Abstract
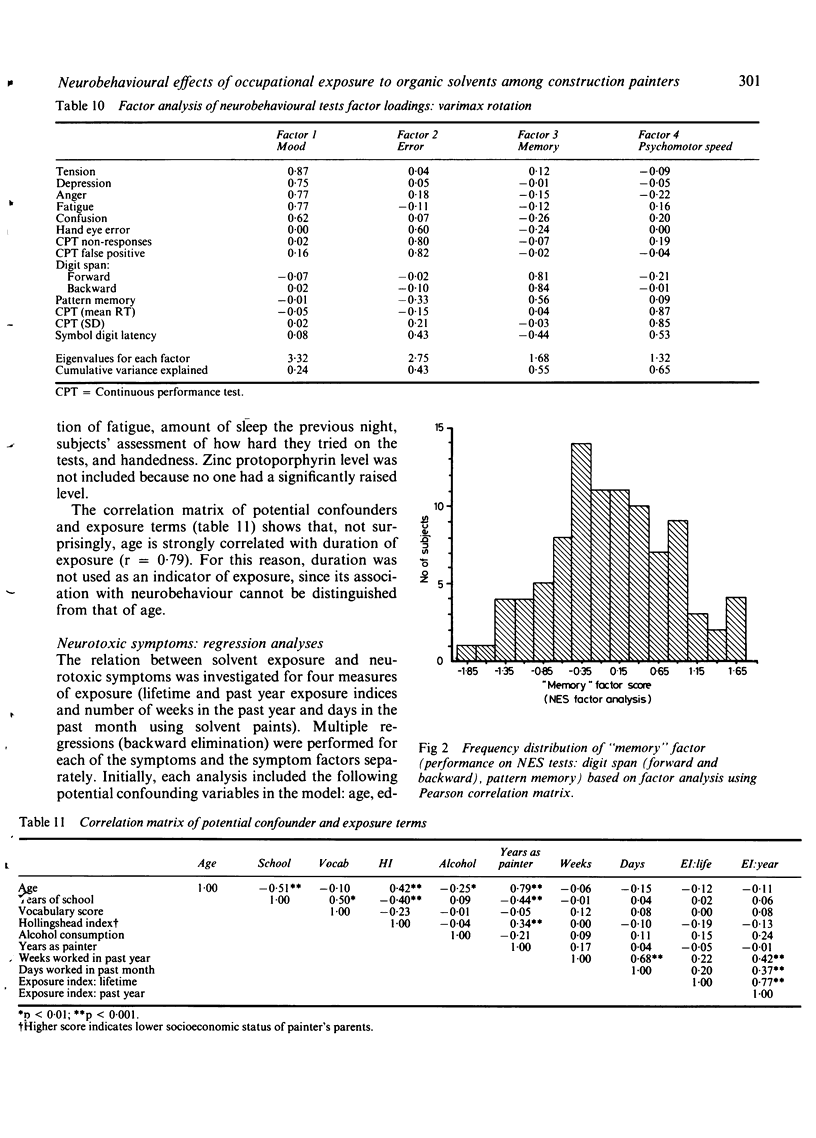
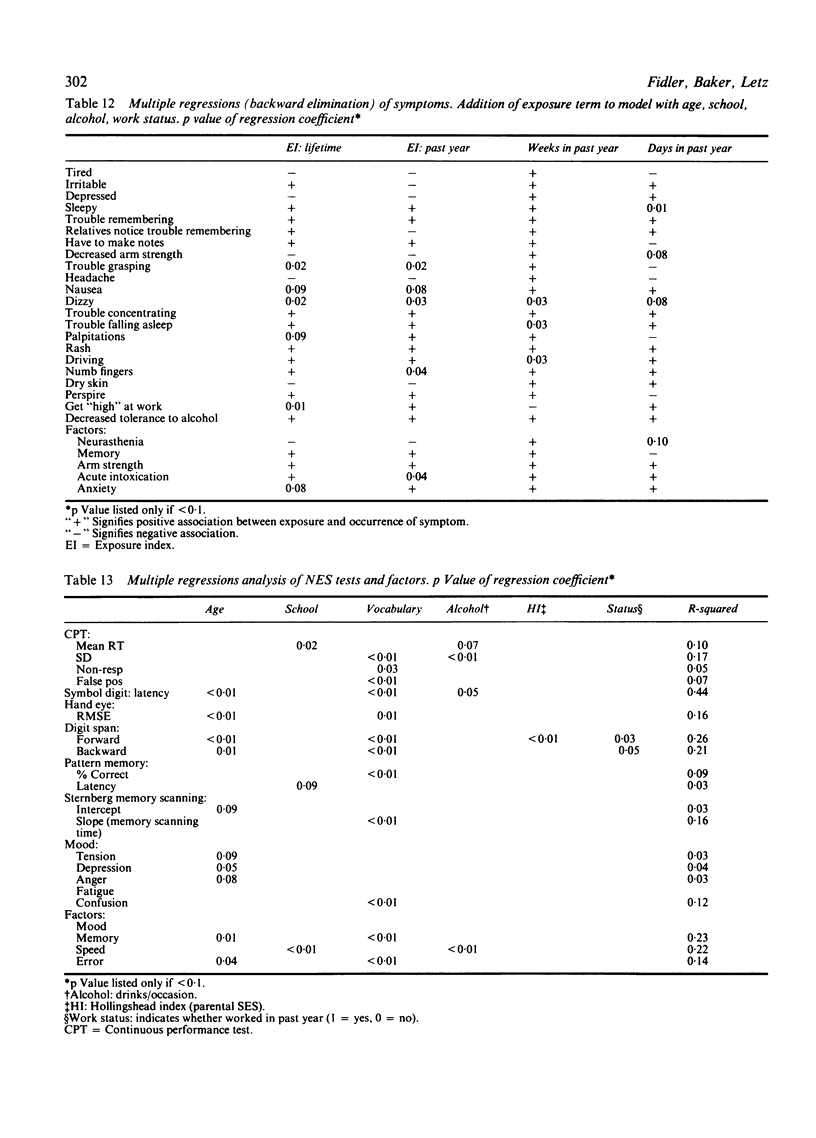
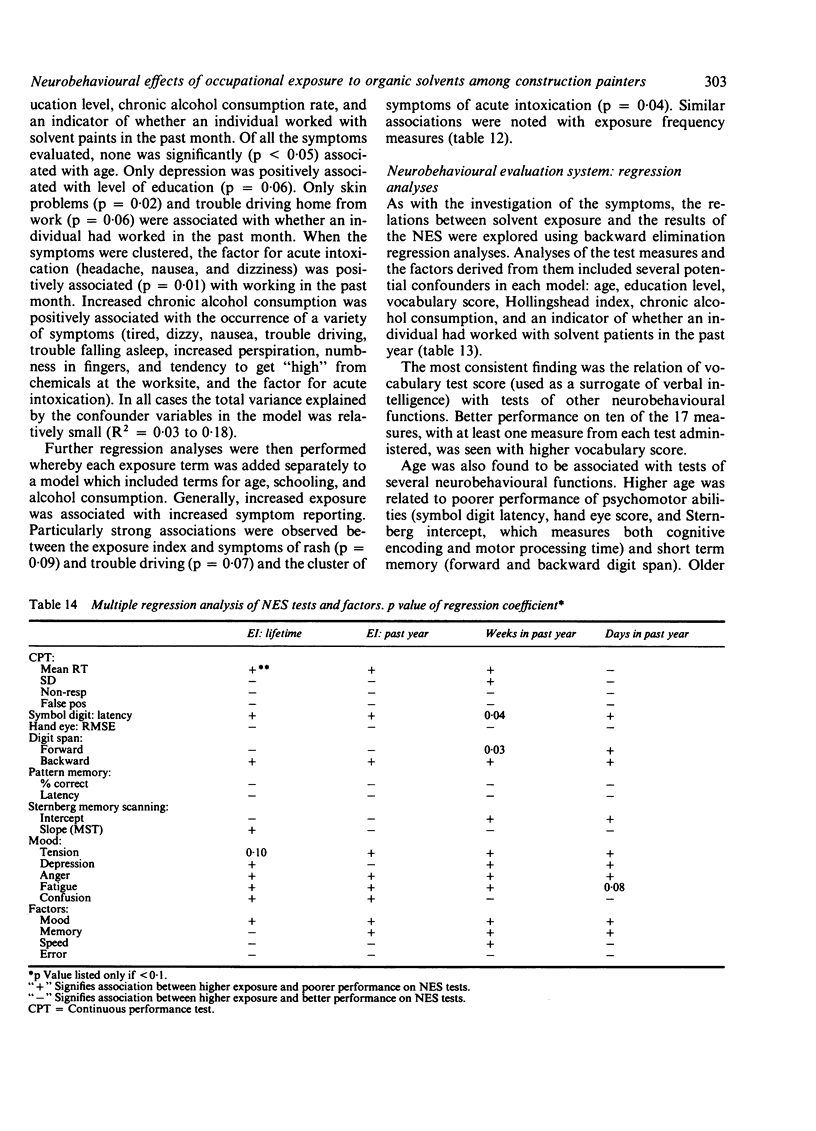
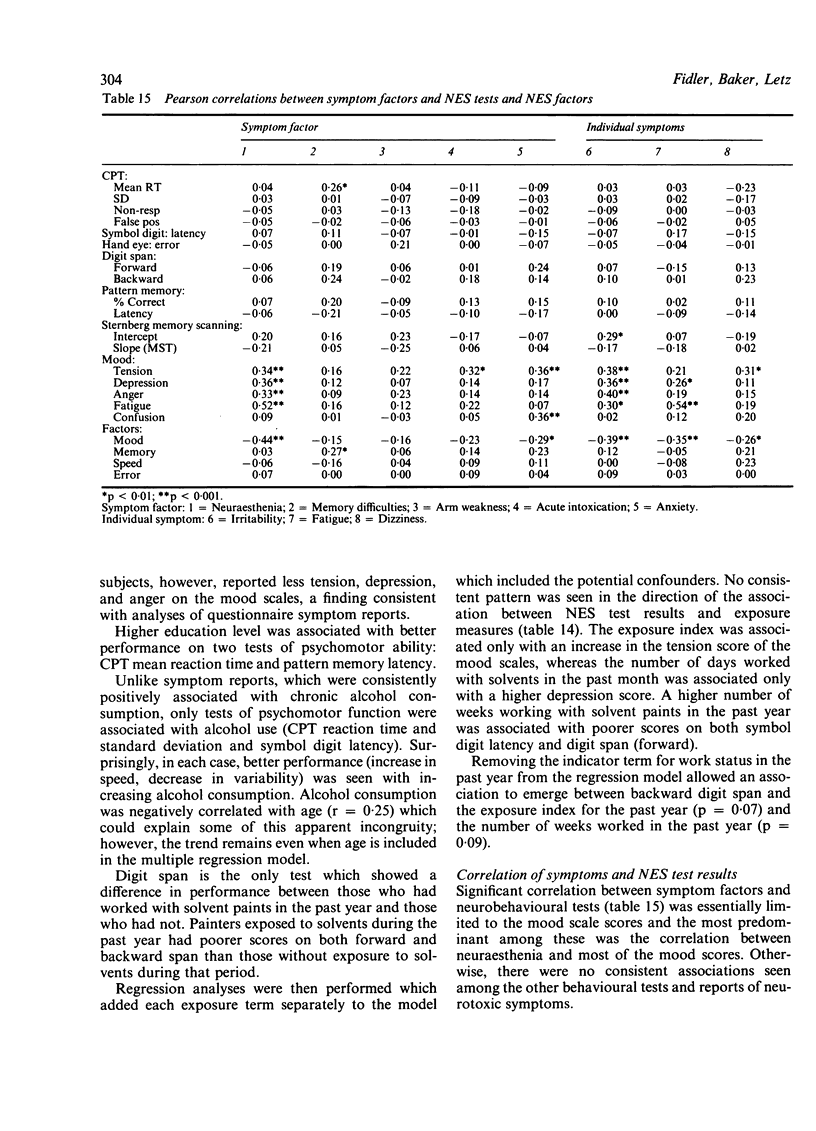
A cross sectional study of 101 construction painters was performed to investigate the relation between exposure to mixed organic solvents and changes in central nervous system function. Solvent exposure was estimated using questionnaire data to derive an exposure index (a measure of intensity of exposure) and to estimate the duration and frequency of exposure. Adverse effects on the central nervous system were assessed by self reported questionnaires and eight tests of a computer administered neurobehavioural evaluation system. Factor analysis of both measures of effect yielded factors both biologically plausible and in agreement with other empirical evidence. A consistent positive association was observed between most measures of exposure and the occurrence of neurotoxic symptoms, notably dizziness, nausea, fatigue, problems with arm strength, and feelings of getting "high" from chemicals at work. Associations with exposure were found with the neurobehavioural evaluation system tests of symbol digit substitution and digit span; however, no consistent pattern of effect on neurobehavioural function was observed. This pattern of the occurrence of neurotoxic symptoms without clear evidence of function deficit is consistent with the type 1 toxic central nervous system disorder as classified by the World Health Organisation.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson K. Effects of cigarette smoking on learning and retention. Psychopharmacologia. 1975;41(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00421296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson K., Hockey G. R. Effects of cigarette smoking on incidental memory. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1977 May 9;52(3):223–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00426703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anger W. K. Neurobehavioral testing of chemicals: impact on recommended standards. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1984 Mar-Apr;6(2):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anshelm Olson B. Effects of organic solvents on behavioral performance of workers in the paint industry. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):703–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlien-Søborg P., Bruhn P., Gyldensted C., Melgaard B. Chronic painters' syndrome. Chronic toxic encephalopathy in house painters. Acta Neurol Scand. 