Abstract
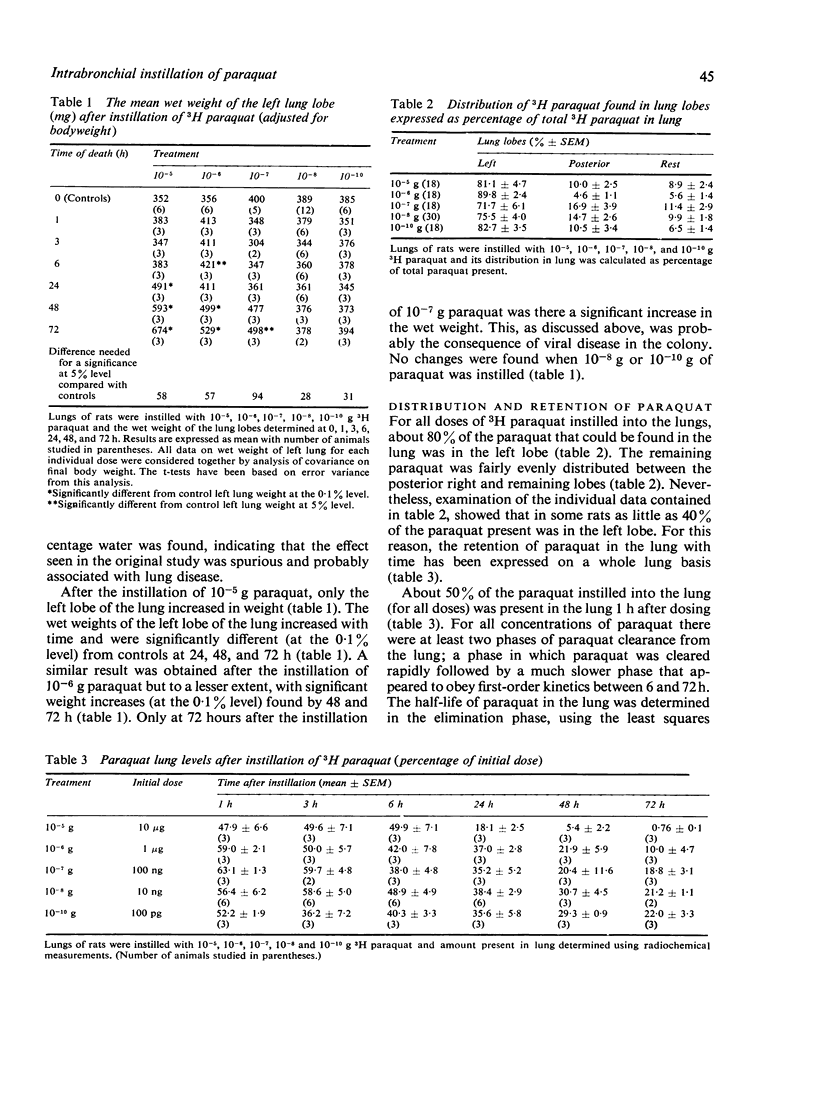
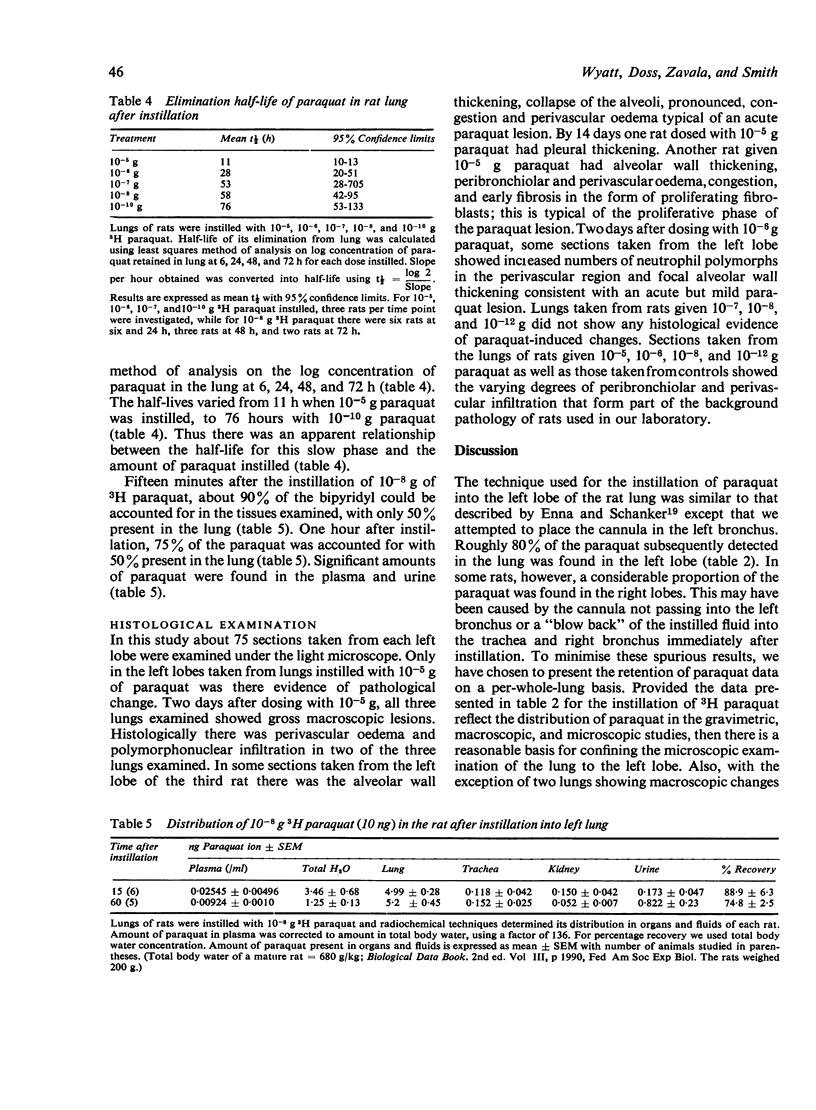
Various amounts of paraquat (10(-5) to 10(-12) g) in 0.1 ml saline were instilled directly into the left bronchus of male adult rats. Gravimetric, macroscopic, and microscopic studies on the left lobe of the lung showed that 10(-5) g of paraquat produced lung oedema and macroscopic lesions two and 14 days after doing. The pathology of the lung was similar to that seen after systemic poisoning. When 10(-6) g of paraquat was instilled, some animals developed lung oedema and macroscopic lesions. Microscopic examination showed subtle changes in the parenchyma of the lung. With amounts of paraquat equal to or less than 10(-7) g (doses as little as 10(-12) g were used), no changes in the lung were seen. This is contrary to published accounts in which amounts as low as 10(-12) g (1 Pg) were reported to cause acute damage to the rabbit lung. When 3H paraquat was instilled into the left lobe (doses of 10(-5) to 10(-10) g were used), the loss of paraquat from the lung was biphasic. The initial half-life was less than one hour. The secondary phase obeyed first-order kinetics, and the half-life was dependent on the dose of paraquat instilled. This half-life was as short as 11 hours when 10(-5) g paraquat was instilled and was 76 hours after the instillation of 10(-10) g paraquat. The decrease in the half-life of the secondary phase with increasing doses of paraquat is possibly associated with the production of oedema or lung cell damage, or both. After the instillation of 10(-8) g 3H paraquat, the initial half-life was less than 15 minutes, and paraquat was detected in the urine and plasma at that time. This suggests that 50% of the instilled paraquat was rapidly absorbed from the lung into the plasma.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks R. E. Ultrastructure of lung lesions produced by ingested chemicals. I. Effect of the herbicide paraquat on mouse lung. Lab Invest. 1971 Dec;25(6):536–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler C., 2nd, Kleinerman J. Paraquat in the rabbit. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Jan;28(1):67–71. doi: 10.1136/oem.28.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., McElligott T. F., Hurst E. W. The toxicity of paraquat. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Apr;23(2):126–132. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. W., Gage J. C. Absorption and excretion of diquat and paraquat in rats. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Apr;23(2):133–136. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Schanker L. S. Absorption of saccharides and urea from the rat lung. Am J Physiol. 1972 Feb;222(2):409–414. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage J. C. Toxicity of paraquat and diquat aerosols generated by a size-selective cyclone: effect of particle size distribution. Br J Ind Med. 1968 Oct;25(4):304–314. doi: 10.1136/oem.25.4.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaultier M., Bescol-Liversac J., Fréjaville J. P., Leclerc J. P., Guillam C. Etude anatomo-clinique et expérimentale de l'intoxication par le paraquat. Lésions ultrastructurales. Sem Hop. 1973 Jun 8;49(27):1972–1987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. D., Gaines T. B. Toxicity of paraquat to rats and its effect on rat lungs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;17(3):679–690. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(70)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modée J., Ivemark B. I., Robertson B. Ultrastructure of the alveolar wall in experimental paraquat poisoning. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1972;80(1):54–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. E., Gibson J. E. A comparative study of paraquat intoxication in rats, guinea pigs and monkeys. Exp Mol Pathol. 1972 Dec;17(3):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(72)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidenfeld J. J., Wycoff D., Zavala D. C., Richerson H. B. Paraquat lung injury in rabbits. Br J Ind Med. 1978 Aug;35(3):245–257. doi: 10.1136/oem.35.3.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. L., Rose M. S. A comparison of the effects of paraquat and diquat on the water content of rat lung and the incorporation of thymidine into lung DNA. Toxicology. 1977 Oct;8(2):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(77)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P., Heath D. The ultrastructure and time sequence of the early stages of paraquat lung in rats. J Pathol. 1974 Dec;114(4):177–184. doi: 10.1002/path.1711140402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. I., Purchase I. F., Smith L. L. Pulmonary ultrastructure after oral and intravenous dosage of paraquat to rats. J Pathol. 1977 Apr;121(4):233–241. doi: 10.1002/path.1711210407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijeyaratnam G. S., Corrin B. Experimental paraquat poisoning: a histological and electron-optical study of the changes in the lung. J Pathol. 1971 Feb;103(2):123–129. doi: 10.1002/path.1711030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavala D. C., Rhodes M. L. An effect of paraquat on the lungs of rabbits. Its implications in smoking contaminated marihuana. Chest. 1978 Oct;74(4):418–420. doi: 10.1378/chest.74.4.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavala D. C., Rhodes M. L., Connor W. E. Selective bronchial catheterization for the study of experimental lung damage in the rabbit. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Nov;144(2):509–512. doi: 10.3181/00379727-144-37624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


