Abstract
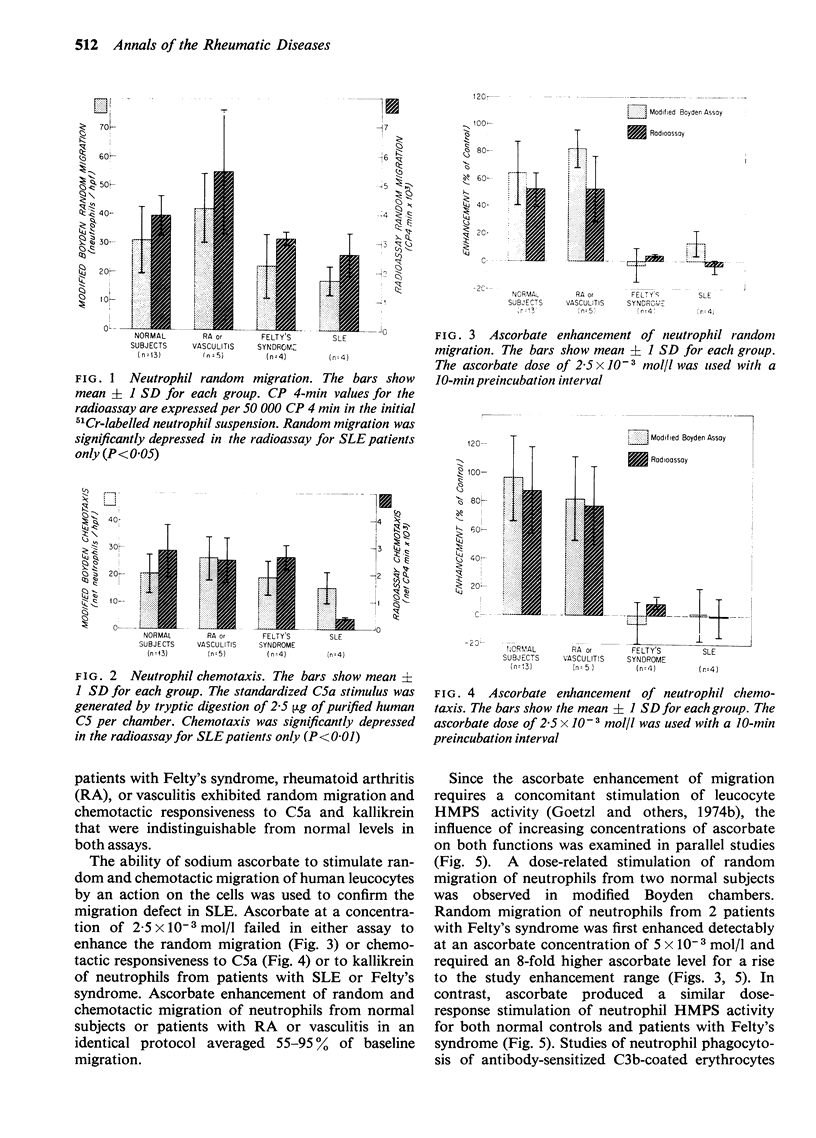
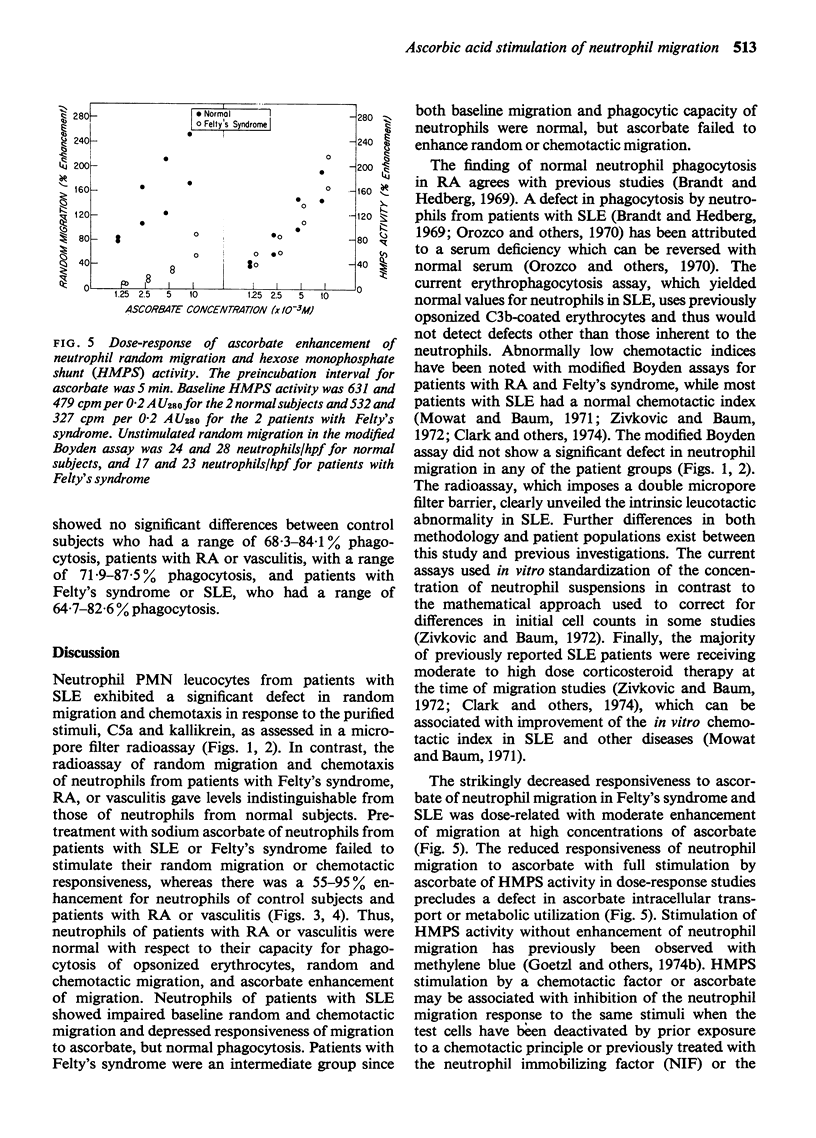
Polymorphonuclear (PMN) leucocytes from 4 patients with untreated systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) showed defective random migration (P less than 0-05) and depressed chemotactic responses to C5a and kallikrein (P less than 0-01) compared to PMN leucocytes from normal subjects, or patients with rheumatoid arthritis (4) or Felty's syndrome (4) when examined at a standardized cell concentration with a micropore filter radioassay but not with a conventional Boyden technique. Normal in vitro enhancement of PMN leucocyte random and chemotactic migration by sodium ascorbate was absent in SLE and Felty's syndrome, but sodium ascorbate gave normal stimulation of hexose monophosphate shunt activity in the PMN leucocytes precluding a defect in ascorbate transport.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt L., Hedberg H. Impaired phagocytosis by peripheral blood granulocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Haematol. 1969;6(5):348–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1969.tb02420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Kimball H. R., Decker J. L. Neutrophil chemotaxis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Mar;33(2):167–172. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes D., Christian C. L. The natural history of systemic lupus erythematosus by prospective analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1971 Mar;50(2):85–95. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197103000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. A neutrophil-immobilizing factor derived from human leukocytes. I. Generation and partial characterization. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1564–1580. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Gigli I., Wasserman S., Austen K. F. A neutrophil immobilizing factor derived from human leukocytes. II. Specificity of action on polymorphonuclear leukocyte mobility. J Immunol. 1973 Sep;111(3):938–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J. Plasma and cell-derived inhibitors of human neutrophil chemotaxis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:210–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Wasserman S. I., Gigli I., Austen K. F. Enhancement of random migration and chemotactic response of human leukocytes by ascorbic acid. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):813–818. doi: 10.1172/JCI107620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Kay A. B., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. 