Abstract
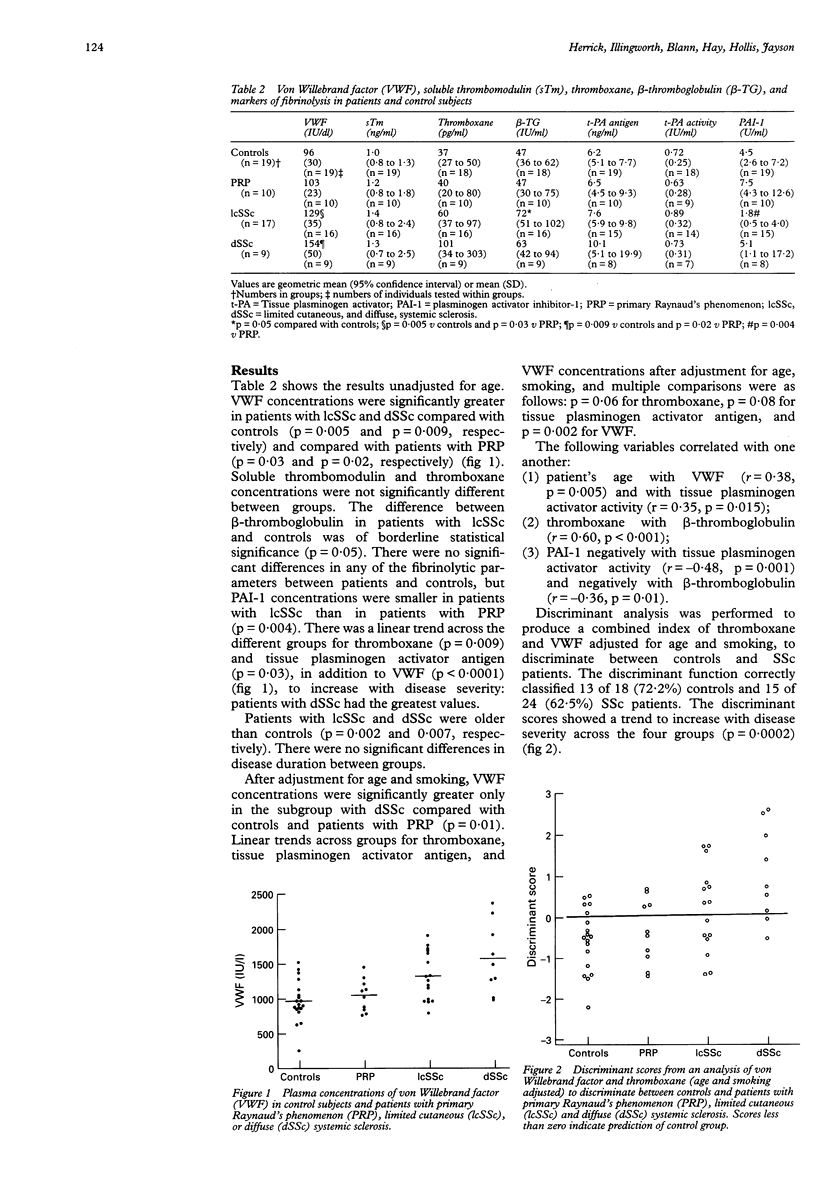
OBJECTIVE: To determine whether measurement of different markers of endothelial damage, activation of coagulation, and platelet activation might differentiate between patients with primary Raynaud's phenomenon (PRP), limited cutaneous and diffuse systemic sclerosis (lcSSc and dSSc), and healthy control subjects. METHODS: Under carefully controlled conditions, fasting blood was drawn from 19 healthy control subjects, 10 patients with PRP, 17 with lcSSc and nine with dSSc for measurement of the following: von Willebrand factor (VWF) and soluble thrombomodulin as markers of endothelial damage/activation, thromboxane (as thromboxane B2) and beta-thromboglobulin as markers of platelet activation, and tissue plasminogen activator antigen, tissue plasminogen activator activity and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) as markers of fibrinolysis. RESULTS: VWF was increased significantly in patients with SSc, and there was also a linear trend for thromboxane and tissue plasminogen activator antigen (in addition to VWF) to differentiate between different subgroups of patients with Raynaud's phenomenon. Patients with dSSc had the highest values. A combined index of VWF and thromboxane showed a highly significant trend across the four groups studied. CONCLUSION: VWF, and to a lesser extent thromboxane and tissue plasminogen activator antigen, are associated with disease severity in patients with Raynaud's phenomenon. Prospective studies are now required to establish if these parameters can be used as markers of disease progression.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann F., Kruithof I. E. Tissue plasminogen activator: chemical and physiological aspects. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Jan;10(1):6–17. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belch J. J., McArdle B. M., Burns P., Lowe G. D., Forbes C. D. The effects of acute smoking on platelet behaviour, fibrinolysis and haemorheology in habitual smokers. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Feb 28;51(1):6–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belch J. J., Zoma A. A., Richards I. M., McLaughlin K., Forbes C. D., Sturrock R. D. Vascular damage and factor-VIII-related antigen in the rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol Int. 1987;7(3):107–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00270462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blann A. D., Hopkins J., Winkles J., Wainwright A. C. Plasma and serum von Willebrand factor antigen concentrations in connective tissue disorders. Ann Clin Biochem. 1992 Jan;29(Pt 1):67–71. doi: 10.1177/000456329202900110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blann A. D., Illingworth K., Jayson M. I. Mechanisms of endothelial cell damage in systemic sclerosis and Raynaud's phenomenon. J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;20(8):1325–1330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blann A. D., McCollum C. N. Adverse influence of cigarette smoking on the endothelium. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Oct 18;70(4):707–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blann A. D. von Willebrand factor as a marker of injury to the endothelium in inflammatory vascular disease. J Rheumatol. 1993 Sep;20(9):1469–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. M., LeRoy E. C. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: a vascular hypothesis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May;4(4):351–368. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(75)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotevall A., Rångemark C., Eriksson E., Kutti J., Wadenvik H., Wennmalm A. Cigarette smoking increases thromboxane A2 formation without affecting platelet survival in young healthy females. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Nov 10;68(5):583–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. C., Endres-Brooks J., Bauer P. J., Marks W. J., Jr, Montgomery R. R. The effect of ABO blood group on the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1987 Jun;69(6):1691–1695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfield M. J., Orchard M. A., Rowell N. R. Whole blood platelet aggregation and coagulation factors in patients with systemic sclerosis. Br J Haematol. 1993 Aug;84(4):675–680. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1993.tb03145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Malia R. G., Milford Ward A., Moult J., Holt C. M., Lindsey N., Hughes P., Goodfield M., Rowell N. R. Elevated von Willebrand factor antigen in systemic sclerosis: relationship to visceral disease. Br J Rheumatol. 