Abstract
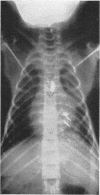
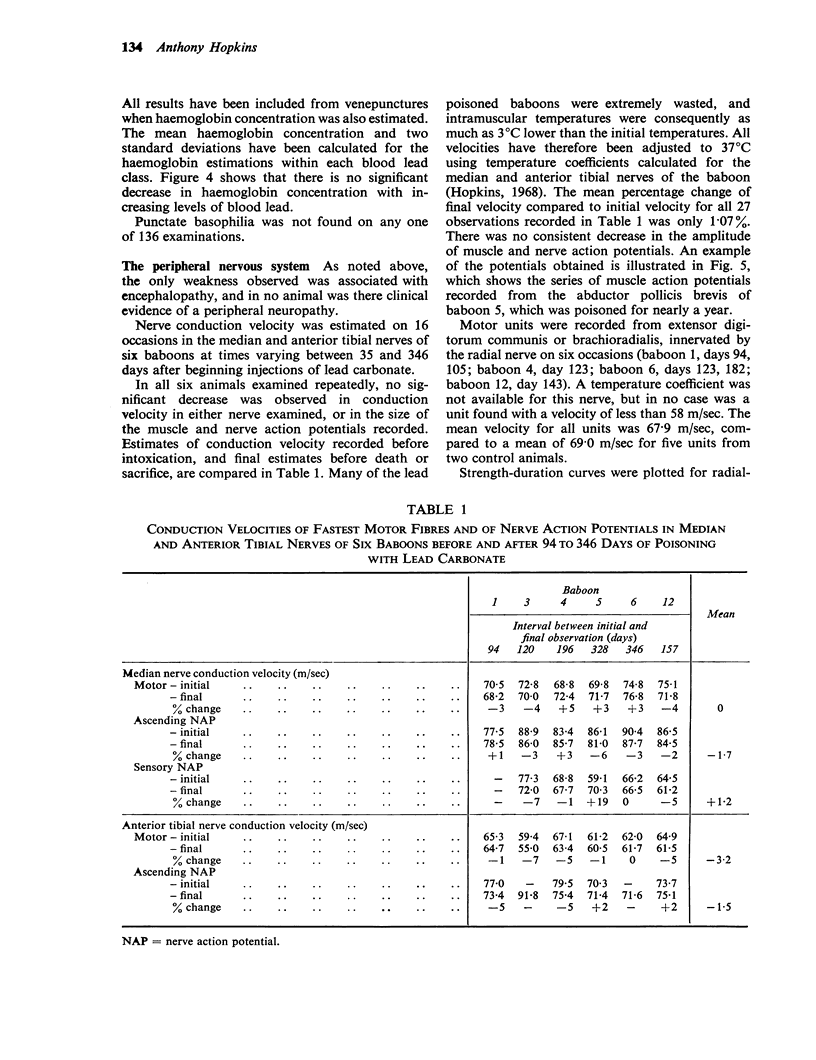
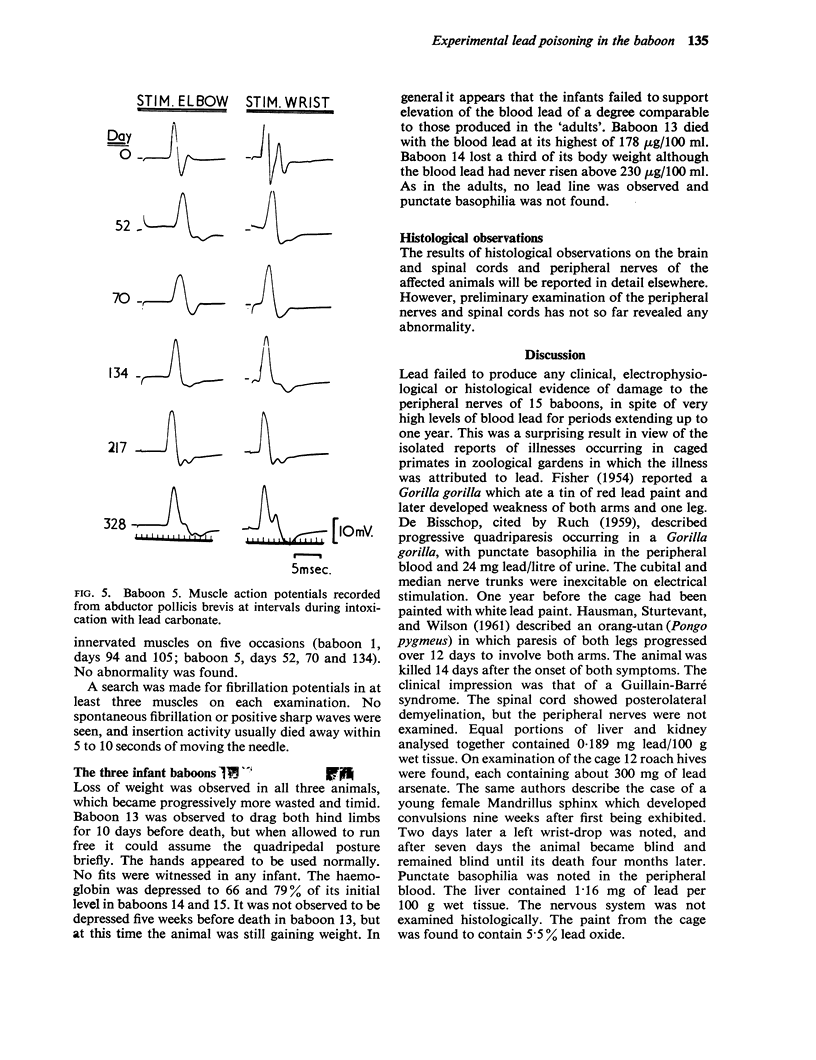
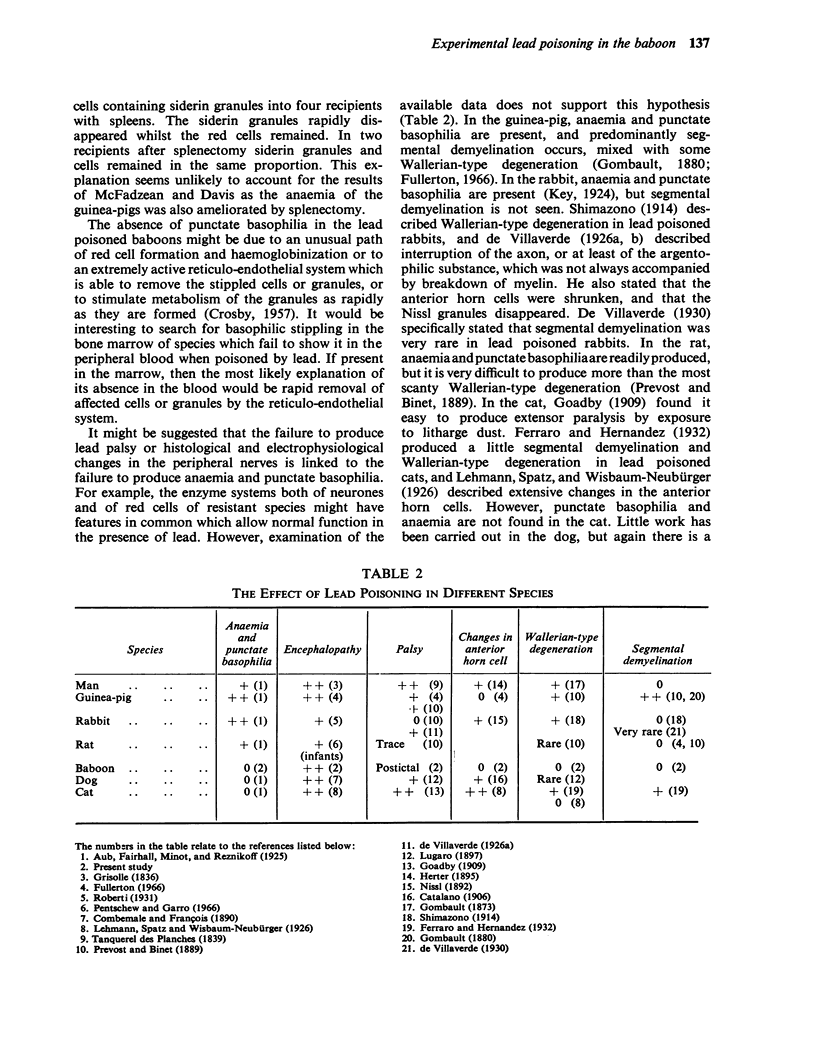
Hopkins, A. (1970).Brit. J. industr. Med.,27, 130-140. Experimental lead poisoning in the baboon. Twelve large and three infant baboons were poisoned by the intratracheal injection of lead carbonate in doses ranging from 50 to 135 mg/kg for 39 to 362 days. Eight baboons had one or more epileptic fits. Weakness of the limbs, believed to be of central origin, was seen in three of them. The effect of single and multiple doses of lead on the blood lead is recorded. Anaemia and punctate basophilia were not found. Measurements of nerve conduction velocity, electromyography and histological examination showed no abnormality of the peripheral nerves. The different effects of lead upon different species are discussed.
Full text
PDF
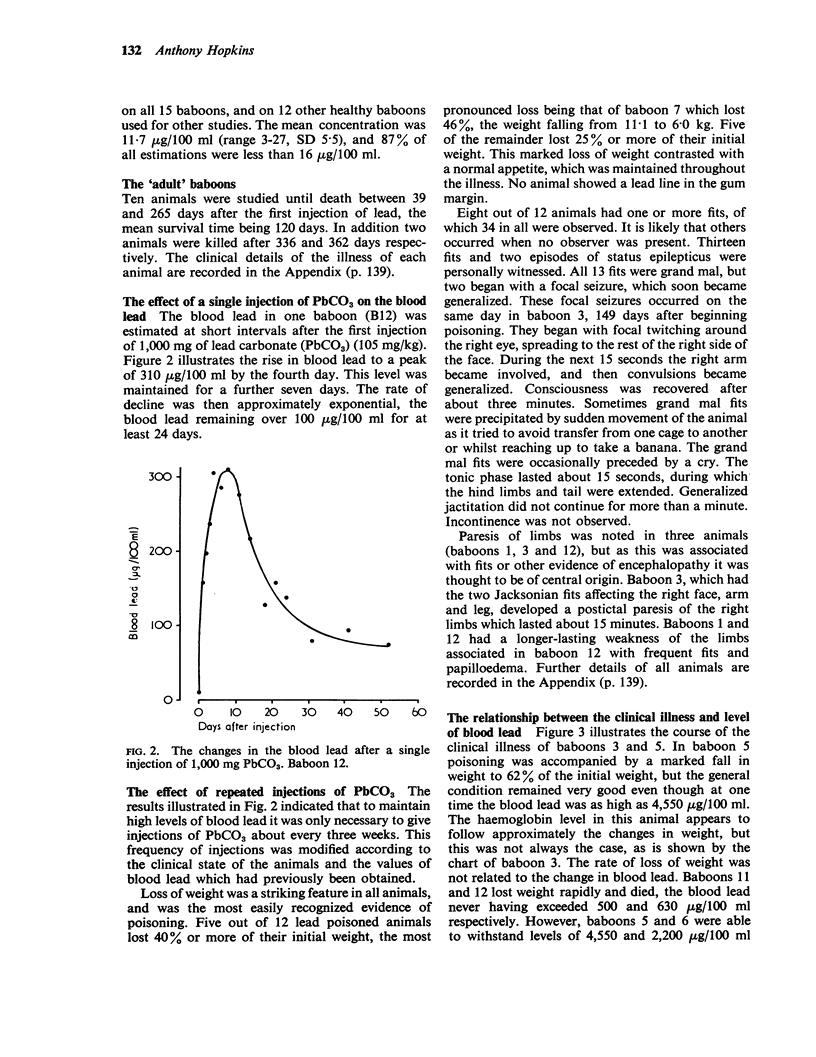
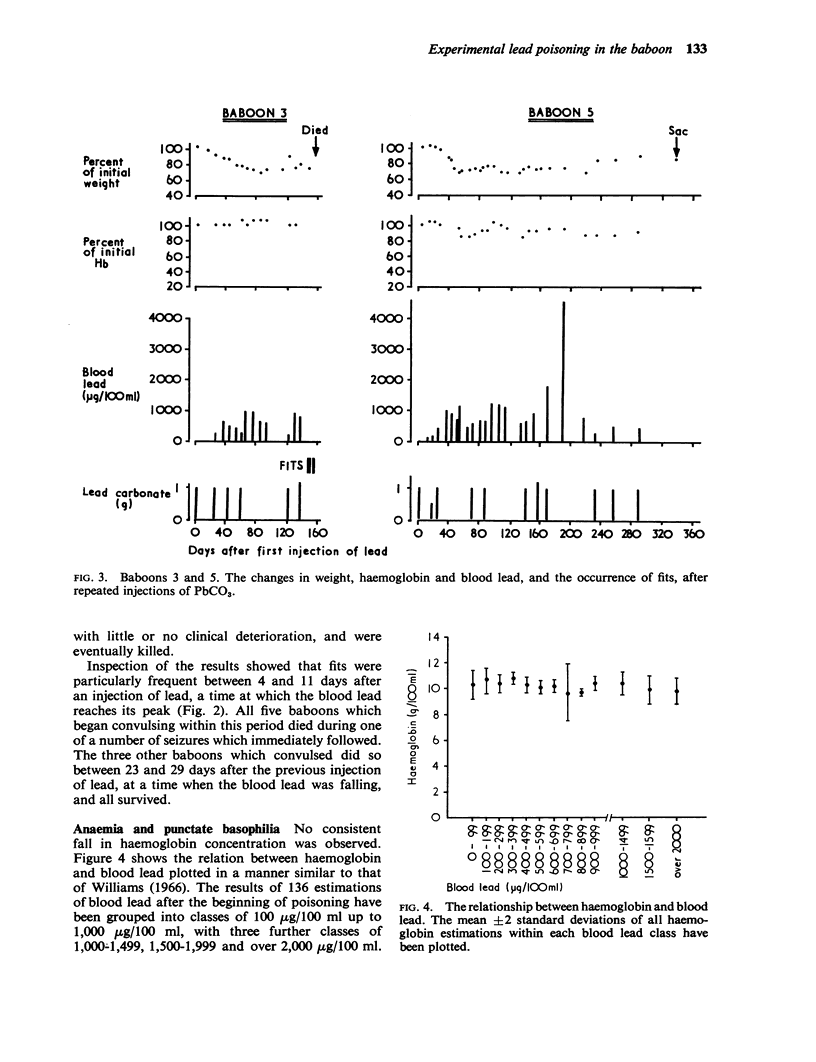




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COMSTOCK C. C., LAWSON L. H., GREENE E. A., OBERST F. W. Inhalation toxicity of hydrazine vapor. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1954 Dec;10(6):476–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSBY W. H. Siderocytes and the spleen. Blood. 