1979 Sep;60(3):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. L., Feldman R. G., White R. A., Harley J. P., Niles C. A., Dinse G. E., Berkey C. S. Occupational lead neurotoxicity: a behavioural and electrophysiological evaluation. Study design and year one results. Br J Ind Med. 1984 Aug;41(3):352–361. doi: 10.1136/oem.41.3.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. L., Letz R. E., Fidler A. T., Shalat S., Plantamura D., Lyndon M. A computer-based neurobehavioral evaluation system for occupational and environmental epidemiology: methodology and validation studies. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):369–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. L., Letz R., Fidler A. A computer-administered neurobehavioral evaluation system for occupational and environmental epidemiology. Rationale, methodology, and pilot study results. J Occup Med. 1985 Mar;27(3):206–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton A. L. Interactive effects of age and brain disease on reaction time. Arch Neurol. 1977 Jun;34(6):369–370. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1977.00500180063013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg W. E., Eisinger J., Lamola A. A., Zuckerman D. M. Zinc protoporphyrin level in blood determined by a portable hematofluorometer: a screening device for lead poisoning. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Apr;89(4):712–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braff D. L., Silverton L., Saccuzzo D. P., Janowsky D. S. Impaired speed of visual information processing in marijuana intoxication. Am J Psychiatry. 1981 May;138(5):613–617. doi: 10.1176/ajp.138.5.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Leading work-related diseases and injuries--United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1983 Jan 21;32(2):24-6, 32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry N., Venables H., Waldron H. A. British studies on the neuropsychological effects of solvent exposure. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1984;10 (Suppl 1):10–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry N., Venables H., Waldron H. A., Wells G. G. Some observations on workers exposed to methylene chloride. Br J Ind Med. 1981 Nov;38(4):351–355. doi: 10.1136/oem.38.4.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culver C. M., King F. W. Neuropsychological assessment of undergraduate marihuana and LSD users. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1974 Nov;31(5):707–711. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1974.01760170093015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly E. F., Nasrallah H. A., Wyatt R. J., Gillin J. C., Bigelow L. B. Effects of dopamine synthesis inhibition on WAIS comprehension. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1978 Jun;46(3):385–388. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.46.3.