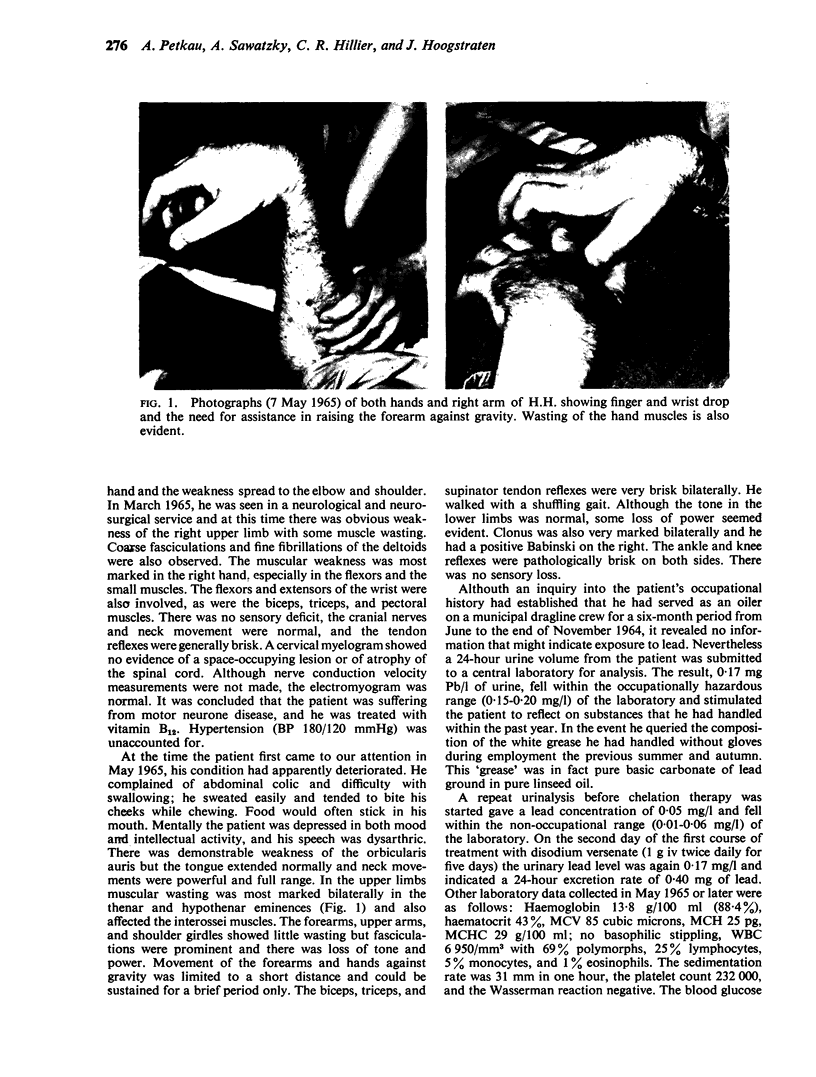
Abstract
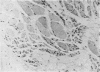
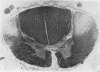
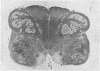
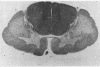
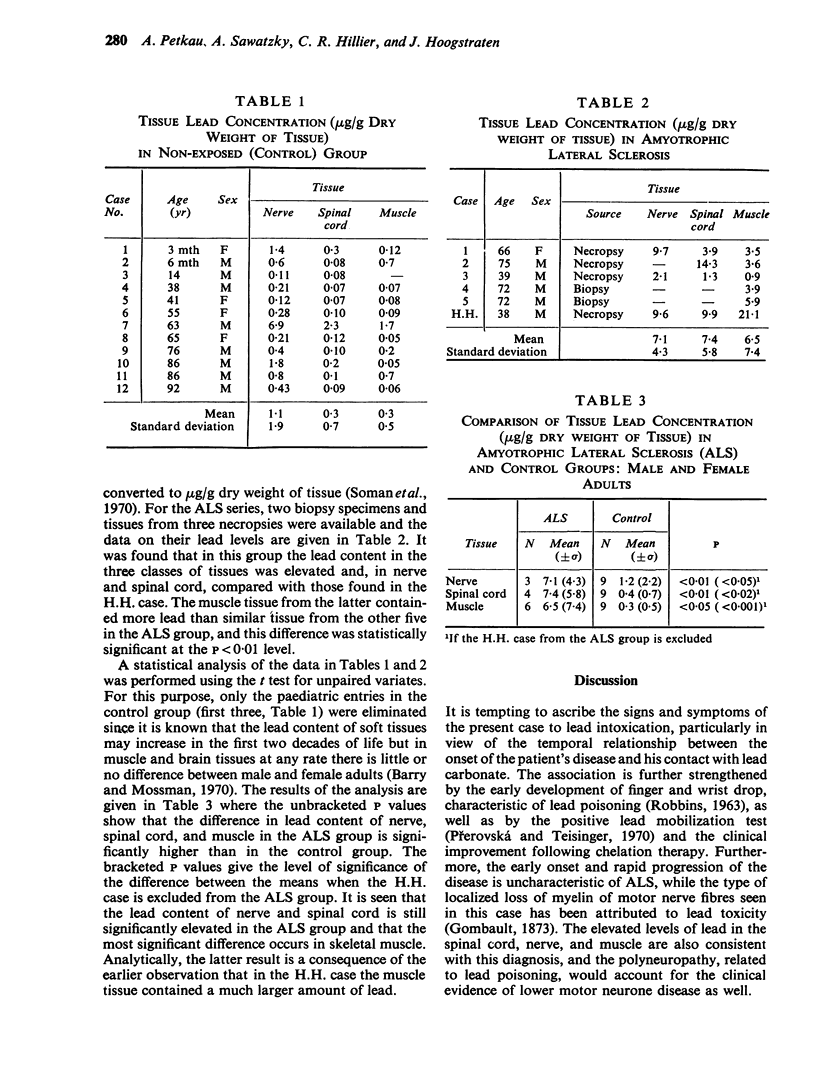
Petkau, A., Sawatzky, A., Hillier, C. R., and Hoogstraten, J. (1974).British Journal of Industrial Medicine,31, 275-287. Lead content of neuromuscular tissue in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Case report and other considerations. In a case of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, in which the occupational history and laboratory evidence indicated that exposure to lead had occured, it was found at necropsy that in tissues of nerve, spinal cord, and cardiac and skeletal muscle the lead content was 9·6 ± 0·3, 9·9 ± 1·7, 17·7, and 21·1 ± 5·1 μg/g of dry weight of tissue, respectively. Significantly elevated levels of lead were also found at necropsy in nerve, spinal cord, and muscle tissue in other cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis that had not been exposed to lead during life. A reassessment of the role of lead in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is indicated.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry P. S., Mossman D. B. Lead concentrations in human tissues. Br J Ind Med. 1970 Oct;27(4):339–351. doi: 10.1136/oem.27.4.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobowick A. R., Brody J. A. Epidemiology of motor-neuron diseases. N Engl J Med. 1973 May 17;288(20):1047–1055. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197305172882005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. M., Williams E. R., Barltrop D. Motor neurone disease and exposure to lead. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Dec;33(6):877–885. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.6.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardona E., Lessler M. A., Brierley G. P. Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation: interaction of lead and inorganic phosphate. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Jan;136(1):300–304. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll K. G., Spinelli F. R., Goyer R. A. Electron probe microanalyser localization of lead in kidney tissue of poisoned rats. Nature. 1970 Sep 5;227(5262):1056–1056. doi: 10.1038/2271056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisolm J. J., Jr Lead poisoning. Sci Am. 1971 Feb;224(2):15–23. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0271-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choie D. D., Richter G. W. Lead poisoning: rapid formation of intranuclear inclusions. Science. 1972 Sep 29;177(4055):1194–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4055.1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier R. D., Haerer A. F. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and metallic toxins. Arch Environ Health. 1968 Nov;17(5):712–719. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1968.10665310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer R. A., Krall R. Ultrastructural transformation in mitochondria isolated from kidneys of normal and lead-intoxicated rats. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):393–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer R. A. Lead toxicity: a problem in environmental pathology. Am J Pathol. 