Abstract
Piotrowski, J. K. (1971).Brit. J. industr. Med.,28, 172-178. Evaluation of exposure to phenol: absorption of phenol vapour in the lungs and through the skin and excretion of phenol in urine. Volunteers were exposed to phenol vapour (5 to 25 mg/m3) by inhalation and through the skin, respectively, and the excretion of phenol in urine was examined.
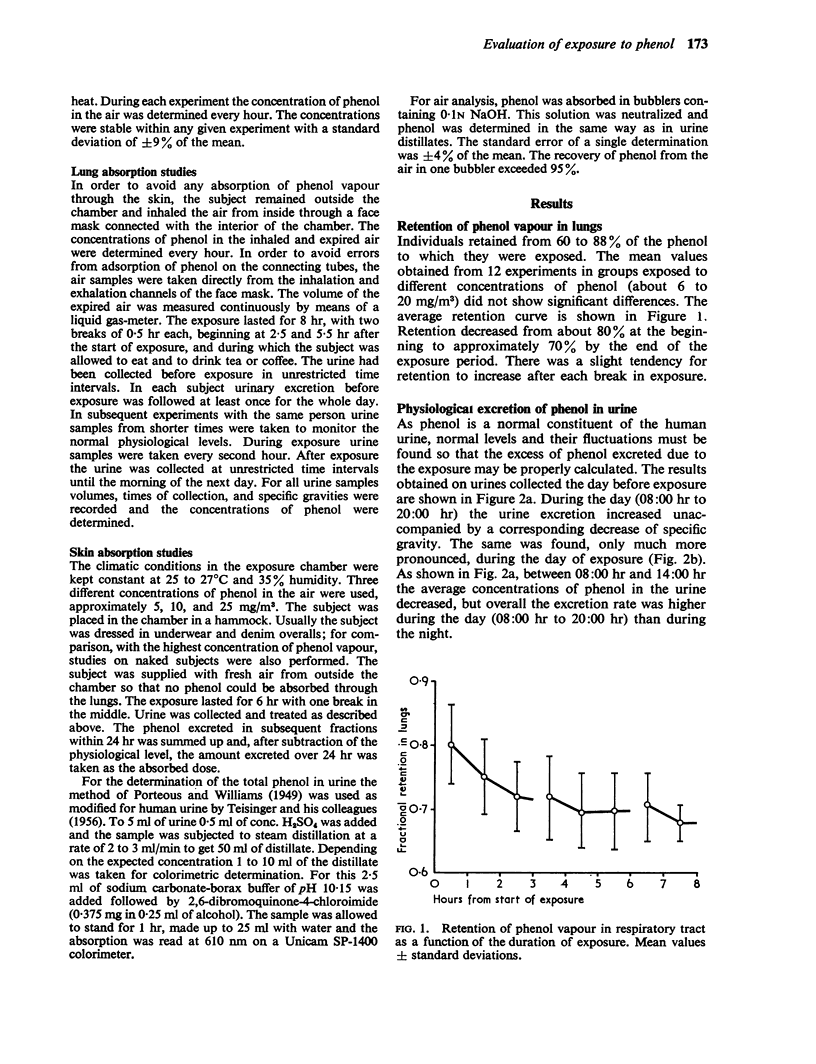
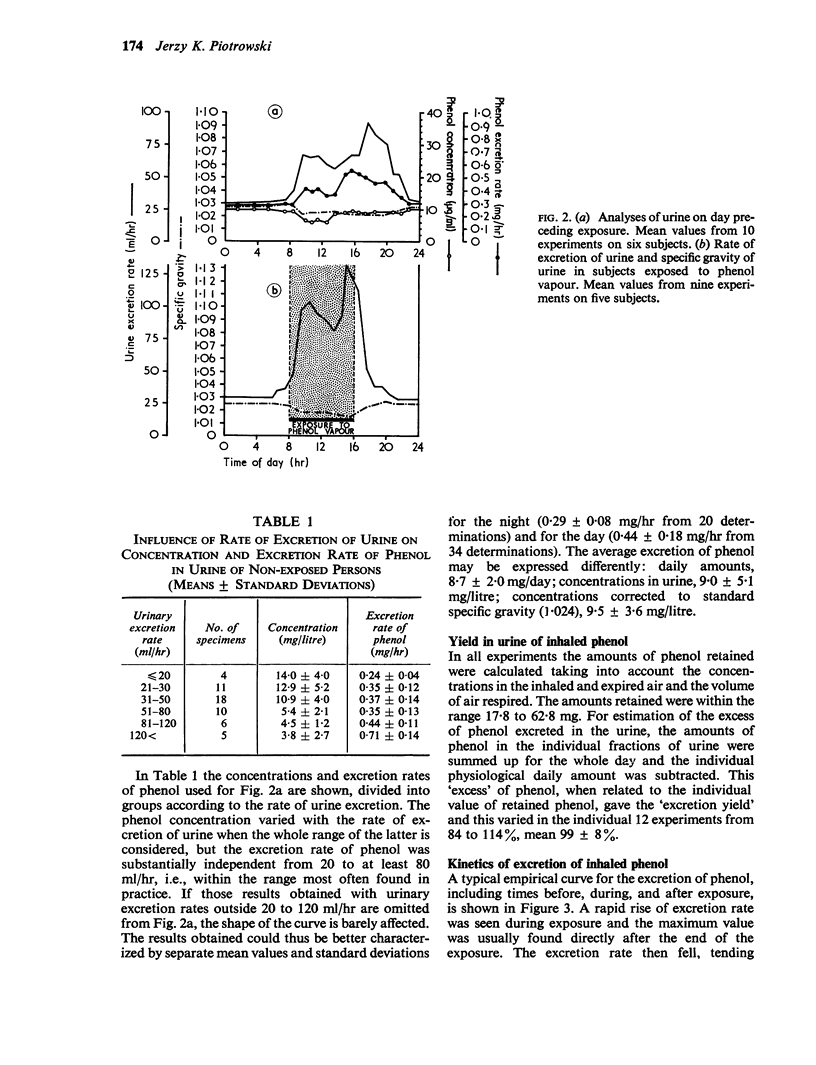
The retention of vapour in the lungs decreased from about 80 to 70% in the course of exposure. The absorption of vapour through the whole of the skin was approximately proportional to the concentration of vapour used, the absorption rate being somewhat lower than in the lungs.
Almost 100% of the phenol was excreted in the urine within one day. The rate of excretion of phenol in the urine may be used as an exposure test which permits the absorbed dose to be estimated with a precision of about ±2 mg.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARDODEJ Z., BARDODEJOVA E., BENES V., KUKACKOVA V., VITOVA A. [Diuresis and the phenol test]. Cesk Hyg. 1962 Feb;7:49–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowski J. Further investigations on the evaluation of exposure to nitrobenzene. Br J Ind Med. 1967 Jan;24(1):60–65. doi: 10.1136/oem.24.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteous J. W., Williams R. T. Studies in detoxication. 19. The metabolism of benzene. I. (a) The determination of phenol in urine with 2:6-dichloroquinonechloroimide. (b) The excretion of phenol, glucuronic acid and ethereal sulphate by rabbits receiving benzene and phenol. (c) Observations on the determination of catechol, quinol and muconic acid in urine. Biochem J. 1949;44(1):46–55. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUEDEMANN R., DEICHMANN W. B. Blood phenol level after topical application of phenol-containing preparations. J Am Med Assoc. 1953 Jun 6;152(6):506–509. doi: 10.1001/jama.1953.03690060022008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEISINGER J., FISEROVA-BERGEROVA V. Vztah säranového a fenolického testu v mo6ci ke koncentraci benzenu ve vzduchu. Prac Lek. 1955 Feb;7(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKLEY J. E., PAGNOTTO L. D., ELKINS H. B. The measurement of phenol in urine as an index of benzene exposure. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1961 Oct;22:362–367. doi: 10.1080/00028896109343422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