1988 Aug;27(4):281–285. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/27.4.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haire W. D., Goldsmith J. C., Rasmussen J. Abnormal fibrinolysis in healthy male cigarette smokers: role of plasminogen activator inhibitors. Am J Hematol. 1989 May;31(1):36–40. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830310107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton R. A., Mikhailidis D. P., Bernstein R. M., Jeremy J. Y., Hughes G. R., Dandona P. Assessment of platelet function in patients with Raynaud's syndrome. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Feb;37(2):182–187. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayson M. I. Systemic sclerosis: a collagen or microvascular disease? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Jun 23;288(6434):1855–1857. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6434.1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahaleh M. B., Osborn I., LeRoy E. C. Increased factor VIII/von Willebrand factor antigen and von Willebrand factor activity in scleroderma and in Raynaud's phenomenon. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Apr;94(4 Pt 1):482–484. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-4-482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahaleh M. B., Osborn I., Leroy E. C. Elevated levels of circulating platelet aggregates and beta-thromboglobulin in scleroderma. Ann Intern Med. 1982 May;96(5):610–613. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-5-610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahaleh M. B., Scharstein K. K., LeRoy E. C. Enhanced platelet adhesion to collagen in scleroderma. Effect of scleroderma plasma and scleroderma platelets. J Rheumatol. 1985 Jun;12(3):468–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C. S., McLaren M., Mackay I., Belch J. J. Baseline plasma fibrinolysis and its correlation with clinical manifestations in patients with Raynaud's phenomenon. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Jun;52(6):443–448. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.6.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Norman C. S., Sukenik S., Alderdice C. A. The clinical significance of coagulation abnormalities in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). J Rheumatol. 1985 Jun;12(3):514–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima J., Fonollosa V., Fernández-Cortijo J., Ordi J., Cuenca R., Khamashta M. A., Vilardell M., Simeón C. P., Picó M. Platelet activation, endothelial cell dysfunction in the absence of anticardiolipin antibodies in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 1991 Dec;18(12):1833–1836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Lombardi R., Lattuada A., Perticucci E., Valsecchi R., Remuzzi G. Supranormal von Willebrand factor multimers in scleroderma. Blood. 1989 May 1;73(6):1586–1591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasini B., Cugno M., Bassani C., Stanzani M., Bottasso B., Agostoni A. Tissue-type plasminogen activator and von Willebrand factor plasma levels as markers of endothelial involvement in patients with Raynaud's phenomenon. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1992 Nov;11(4):375–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matucci-Cerinic M., Pignone A., Lotti T., Spillantini G., Curradi C., Leoncini G., Iannone F., Falcini F., Cagnoni M. Reduced angiotensin converting enzyme plasma activity in scleroderma. A marker of endothelial injury? J Rheumatol. 1990 Mar;17(3):328–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohdama S., Takano S., Miyake S., Kubota T., Sato K., Aoki N. Plasma thrombomodulin as a marker of vascular injuries in collagen vascular diseases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 Jan;101(1):109–113. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/101.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly I. A., Roy L., Fitzgerald G. A. Biosynthesis of thromboxane in patients with systemic sclerosis and Raynaud's phenomenon. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Apr 19;292(6527):1037–1039. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6527.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soma Y., Takehara K., Sato S., Ishibashi Y. Increase in plasma thrombomodulin in patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;20(8):1444–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