1957 Feb;12(2):165–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DILL D. B., JACOBSON K. H. Toxicity of propellant fuels and oxidizers. U S Armed Forces Med J. 1960 Feb;11:125–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delves H. T., Vinter P. Semi-automatic determination of lead in whole blood. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Sep;19(5):504–509. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.5.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER L. E. Lead poisoning in a gorilla. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1954 Dec;125(933):478–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton P. M. Chronic peripheral neuropathy produced by lead poisoning in guinea-pigs. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1966 Apr;25(2):214–236. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196604000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUSMANOWA-PETRUSEWICZ I., EMERYK B., SOBKOWICZ H., WASOWICZ B., TUR J. [Electromyographic studies in lead poisoning]. Pol Tyg Lek. 1962 Sep 3;17:1405–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUSMAN R., STURTEVANT R. A., WILSON W. J., Jr Lead intoxication in primates. J Forensic Sci. 1961 Apr;6(2):180–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISSELBACHER K. J., GREENBERGER N. J. METABOLIC EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON THE LIVER. N Engl J Med. 1964 Feb 13;270:351–CONTD. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196402132700707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON K. H., CLEM J. H., WHEELWRIGHT H. J., Jr, RINEHART W. E., MAYES N. The acute toxicity of the vapors of some methylated hydrazine derivatives. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1955 Dec;12(6):609–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALLAI L., HAHN A., ROEDER V., ZUPANIC V. CORRELATION BETWEEN HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS AND SERUM TRANSAMINASE VALUES IN CHRONIC DISEASES OF THE LIVER. Acta Med Scand. 1964 Jan;175:49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1964.tb00549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KROP S. Toxicology of hydrazine; a review. AMA Arch Ind Hyg Occup Med. 1954 Mar;9(3):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURSEN T., FROM HANSEN P. A fluorimetric method for measuring the activity in serum of the enzyme glutamic pyruvic transaminase. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1958;10(1):53–58. doi: 10.3109/00365515809079917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURSEN T., SVENDSEN B. B. Glutamic pyruvic transaminase in the serum during treatment with chlorpromazine. Dan Med Bull. 1959 Mar;6(2):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G., Wray S. H. Conduction velocity and fibre diameter of the median and ulnar nerves of the baboon. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1967 Jun;30(3):240–247. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.30.3.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxnard C. E., Smith W. T. Neurological degeneration and reduced serum vitamin B12-levels in captive monkeys. Nature. 1966 Apr 30;210(5035):507–509. doi: 10.1038/210507a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARE C. M., SANDLER M. Acute hepatic necrosis following iproniazid therapy; value of glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase estimation in early detection. Lancet. 1959 Feb 7;1(7067):282–284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREISKEL D. Chronic lead poisoning: myopathy or neuritis. Ann Phys Med. 1958 Nov;4(8):293–296. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/iv.8.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentschew A., Garro F. Lead encephalo-myelopathy of the suckling rat and its implications on the porphyrinopathic nervous diseases. With special reference to the permeability disorders of the nervous system's capillaries. Acta Neuropathol. 1966 Jun 1;6(3):266–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00687857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REES K. R., SINHA K. P. Blood enzymes in liver injury. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80:297–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOOK B. S., COWART O. H. Health hazards associated with unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine. Ind Med Surg. 1957 Jul;26(7):333–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON J. A., SEATON D. A., ADAMS J. F. RESPONSE TO TREATMENT WITH CHELATING AGENTS OF ANAEMIA, CHRONIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, AND MYELOPATHY DUE TO LEAD POISONING. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1964 Dec;27:536–541. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.27.6.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUMPE A. R. Health hazards of new aircraft and rocket propellants; a review of the literature. J Aviat Med. 1958 Sep;29(9):650–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERMANDE-VAN ECK G. J., MEIGS J. W. Changes in the ovary of the rhesus monkey after chronic lead intoxication. Fertil Steril. 1960 Mar-Apr;11:223–234. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)33730-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron H. A. The anaemia of lead poisoning: a review. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Apr;23(2):83–100. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.2.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. K. Blood lead and haemoglobin in lead absorption. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Apr;23(2):105–111. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]