1971 Jul;64(1):167–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer R. A., Leonard D. L., Moore J. F., Rhyne B., Krigman M. R. Lead dosage and the role of the intranuclear inclusion body. An experimental study. Arch Environ Health. 1970 Jun;20(6):705–711. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1970.10665647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeger-Aronsen B. An assessment of the laboratory tests used to monitor the exposure of lead workers. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Jan;28(1):52–58. doi: 10.1136/oem.28.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEHOE R. A. NORMAL METABOLISM OF LEAD. Arch Environ Health. 1964 Feb;8:232–235. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1964.10663660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe D. E., Miller R. J. Lead effects on corn mitochondrial respiration. Science. 1970 Mar 6;167(3923):1376–1378. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3923.1376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELLORS R. C., CARROLL K. G. A new method for local chemical analysis of human tissue. Nature. 1961 Dec 16;192:1090–1092. doi: 10.1038/1921090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire M. S., Angle C. R. Air lead: relation to lead in blood of black school children deficient in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Science. 1972 Aug 11;177(4048):520–522. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4048.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON C. C. CONTAMINATED AND NATURAL LEAD ENVIRONMENTS OF MAN. Arch Environ Health. 1965 Sep;11:344–360. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1965.10664229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prerovská I., Teisinger J. Excretion of lead and its biological activity several years after termination of exposure. Br J Ind Med. 1970 Oct;27(4):352–355. doi: 10.1136/oem.27.4.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON J. A., SEATON D. A., ADAMS J. F. RESPONSE TO TREATMENT WITH CHELATING AGENTS OF ANAEMIA, CHRONIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, AND MYELOPATHY DUE TO LEAD POISONING. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1964 Dec;27:536–541. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.27.6.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. M., Zook B. C., Garner F. M. Demyelinating encephalomyelopathy associated with lead poisoning in nonhuman primates. Science. 1970 Sep 11;169(3950):1091–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3950.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman S. D., Joseph K. T., Raut S. J., Mulay C. D., Parameshwaran M., Panday V. K. Studies on major and trace element content in human tissues. Health Phys. 1970 Nov;19(5):641–656. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197011000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOUSIMIS A. J. SCANNING ELECTRON PROBE MICROANALYSIS OF BIOLOGICAL SPECIMENS. Biomed Sci Instrum. 1963;1:249–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P., Johnson R. T., Herndon R. M. Viral infections and demyelinating diseases. N Engl J Med. 1973 May 24;288(21):1103–1110. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197305242882106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M., Harvey D. R. Defective synthesis of and globin chains in lead poisoning. Nature. 1972 Mar 10;236(5341):71–73. doi: 10.1038/236071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]