Abstract
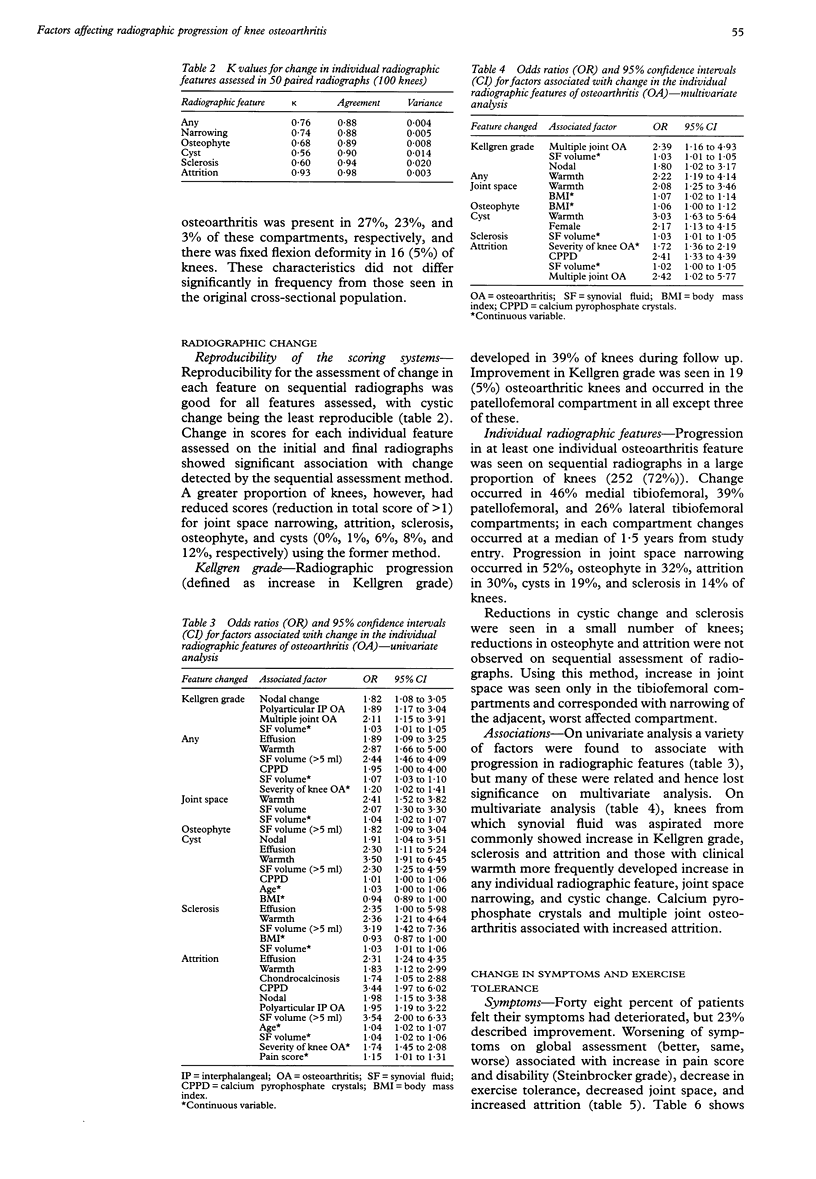
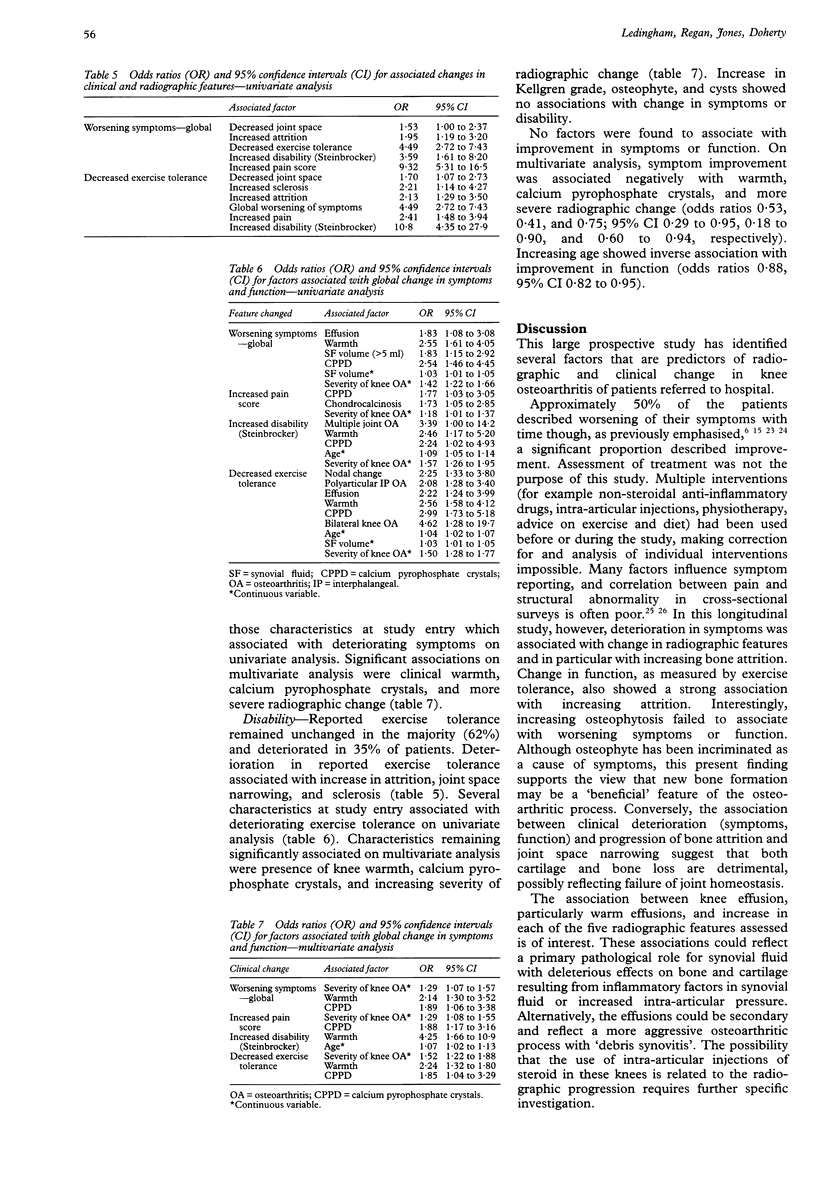
OBJECTIVES--To evaluate the prognostic significance of patient characteristics and radiographic features at the knee for outcome of knee osteoarthritis. METHODS--This was a prospective observational study of 350 osteoarthritic knees. Clinical and radiographic data were obtained on 188 hospital referred patients (mean age 70, range 34-91 years). RESULTS--Median duration of follow up was two years (range 1-5 years). The majority of patients (48%) reported deterioration, but 23% experienced improvement in symptoms during the study period. Reported exercise tolerance remained unchanged in the majority (62%) and deteriorated in 35%. Change in at least one individual radiographic feature of osteoarthritis was seen in 252 (72%) knees: increase in joint space narrowing occurred in 52%, osteophyte in 32%, cysts in 19%, sclerosis in 14%, and attrition in 30%. Increase in Kellgren grade occurred in 137 (39%) knees. Knee effusion, osteoarthritis at multiple joint sites, and nodal change associated with change in Kellgren grade (odds ratios 1.03, 2.39, and 1.80; 95% confidence intervals (CI) 1.01 to 1.05, 1.16 to 4.93, and 1.02 to 3.17, respectively); warmth at the knee associated with change in any radiographic feature (odds ratio 2.22; 95% CI 1.19 to 4.14). Development of, or increase in, attrition and joint space narrowing associated with worsening symptoms and function and occurred with increased frequency in knees with effusions, clinical warmth and calcium pyrophosphate crystals in synovial fluid (p < 0.05). CONCLUSIONS--A high rate of change, radiographic more than clinical, was seen in osteoarthritic knees during this study. Poor clinical and radiographic outcome associated with calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition and clinical inflammation as reflected by knee effusion and warmth.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cushnaghan J., Dieppe P. Study of 500 patients with limb joint osteoarthritis. I. Analysis by age, sex, and distribution of symptomatic joint sites. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Jan;50(1):8–13. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson L., Hernborg J. Clinical and roentgenologic study of knee joints with osteophytes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1970 Mar-Apr;69:302–312. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197003000-00035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. A., Ettinger W. H., Neuhaus J. M., Cho S. A., Hauck W. W. The association of knee injury and obesity with unilateral and bilateral osteoarthritis of the knee. Am J Epidemiol. 1989 Aug;130(2):278–288. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieppe P. A. Why is there such a poor correlation between radiographic joint damage and both symptoms and functional impairment in osteoarthritis? Br J Rheumatol. 1989 Jun;28(3):242–242. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/28.3.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieppe P., Cushnaghan J., Young P., Kirwan J. Prediction of the progression of joint space narrowing in osteoarthritis of the knee by bone scintigraphy. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Aug;52(8):557–563. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.8.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty M., Dieppe P. Clinical aspects of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1988 Aug;14(2):395–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T. The epidemiology of knee osteoarthritis: results from the Framingham Osteoarthritis Study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Dec;20(3 Suppl 1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(90)90046-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halverson P. B., McCarty D. J. Patterns of radiographic abnormalities associated with basic calcium phosphate and calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition in the knee. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Jul;45(7):603–605. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.7.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton E., Pattrick M., Hornby J., Derrick G., Doherty M. Synovial fluid calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals and alizarin red positivity: analysis of 3000 samples. Br J Rheumatol. 1990 Apr;29(2):101–104. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/29.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLGREN J. H., LAWRENCE J. S. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957 Dec;16(4):494–502. doi: 10.1136/ard.16.4.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannus P., Järvinen M., Kontiala H., Bergius L., Hyssy E., Salminen E., Tuomi A., Unkila T., Valtanen I. Occurrence of symptomatic knee osteoarthrosis in rural Finland: a prospective follow up study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Nov;46(11):804–808. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.11.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. S., Bremner J. M., Bier F. Osteo-arthrosis. Prevalence in the population and relationship between symptoms and x-ray changes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1966 Jan;25(1):1–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledingham J., Dawson S., Preston B., Milligan G., Doherty M. Radiographic progression of hospital referred osteoarthritis of the hip. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Apr;52(4):263–267. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.4.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledingham J., Regan M., Jones A., Doherty M. Radiographic patterns and associations of osteoarthritis of the knee in patients referred to hospital. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Jul;52(7):520–526. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.7.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massardo L., Watt I., Cushnaghan J., Dieppe P. Osteoarthritis of the knee joint: an eight year prospective study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Nov;48(11):893–897. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.11.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattrick M., Hamilton E., Wilson R., Austin S., Doherty M. Association of radiographic changes of osteoarthritis, symptoms, and synovial fluid particles in 300 knees. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Feb;52(2):97–103. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyron J. G. Epidemiologic and etiologic approach of osteoarthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1979 May;8(4):288–306. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(79)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick D., Niwayama G., Goergen T. G., Utsinger P. D., Shapiro R. F., Haselwood D. H., Wiesner K. B. Clinical, radiographic and pathologic abnormalities in calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease (CPPD): pseudogout. Radiology. 1977 Jan;122(1):1–15. doi: 10.1148/122.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schouten J. S., van den Ouweland F. A., Valkenburg H. A. A 12 year follow up study in the general population on prognostic factors of cartilage loss in osteoarthritis of the knee. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Aug;51(8):932–937. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.8.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon L. Patterns of osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1976 May;58(2):176–183. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.58B2.932079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. D., Dacre J. E., Harris P. A., Huskisson E. C. Radiological progression of osteoarthritis: an 11 year follow up study of the knee. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Oct;51(10):1107–1110. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.10.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. H., Resnick D., Alazraki N. P., Daniel D., Greenfield R. Compartmental evaluation of osteoarthritis of the knee. A comparative study of available diagnostic modalities. Radiology. 1975 Sep;116(3):585–594. doi: 10.1148/116.3.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