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elofsson S. A., Gamberale F., Hindmarsh T., Iregren A., Isaksson A., Johnsson I., Knave B., Lydahl E., Mindus P., Persson H. E. Exposure to organic solvents. A cross-sectional epidemiologic investigation on occupationally exposed care and industrial spray painters with special reference to the nervous system. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1980 Dec;6(4):239–273. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler A. T., Baker E. L., Letz R. E. Estimation of long term exposure to mixed solvents from questionnaire data: a tool for epidemiological investigations. Br J Ind Med. 1987 Feb;44(2):133–141. doi: 10.1136/oem.44.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkard S., Knauth P., Monk T. H. The effect of memory load on the circadian variation in performance efficiency under a rapidly rotating shift system. Ergonomics. 1976 Jul;19(4):479–488. doi: 10.1080/00140137608931559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Kaizer S., Warren R. Psychotropic effects of caffeine in man. II. Alertness, psychomotor coordination, and mood. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Oct;150(1):146–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen P., Angelsø B., Nielsen T. E., Nørgaard B., Uldal C. Neurotoxic effects of organic solvents in exposed workers: an occupational, neuropsychological, and neurological investigation. Am J Ind Med. 1984;5(3):201–225. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700050305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M., Axelson O., Blume J., Hogstedt C., Sundell L., Ydreborg B. Psychological function changes among house painters. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1977 Jun;3(2):91–99. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks L. H., Birren J. E. Aging, brain damage, and psychomotor slowing. Psychol Bull. 1970 Dec;74(6):377–396. doi: 10.1037/h0033064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. Y. Alcohol and brain damage: cause or association? Am J Public Health. 1983 May;73(5):487–489. doi: 10.2105/ajph.73.5.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husman K. Symptoms of car painters with long-term exposure to a mixture of organic solvents. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1980 Mar;6(1):19–32. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen H., Eskelinen L., Husman K., Nurminen M. Behavioral effects of long-term exposure to a mixture of organic solvents. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1976 Dec;2(4):240–255. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen H. Psychological picture of manifest and latent carbon disulphide poisoning. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Oct;28(4):374–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen H. Psychological test methods: sensitivity to long term chemical exposure at work. Neurobehav Toxicol. 1979;1 (Suppl 1):157–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen H. Twenty-five years of behavioral toxicology within occupational medicine: a personal account. Am J Ind Med. 1985;7(1):19–30. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700070104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härkönen H. Relationship of symptoms to occupational styrene exposure and to the findings of electroencephalographic and psychological examinations. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1977 Dec 22;40(4):231–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00381410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iregren A. Effects on psychological test performance of workers exposed to a single solvent (toluene)--a comparison with effects of exposure to a mixture of organic solvents. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):695–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. M., Vega A. Cognitive performance measured on the ascending and descending limb of the blood alcohol curve. Psychopharmacologia. 1972;23(2):99–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00401185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinknecht R. A., Donaldson D. A review of the effects of diazepam on cognitive and psychomotor performance. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1975 Dec;161(6):399–414. doi: 10.1097/00005053-197512000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinknecht R. A., Goldstein S. G. Neuropsychological deficits associated with alcoholism. A review and discussion. Q J Stud Alcohol. 1972 Dec;33(4):999–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knave B., Olson B. A., Elofsson S., Gamberale F., Isaksson A., Mindus P., Persson H. E., Struwe G., Wennberg A., Westerholm P. Long-term exposure to jet fuel. II. A cross-sectional epidemiologic investigation on occupationally exposed industrial workers with special reference to the nervous system. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1978 Mar;4(1):19–45. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström K. Changes in psychological performances of solvent-poisoned and solvent-exposed workers. Am J Ind Med. 1980;1(1):69–84. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700010109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod C. M., Dekabian A. S., Hunt E. Memory impairment in epileptic patients: selective effects of phenobarbital concentration. Science. 