Abstract
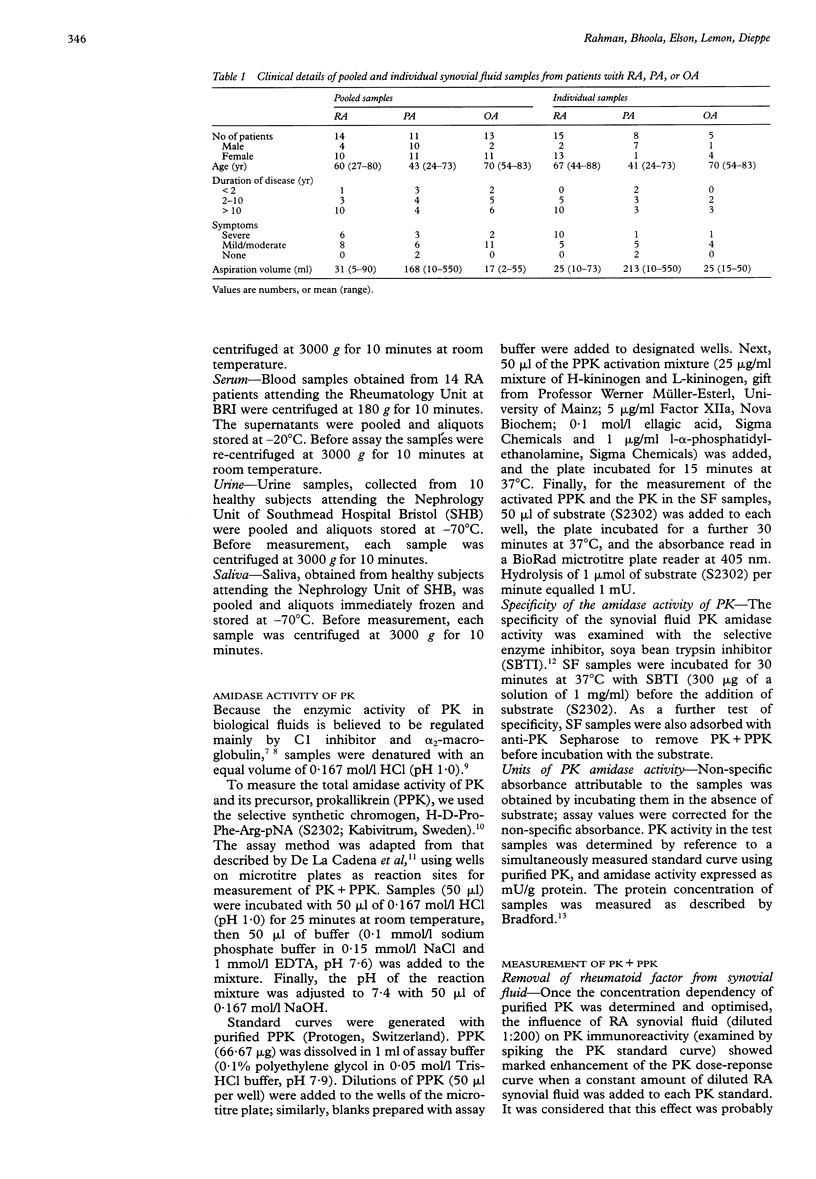
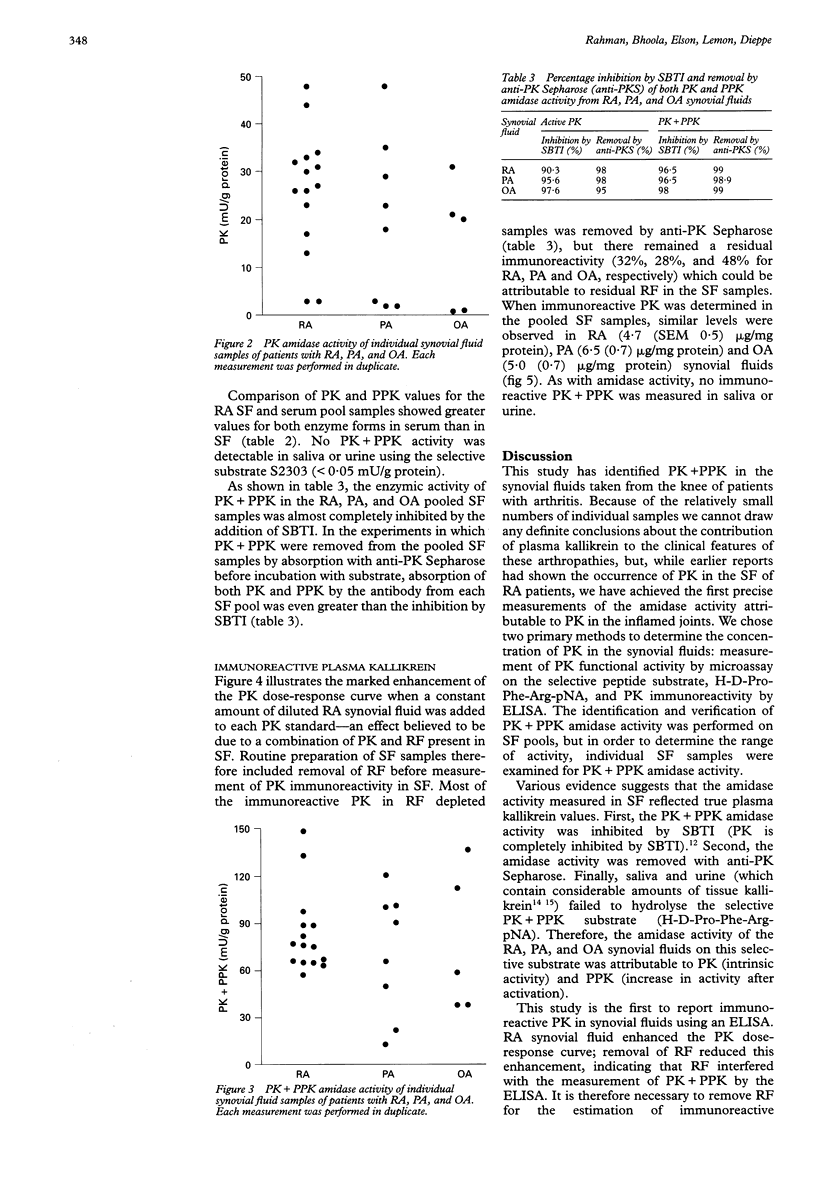
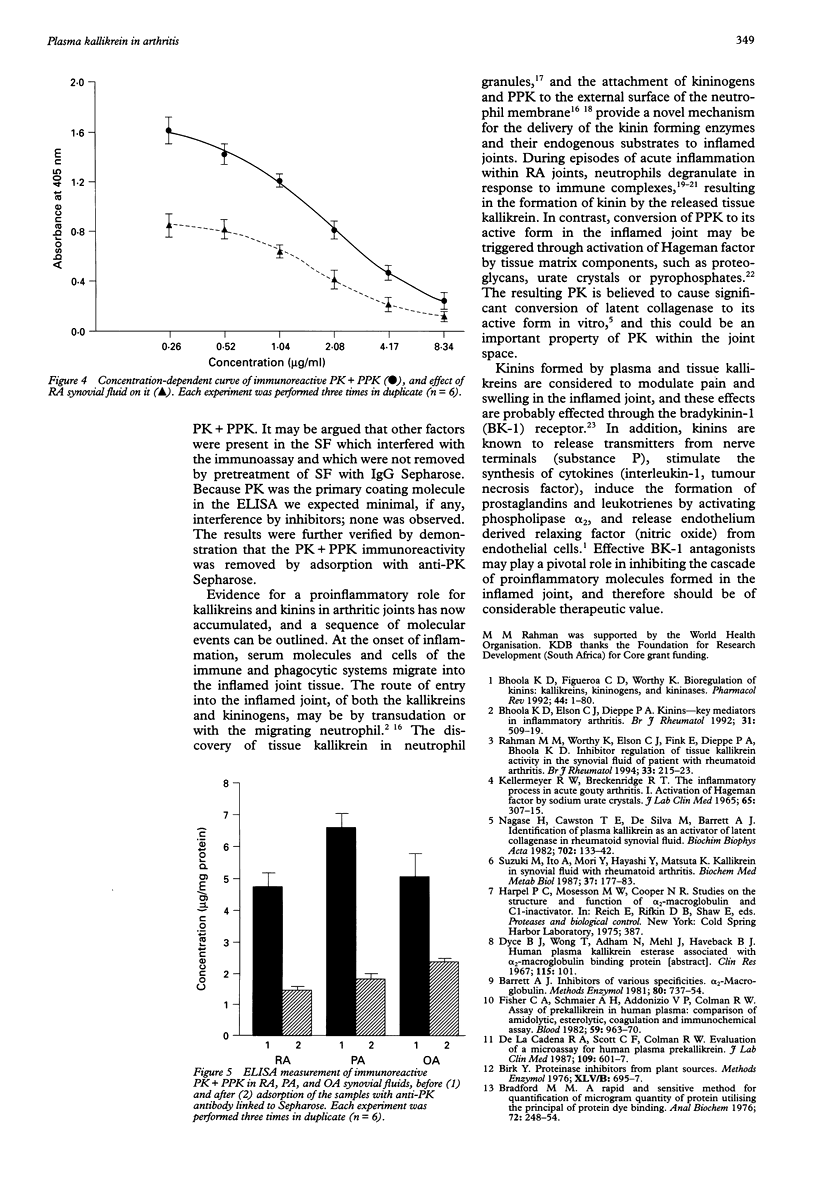
OBJECTIVES--To determine and identify, unequivocally, if plasma kallikrein (PK) is present in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid (RA), psoriatic (PA) and osteo (OA) arthritis, and to consider its functional importance in the inflamed joint. METHODS--Therapeutically aspirated synovial fluids (pooled and individual samples, n = 66) were obtained from patients with arthritis. In addition, serum (n = 14) was collected from RA patients, and saliva (n = 10) and urine (n = 10) from normal individuals. Enzymic (amidase) and immunoreactive activities of PK and its precursor, prokallikrein (PPK), were determined. The presence of PK was assessed by incubation with soya bean trypsin inhibitor (SBTI), and by adsorption with anti-PK antibody linked to Sepharose. An enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA) for PK was developed for quantitative measurement of total PK in biological fluids. Enhancement of the PK dose-response by RA synovial fluid made it necessary to remove RF from synovial fluids before determination of PK by ELISA. RESULTS--Amidase activity was demonstrated in synovial fluid pools and shown to be inhibited completely by SBTI, and removed by prior treatment with anti-PK Sepharose. Total PK activity (PK + PPK) from individual synovial fluid specimens did not differ significantly between patients with RA (median activity 76 mU/g protein), PA (80 mU/g protein) or OA (60 mU/g protein). Similar results were obtained when active PK alone was measured. No correlation was found between active PK or total PK values and the severity score for individual joints. Most of the measured immunoreactivity was removed by adsorption with anti-PK antibody linked to Sepharose. CONCLUSION--The results support the hypothesis that plasma kallikrein is present in synovial fluid. The enzyme may be important in the pathogenesis of inflamed joints.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J. Alpha 2-macroglobulin. