A., Hazevoet H. M. Significance of positive tests for rheumatoid factor in the prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis. A follow-up study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 May;29(3):254–260. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.3.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery P., Salmon M., Bradley H., Wordsworth P., Tunn E., Bacon P. A., Waring R. Genetically determined factors as predictors of radiological change in patients with early symmetrical arthritis. BMJ. 1992 Dec 5;305(6866):1387–1389. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6866.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen P. K., Silver J., Winchester R. J. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Nov;30(11):1205–1213. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneshige T., Murayama A., Hirasawa T., Sada M., Amemiya H., Uchida K. Rapid and practical HLA class II genotyping by reverse dot blotting. Transplant Proc. 1993 Feb;25(1 Pt 1):194–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Dale K., Eek M. Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1977 Jul;18(4):481–491. doi: 10.1177/028418517701800415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Pike M. C., Armitage P., Breslow N. E., Cox D. R., Howard S. V., Mantel N., McPherson K., Peto J., Smith P. G. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. analysis and examples. Br J Cancer. 1977 Jan;35(1):1–39. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silman A. J., Reeback J., Jaraquemada D. HLA-DR4 as a predictor of outcome three years after onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1986;6(5):233–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00541373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Tokunaga K., Matsuki K., Takeuchi F., Matsuta K., Maeda H., Omoto K., Juji T. Putative amino acid sequence of HLA-DRB chain contributing to rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2263–2268. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Hicok K. C., Conn D. L., Goronzy J. J. The influence of HLA-DRB1 genes on disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Nov 15;117(10):801–806. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-10-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]