1978 Dec 8;202(4372):1102–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.715461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVane J., Butters N., Montgomery K., Farber J. Cognitive functioning in men social drinkers; a replication study. J Stud Alcohol. 1982 Jan;43(1):81–95. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1982.43.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh G. R. Age differences in evoked potential correlates of a memory scanning process. Exp Aging Res. 1975 Sep;1(1):3–16. doi: 10.1080/03610737508257942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohs R. C., Tinklenberg J. R., Roth W. T., Kopell B. S. Slowing of short-term memory scanning in alcoholics. J Stud Alcohol. 1978 Nov;39(11):1908–1915. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1978.39.1908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naus M. J., Cermak L. S., DeLuca D. Retrieval processes in alcoholic Korsakoff patients. Neuropsychologia. 1977;15(6):737–742. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(77)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker E. S., Birnbaum I. M., Boyd R. A., Noble E. P. Neuropsychologic decrements as a function of alcohol intake in male students. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1980 Jul;4(3):330–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1980.tb04823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker E. S., Noble E. P. Alcohol consumption and cognitive functioning in social drinkers. J Stud Alcohol. 1977 Jul;38(7):1224–1232. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1977.38.1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker E. S., Parker D. A., Brody J. A., Schoenberg R. Cognitive patterns resembling premature aging in male social drinkers. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1982 Winter;6(1):46–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1982.tb05380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratanatharathorn V., Samson M. K., Haas C. D., Cummings G. D., O'Connor E. J., Baker L. H. Phase II evaluation of 1-(2-chloroethyl)-3-(2,6-dioxo-(piperidyl)-1 nitrosourea (PCNU)(NSC-95466) in patients with advanced carcinoma of the lung. Am J Clin Oncol. 1983 Feb;6(1):99–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. T., Tinklenberg J. R., Kopell B. S. Ethanol and marihuana effects on event-related potentials in a memory retrieval paradigm. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1977 Mar;42(3):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(77)90174-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. Alcoholism and premature aging: a neuropsychological perspective. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1982 Winter;6(1):22–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1982.tb05378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C., Butters N. Further evidence for a continuum-of-impairment encompassing male alcoholic Korsakoff patients and chronic alcoholic men. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1980 Apr;4(2):190–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1980.tb05634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savolainen K., Riihimäki V., Linnoila M. Effects of short-term xylene exposure on psychophysiological functions in man. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1979 Nov;44(4):201–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00381655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer J., Andrysiak T., Ungerleider J. T. Cognition and long-term use of ganja (Cannabis). Science. 1981 Jul 24;213(4506):465–466. doi: 10.1126/science.6972600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidell F. R., Pless J. E. Ethyl alcohol: blood levels and performance decrements after oral administration to man. Psychopharmacologia. 1971;19(3):246–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00401941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. J., Langolf G. D. The use of Sternberg's memory-scanning paradigm in assessing effects of chemical exposure. Hum Factors. 1981 Dec;23(6):701–708. doi: 10.1177/001872088102300607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg S. Memory-scanning: mental processes revealed by reaction-time experiments. Am Sci. 1969 Winter;57(4):421–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struwe G., Mindus P., Jönsson B. Psychiatric ratings in occupational health research: a study of mental symptoms in lacquerers. Am J Ind Med. 1980;1(1):23–30. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tharp V. K., Jr, Rundell O. H., Jr, Lester B. K., Williams H. L. Alcohol and information processing. Psychopharmacologia. 1974;40(1):33–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00429446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega A., Jr, Parsons O. A. Cross-validation of the Halstead-Reitan tests for brain damage. J Consult Psychol. 1967 Dec;31(6):619–625. doi: 10.1037/h0025112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G. Effects of cigarette smoking on immediate memory and performance in different kinds of smoker. Br J Psychol. 1980 Feb;71(1):83–90. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1980.tb02732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. M., Goldman M. S., Williams D. L. Expectancy and pharmacological effects of alcohol on human cognitive and motor performance: the compensation for alcohol effect. J Abnorm Psychol. 1981 Jun;90(3):267–270. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.90.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


