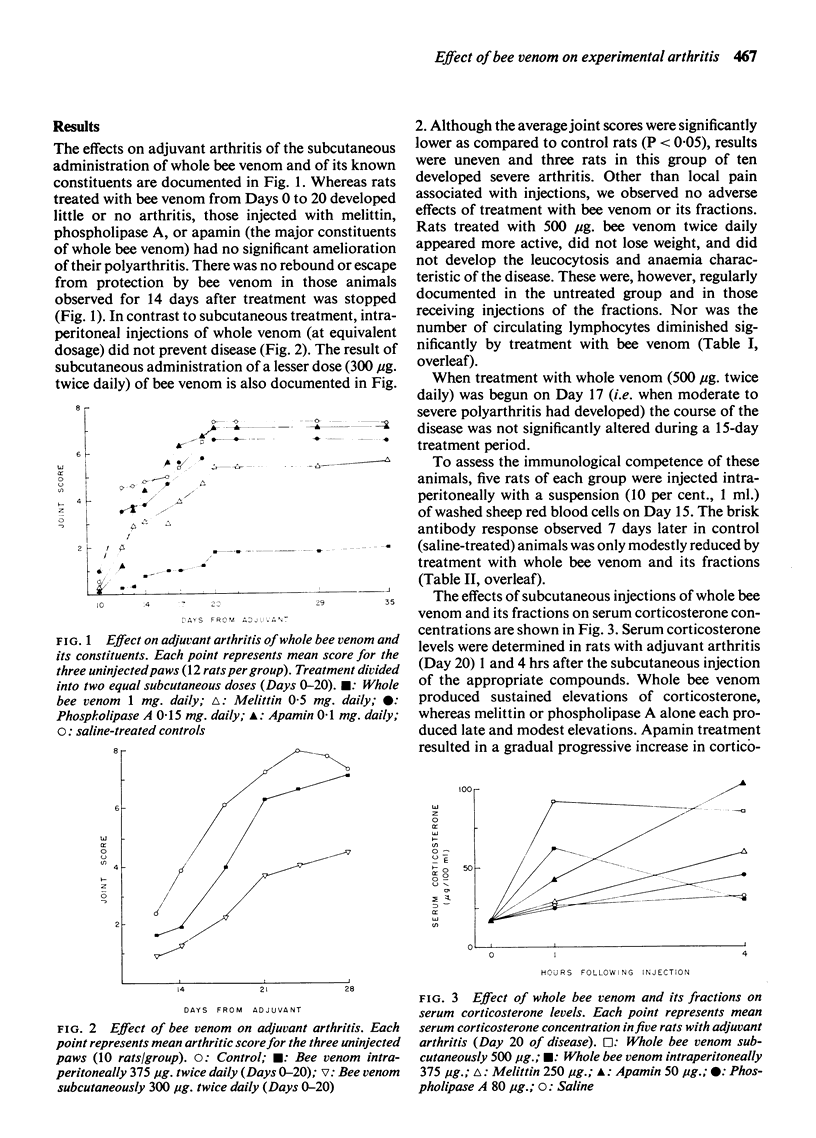
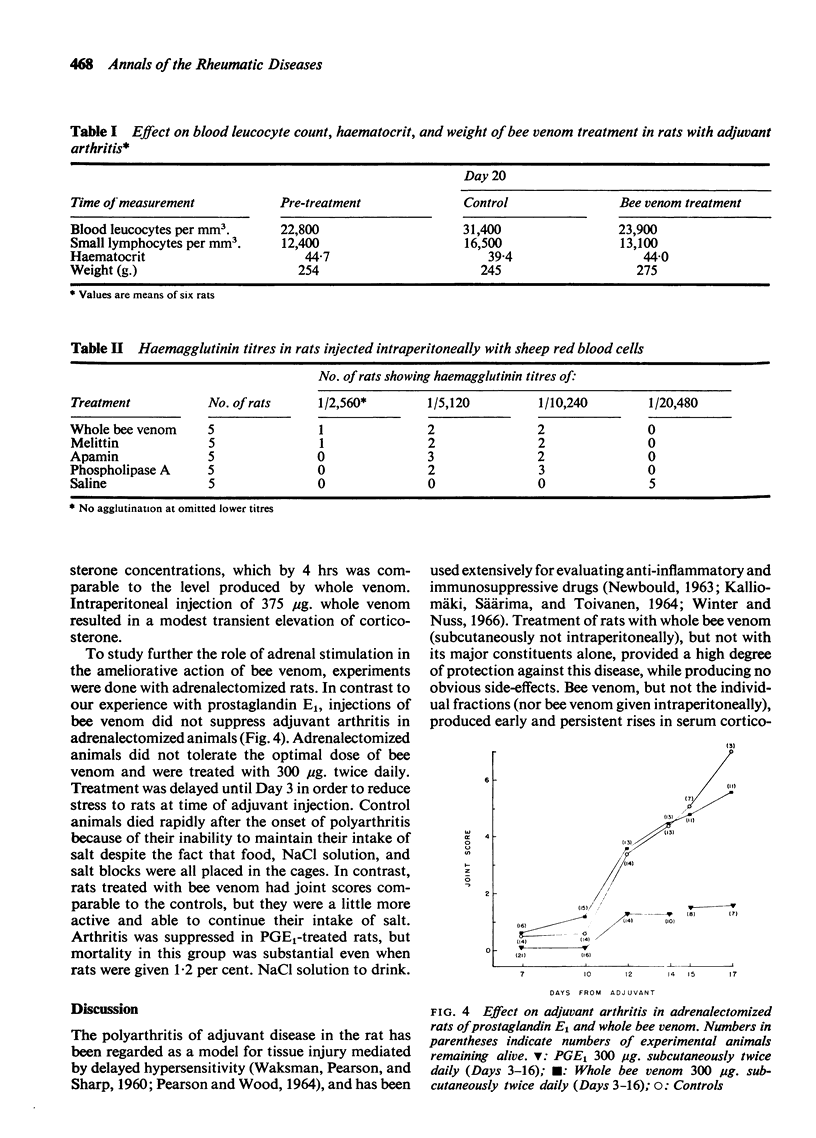
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole L. J., Shipman W. H. Chromatographic fractions of bee venom: cytotoxicity for mouse bone marrow stem cells. Am J Physiol. 1969 Oct;217(4):965–968. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.4.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGHERTY T. F., BERLINER M. L., BERLINER D. L. Hormonal influence on lymphocyte differentiation from RES cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jun 21;88:78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALLIOMAEKI J. L., SAARIMAA H. A., TOIVANEN P. INHIBITION BY 6-MERCAPTOPURINE OF POLYARTHRITIS INDUCED BY FREUND'S ADJUVANT. Ann Rheum Dis. 1964 Jan;23:78–80. doi: 10.1136/ard.23.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. B., Levytska V. A sensitive hemagglutination assay method for dinitrophenyl-specific antibodies. The effect of antibody binding affinity on titers. J Immunol. 1967 Mar;98(3):648–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWBOULD B. B. CHEMOTHERAPY OF ARTHRITIS INDUCED IN RATS BY MYCOBACTERIAL ADJUVANT. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Aug;21:127–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON R. E. Plasma corticosterone and hydrocortisone levels in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1957 Oct;17(10):1150–1157. doi: 10.1210/jcem-17-10-1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quagliata F., Sanders P. M., Gardner D. L. Suppression of adjuvant arthritis by a new cytotoxic compound, rubidomycin. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Mar;28(2):163–171. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vick J. A., Shipman W. H. Effects of whole bee venom and its fractions (apamin and melittin) on plasma cortisol levels in the dog. Toxicon. 1972 Jun;10(4):377–380. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(72)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt W., Meyer U., Kunze H., Lufft E., Babilli S. Entstehung von SRS-C in der durchströmten Meerschweinchenlunge durch Phospholipase A. Identifizierung mit Prostaglandin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1969;262(1):124–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H., PEARSON C. M., SHARP J. T. Studies of arthritis and other lesions induced in rats by injection of mycobacterial adjuvant. II. Evidence that the disease is a disseminated immunologic response to exogenous antigen. J Immunol. 1960 Oct;85:403–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter C. A., Nuss G. W. Treatment of adjuvant arthritis in rats with anti-inflammatory drugs. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Jun;9(3):394–404. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Quagliata F. Effect of prostaglandin E 1 on adjuvant arthritis. Nature. 1971 Dec 3;234(5327):304–305. doi: 10.1038/234304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


