Abstract
The neurotoxicity of n-pentane, n-hexane, and n-heptane have been studied in Wistar strain male rats after exposure to 3000 ppm of n-pentane, n-hexane, or n-heptane for 12 hours a day for 16 weeks. The nerve conduction velocity and the distal latency were measured before the beginning of the exposure and after exposure for four, eight, 12, and 16 weeks. The experiment showed that n-hexane disturbed the conduction velocity of the motor nerve and the mixed nerve and prolonged the distal latency in the rat's tail, but that n-pentane and n-heptane did not. The light and electron microscopic examination showed that the peripheral nerve, the neuromuscular junction, and the muscle fibre of the rats exposed to n-hexane were severely impaired, but those of the rats exposed to n-pentane or n-heptane showed no particular changes even after 16 weeks of exposure. These results show that n-hexane is far more toxic to the peripheral nerve of the rat than n-pentane or n-heptane. It is necessary to study the neurotoxicity of other petroleum hydrocarbons, since some reports suggest that petroleum solvents might possibly contain neurotoxic hydrocarbons other than n-hexane.
Full text
PDF
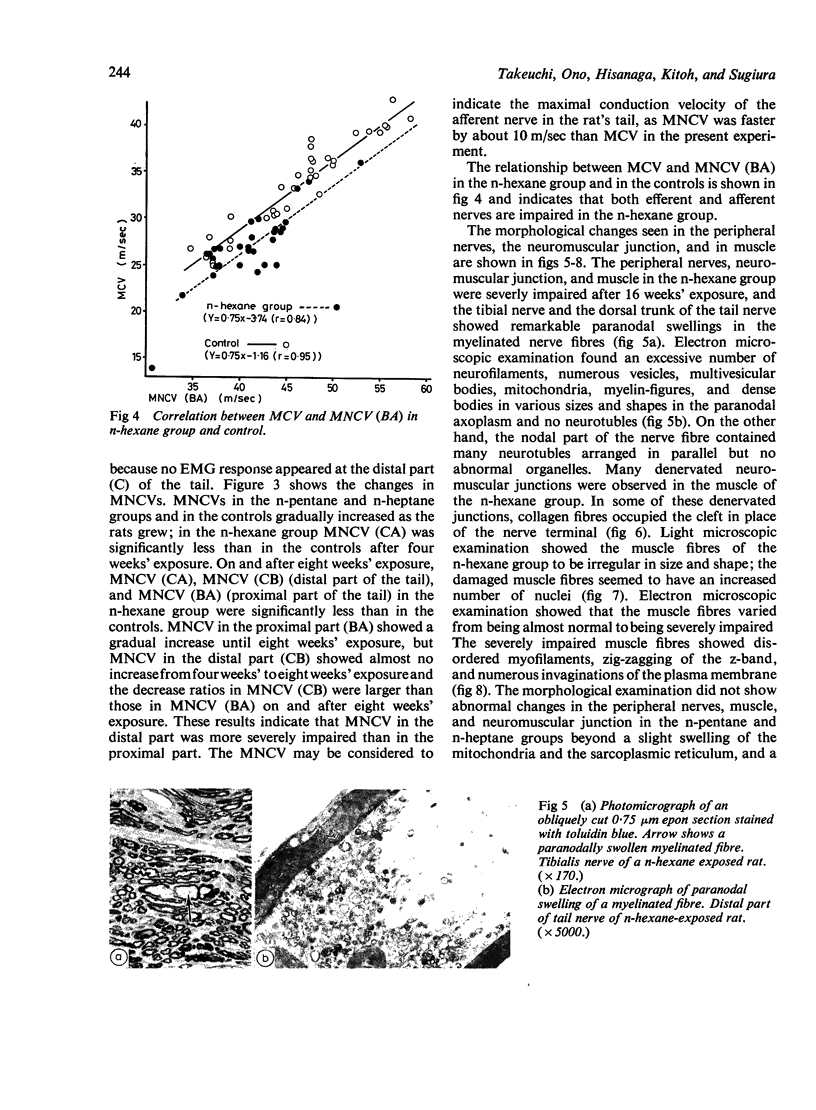
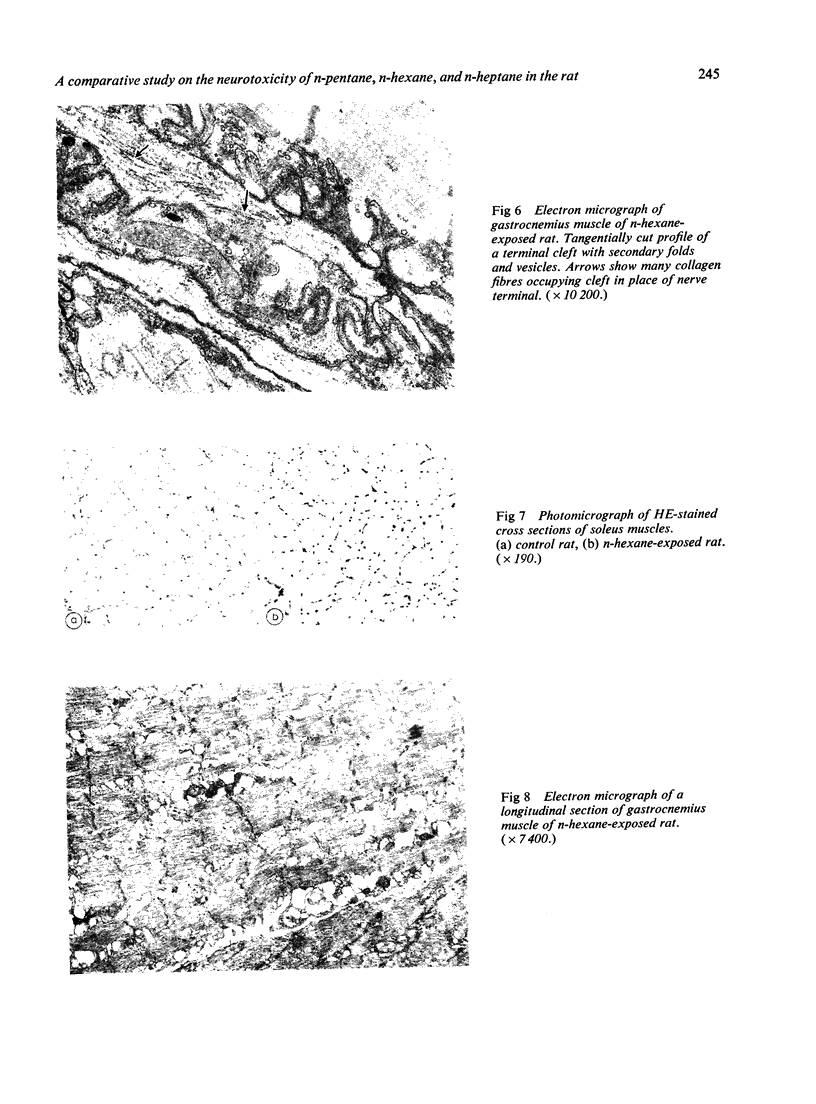


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbritti G., Siracusa A., Cianchetti C., Coli A., Curradi F., Perticoni G. F., De Rosa F. Shoe-makers' polyneuropathy in Italy: the aetiological problem. Br J Ind Med. 1976 May;33(2):92–99. doi: 10.1136/oem.33.2.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couri D., Abdel-Rahman M. S., Hetland L. B. Biotransformation of n-hexane and methyl n-butyl ketone in guinea pigs and mice. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1978 Apr;39(4):295–300. doi: 10.1080/0002889778507761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frommer U., Ullrich V., Staudinger H., Orrenius S. The monooxygenation of N-heptane by rat liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 8;280(4):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaultier M., Rancurel G., Piva C., Efthymiou M. L. Polynévrites et hydrocarbures aliphatiques. Eur J Toxicol Hyg Environ. 