Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was differentiated from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) by direct immunofluorescent techniques on skin specimens, using monospecific antisera for IgG, IgM, C3, C1q, properdin, and fibrin. Of 30 patients with RA studied, 20 had dermal vessel deposits of immunoglobulins and complement components in unaffected skin without the characteristic dermal-epidermal junctional fluorescence of SLE. Of 24 SLE patients studied, 24 had granular deposits of immunoglobulins and complement components in unaffected skin at the dermal-epidermal junction.
Full text
PDF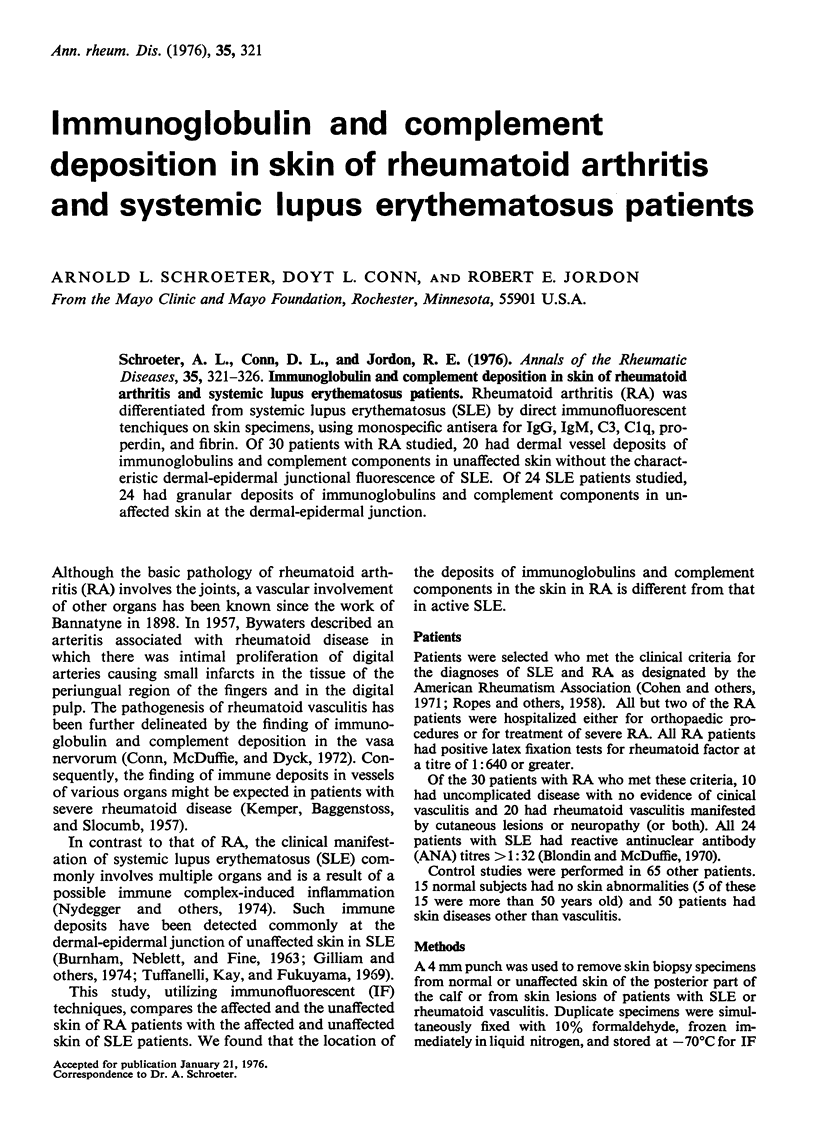

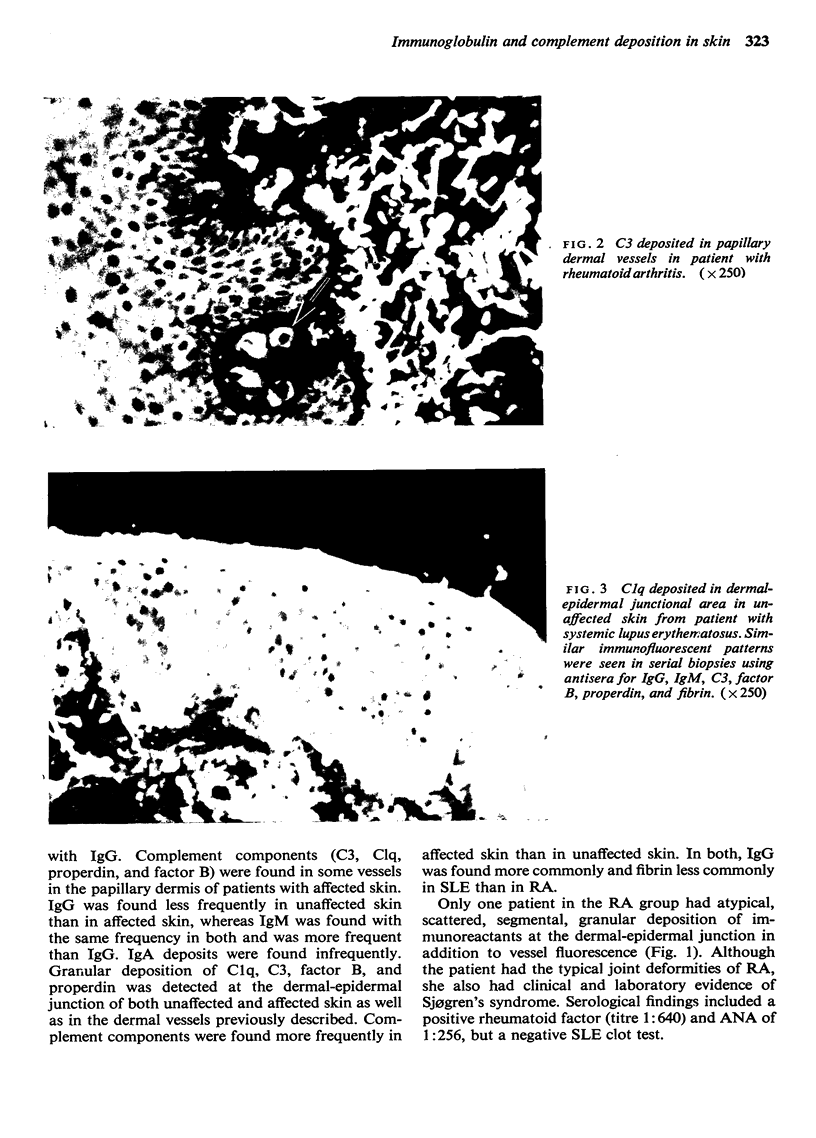
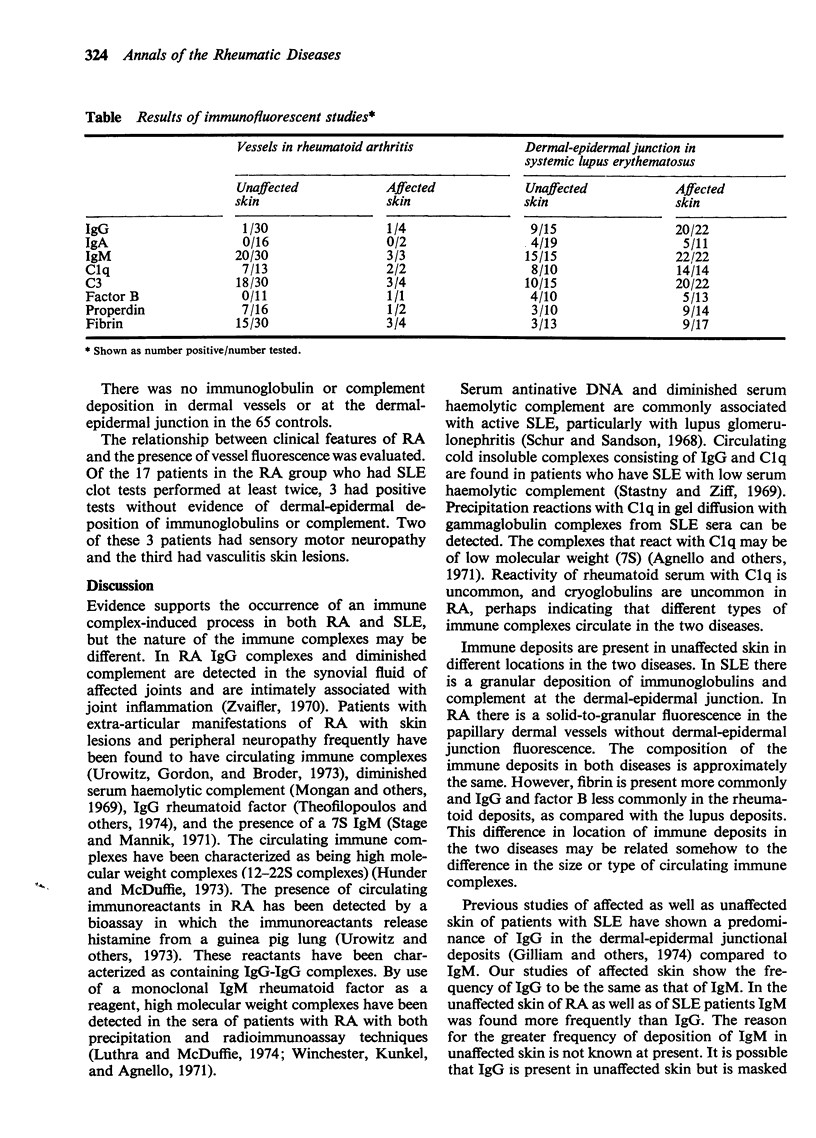


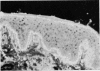
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNHAM T. K., NEBLETT T. R., FINE G. THE APPLICATION OF THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY TECHNIC TO THE INVESTIGATION OF LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS AND VARIOUS DERMATOSES. J Invest Dermatol. 1963 Dec;41:451–456. doi: 10.1038/jid.1963.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYWATERS E. G. Peripheral vascular obstruction in rheumatoid arthritis and its relationship to other vascular lesions. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957 Mar;16(1):84–103. doi: 10.1136/ard.16.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondin C., McDuffie F. C. Role of IgG and IgM antinuclear antibodies in formation of lupus erythematosus cells and extracellular material. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):786–797. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn D. L., McDuffie F. C., Dyck P. J. Immunopathologic study of sural nerves in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Mar-Apr;15(2):135–143. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensky J., Hinz C. F., Jr, Todd E. W., Wedgwood R. J., Boyer J. T., Lepow I. H. Properties of highly purified human properdin. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):142–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam J. N., Cheatum D. E., Hurd E. R., Stastny P., Ziff M. Immunoglobulin in clinically uninvolved skin in systemic lupus erythematosus: association with renal disease. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1434–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI107691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunder G. G., McDuffie F. C. Hypocomplementemia in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1973 Apr;54(4):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordon R. E., Schroeter A. L., Good R. A., Day N. K. The complement system in bullous pemphigoid. II. Immunofluorescent evidence for both classical and alternate-pathway activation. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Jan;3(3):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordon R. E., Schroeter A. L., Winkelmann R. K. Dermal-epidermal deposition of complement components and properdin in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 1975 Mar;92(3):263–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1975.tb03075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMPER J. W., BAGGENSTOSS A. H., SLOCUMB C. H. The relationship of therapy with cortisone to the incidence of vascular lesions in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1957 May;46(5):831–851. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-46-5-831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson O., Lithner F. Localization of various plasma proteins in the skin in rheumatoid arthritis. An immunofluorescent microscopic study of skin biopsies. Acta Med Scand. 1972 Jul-Aug;192(1-2):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1972.tb04770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE J. H., CHRISTIAN C. L. IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES OF THE 11S PROTEIN COMPONENT OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT SYSTEM. J Exp Med. 1964 Feb 1;119:195–209. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongan E. S., Cass R. M., Jacox R. F., Vaughen J. H. A study of the relation of seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis to each other and to necrotizing vasculitis. Am J Med. 1969 Jul;47(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muijs van de Moer W. W., Cats A. Immunofluorescence of the skin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A preliminary report. Dermatologica. 1967;134(5):351–355. doi: 10.1159/000254275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Lambert P. H., Gerber H., Miescher P. A. Circulating immune complexes in the serum in systemic lupus erythematosus and in carriers of hepatitis B antigen. Quantitation by binding to radiolabeled C1q. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost T. T., Tomasi T. B., Jr Evidence for complement activation via the alternate pathway in skin diseases, I. Herpes gestationis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and bullous pemphigoid. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1779–1787. doi: 10.1172/JCI107359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield N., Ross H. A., Minta J. O., Lepow I. H. Glomerular and dermal depostion of properdin in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 5;287(14):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210052871402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Sandson J. Immunologic factors and clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 7;278(10):533–538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803072781004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stage D. E., Mannik M. 7S M-globulin in rheumatoid arthritis. Evaluation of its clinical significance. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Jul-Aug;14(4):440–450. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Ziff M. Cold-insoluble complexes and complement levels in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jun 19;280(25):1376–1381. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196906192802503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Burtonboy G., LoSpalluto J. J., Ziff M. IgM rheumatoid factor and low molecular weight IgM. An association with vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 May-Jun;17(3):272–284. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triftshauser C., Hayden D. W., Beutner E. H. Procedures for the immunization of goats with human immunoglobulins and complement. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;38(3):315–319. doi: 10.1159/000230284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuffanelli D. L., Kay D., Fukuyama K. Dermal-epidermal junction in lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol. 1969 Jun;99(6):652–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urowitz M. B., Gordon D. A., Broder I. Studies into the occurrence of soluble antigen-antibody complexes in disease. V. Second assessment of correlation between the rheumatoid biologically active factor (RBAF) and the clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Mar-Apr;16(2):225–230. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. Further speculation on the pathogenesis of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):895–901. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]