3. Appearance of chemotactic activity for human neutrophils by the conversion of human prekallikrein to kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):81–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie J. S., Pearson C. M. Felty's syndrome. Semin Hematol. 1971 Jul;8(3):216–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. G., Baum J. Chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2541–2549. doi: 10.1172/JCI106754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. G. Hematologic abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Winter;1(3):195–219. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(72)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman M., Miller L. M., Pinals R. S. Clinical and serologic observations on 27 patients with Felty's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Jun;11(3):377–384. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEARN M. A., PIROFSKY B. Disseminated lupus erythematosus; analysis of thirty-four cases. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1952 Dec;90(6):790–807. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1952.00240120065007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples P. J., Gerding D. N., Decker J. L., Gordon R. S., Jr Incidence of infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jan-Feb;17(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Townes A. S., Robinson H., Kaplan S. B., Chandler R. W., Hanissian A. S., Masi A. T. Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Evaluation in early diagnosed SLE and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Mar-Apr;17(2):184–188. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. The deactivation of rabbit neutrophils by chemotactic factor and the nature of the activatable esterase. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):693–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger M. E., Bole G. G. Nitroblue tetrazolium dye reduction by peripheral leukocytes from rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus patients measured by a histochemical and spectrophotometric method. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Sep;82(3):513–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zivkovic M., Baum J. Chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and Felty's syndrome. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(1):39–49. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