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):737–754. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Elson C. J., Dieppe P. A. Kinins--key mediators in inflammatory arthritis? Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Aug;31(8):509–518. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.8.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Figueroa C. D., Worthy K. Bioregulation of kinins: kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol Rev. 1992 Mar;44(1):1–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., McNicol M. W., Oliver S., Foran J. Changes in salivary enzymes in patients with sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1969 Oct 16;281(16):877–879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196910162811605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birk Y. Proteinase inhibitors from plant sources. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:695–697. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Cadena R. A., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Evaluation of a microassay for human plasma prekallikrein. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 May;109(5):601–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dularay B., Dieppe P. A., Elson C. J. Depressed degranulation response of synovial fluid polymorphonuclear leucocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis to IgG aggregates. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Feb;79(2):195–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa C. D., Henderson L. M., Kaufmann J., De La Cadena R. A., Colman R. W., Müller-Esterl W., Bhoola K. D. Immunovisualization of high (HK) and low (LK) molecular weight kininogens on isolated human neutrophils. Blood. 1992 Feb 1;79(3):754–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa C. D., MacIver A. G., Bhoola K. D. Identification of a tissue kallikrein in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jul;72(3):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. A., Schmaier A. H., Addonizio V. P., Colman R. W. Assay of prekallikrein in human plasma: comparison of amidolytic, esterolytic, coagulation, and immunochemical assays. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):963–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. M., Figueroa C. D., Müller-Esterl W., Bhoola K. D. Assembly of contact-phase factors on the surface of the human neutrophil membrane. Blood. 1994 Jul 15;84(2):474–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLERMEYER R. W., BRECKENRIDGE R. T. THE INFLAMMATORY PROCESS IN ACUTE GOUTY ARTHRITIS. I. ACTIVATION OF HAGEMAN FACTOR BY SODIUM URATE CRYSTALS. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Cawston T. E., De Silva M., Barrett A. J. Identification of plasma kallikrein as an activator of latent collagenase in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 18;702(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurcombe H. L., Bucknall R. C., Edwards S. W. Activation of the neutrophil myeloperoxidase-H2O2 system by synovial fluid isolated from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Apr;50(4):237–242. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.4.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oza N. B., Lieberthal W., Bernard D. B., Levinsky N. G. Antibody that recognizes total human urinary kallikrein: radioimmunological determination of inactive kallikrein. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2361–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman M. M., Worthy K., Elson C. J., Fink E., Dieppe P. A., Bhoola K. D. Inhibitor regulation of tissue kallikrein activity in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Mar;33(3):215–223. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.3.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Ito A., Mori Y., Hayashi Y., Matsuta K. Kallikrein in synovial fluid with rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1987 Apr;37(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0885-4505(87)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