1973 Nov-Dec;6(6):294–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida M., Yamamura Y., Sobue I. Electromyographic findings and conduction velocity on N-hexane polyneuropathy. Electromyography. 1969 Aug-Oct;9(3):247–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. L., Setzer J. V., Lewis T. R., Hornung R. W. An electrodiagnostic study of the neurotoxicity of methyl n-amyl ketone. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1978 Nov;39(11):866–872. doi: 10.1080/0002889778507876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto S., Shirabe T., Kurihara T., Araki S. [N-hexane polyneuropathy in an interior decorator and experimental n-hexane neuropathy]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1977 Apr;17(4):237–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
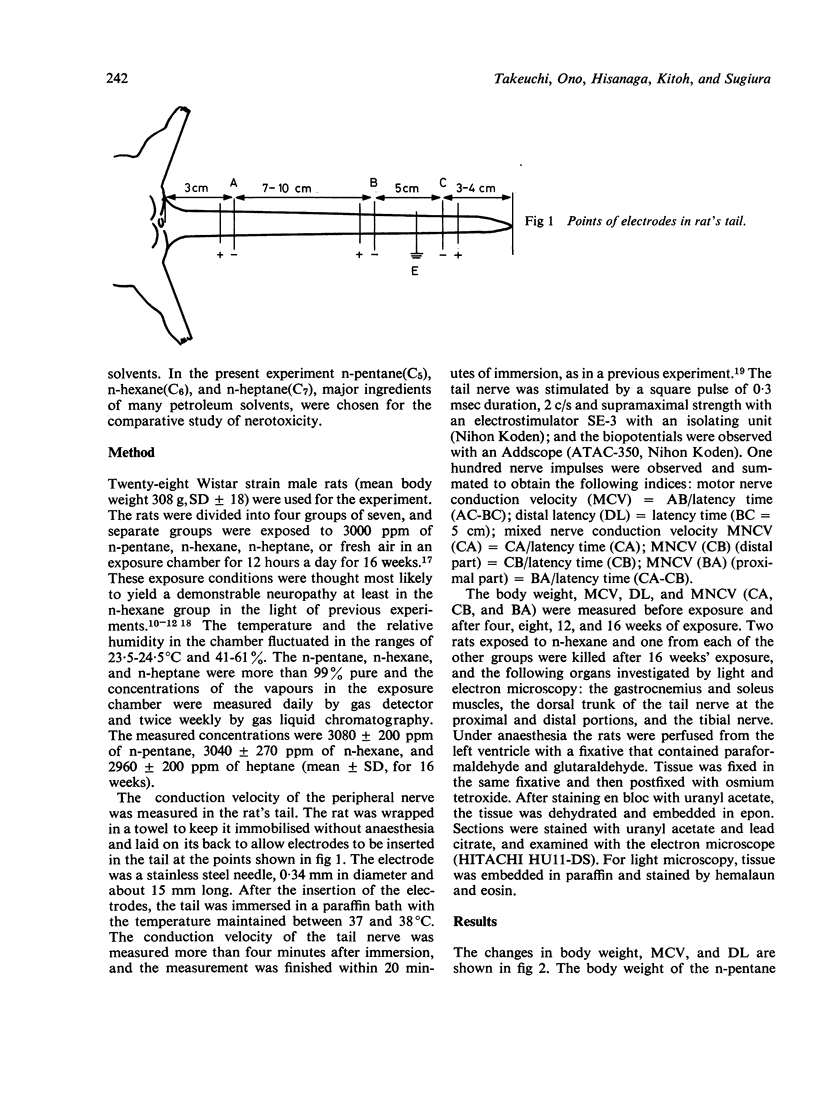
- Ono Y., Takeuchi Y., Hisanaga N. [Studies on the method of measuring nerve conduction velocity in rat's tail and on the comparative toxicity of n-hexane, methyl n-butyl ketone and 5,5-hexanedione (author's transl)]. Sangyo Igaku. 1979 Nov;21(6):528–538. doi: 10.1539/joh1959.21.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabri M. I., Moore C. L., Spencer P. S. Studies on the biochemical basis of distal axonopathies--I. Inhibition of glycolysis by neurotoxic hexacarbon compounds. J Neurochem. 1979 Mar;32(3):683–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saida K., Mendell J. R., Weiss H. S. Peripheral nerve changes induced by methyl n-butyl ketone and potentiation by methyl ethyl ketone. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1976 May;35(3):207–225. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197605000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaumburg H. H., Spencer P. S. Degeneration in central and peripheral nervous systems produced by pure n-hexane: an experimental study. Brain. 1976 Jun;99(2):183–192. doi: 10.1093/brain/99.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaumburg H. H., Spencer P. S. Environmental hydrocarbons produce degeneration in cat hypothalamus and optic tract. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):199–200. doi: 10.1126/science.413192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Bischoff M. C., Schaumburg H. H. On the specific molecular configuration of neurotoxic aliphatic hexacarbon compounds causing central--peripheral distal axonopathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1978 Apr;44(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(78)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Schaumburg H. H., Raleigh R. L., Terhaar C. J. Nervous system degeneration produced by the industrial solvent methyl n-butyl ketone. Arch Neurol. 1975 Apr;32(4):219–222. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490460035002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Schaumburg H. H. Ultrastructural studies of the dying-back process. III. The evolution of experimental peripheral giant axonal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1977 Mar-Apr;36(2):276–299. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197703000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Schaumburg H. H. Ultrastructural studies of the dying-back process. IV. Differential vulnerability of PNS and CNS fibers in experimental central-peripheral distal axonopathies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1977 Mar-Apr;36(2):300–320. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197703000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takeuchi H., Kyo S., Yorifuji S., Sanagi S., Seki Y., Hara I. N-hexane polyneuropathy--a case report with a review of the literature. Med J Osaka Univ. 1977 Sep;28(1):77–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Mabuchi C., Takagi S. Polyneuropathy caused by petroleum benzine. Int Arch Arbeitsmed. 1975;34(3):185–197. doi: 10.1007/BF01371740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura Y. n-Hexane polyneuropathy. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1969;23(1):45–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1969.tb01441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Yanagisawa H., Muneyuki T., Shigiya R. [Electrophysiological studies of n-hexane polyneuropathy]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1974 May;14(5):454–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]