Abstract
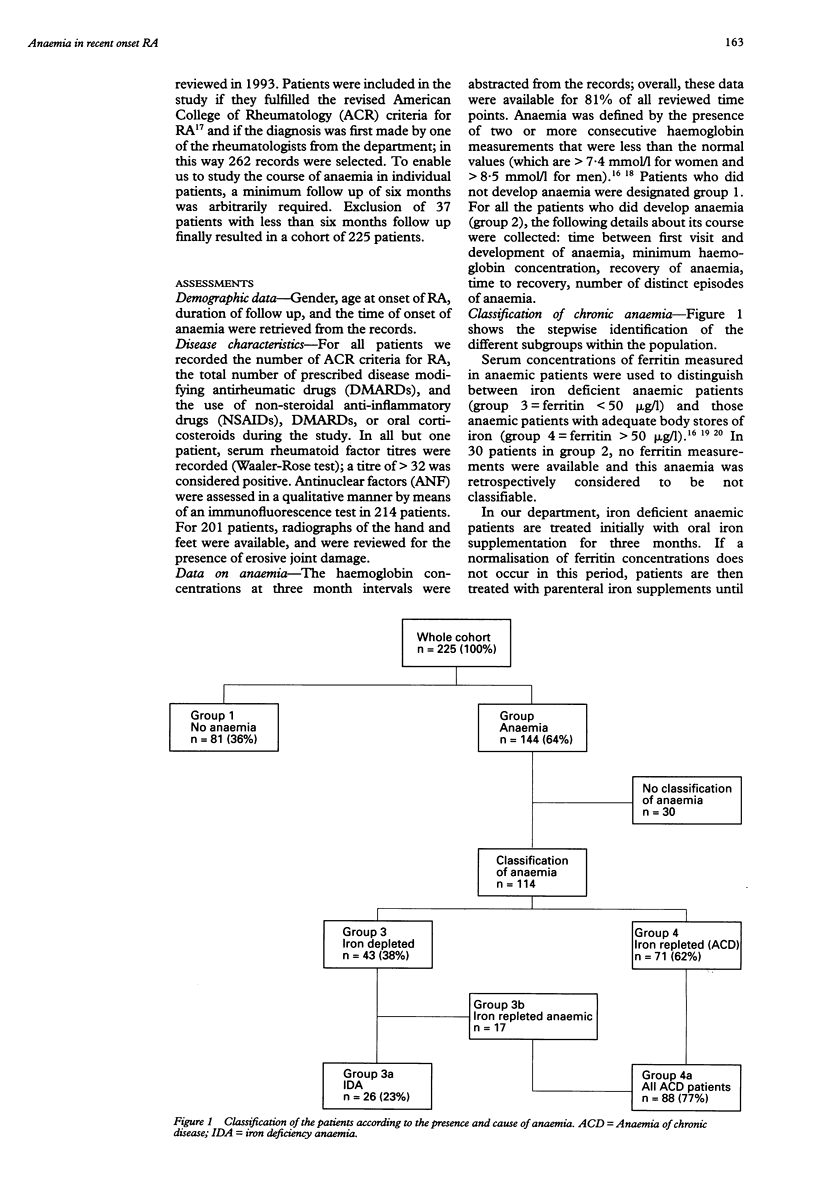
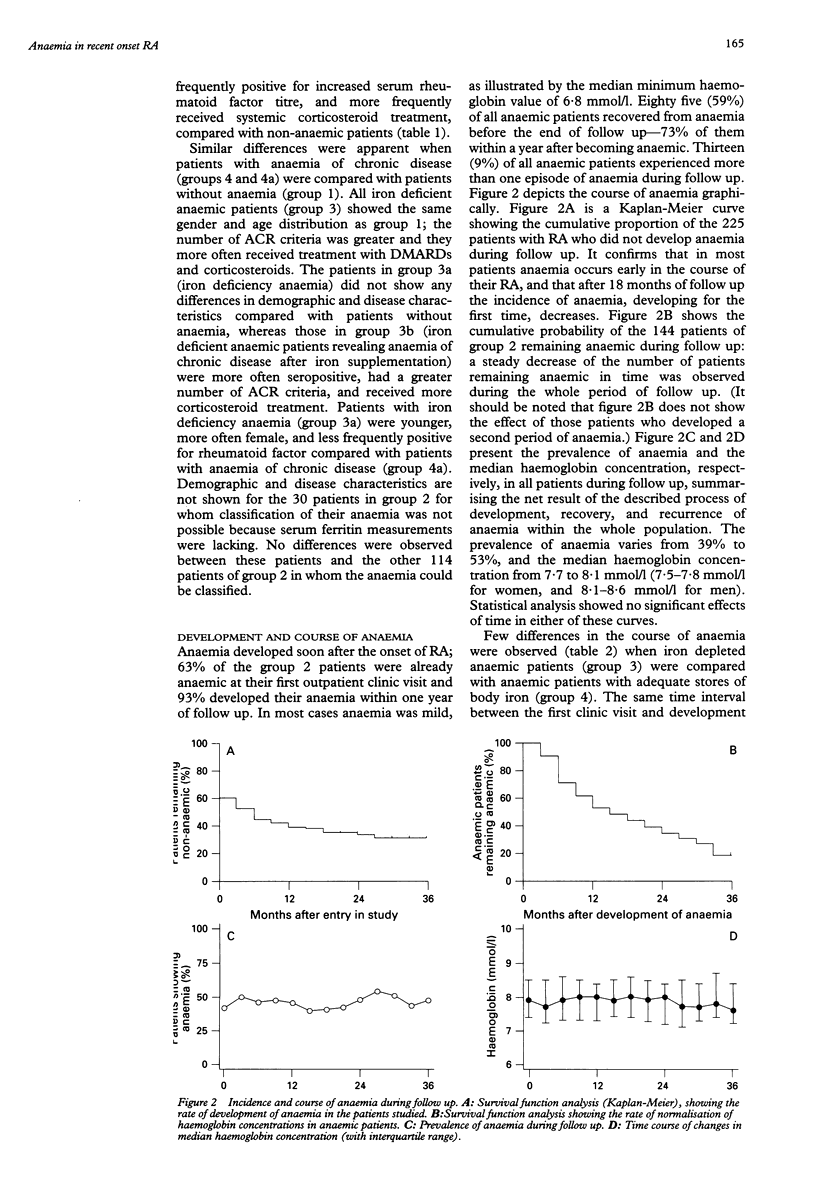
OBJECTIVE: To describe the incidence, cause, and course of anaemia in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). METHODS: Medical records of 225 patients who received a diagnosis of RA between 1990 and 1992 were reviewed longitudinally for mention of anaemia. Anaemia was classified as anaemia of chronic disease if ferritin concentrations reflected adequate body iron stores. Among iron depleted anaemic patients, iron deficiency anaemia was identified using the response to iron supplementation. RESULTS: Anaemia developed in 64% of the patients, mostly within 18 months of follow up, but disappeared again in 54% of those patients. The prevalence of anaemia varied from 39% to 53% throughout follow up. Iron depletion was found in 38% of anaemic patients; 40% of them did not recover from their anaemia after iron supplementation and were classified as having anaemia of chronic disease. Anaemia of chronic disease thus caused 77% and iron deficiency anaemia 23% of observed anaemia. Recovery from anaemia occurred in 42% of the patients with anaemia of chronic disease and in 72% of iron depleted patients after iron supplementation. Anaemic patients, particularly those with anaemia of chronic disease, had a significantly greater number of the American College of Rheumatism criteria for RA, significantly more erosive joint damage, and significantly increased concentrations of serum rheumatoid factor than patients without anaemia. CONCLUSION: Anaemia appeared as a frequent and dynamic manifestation. Recovery and recurrence of anaemia was observed throughout follow up, leading to a longstanding and relatively high prevalence of the condition. Iron deficiency was diagnosed frequently and follow up revealed a considerable overlap with anaemia of chronic disease, making this the most important cause of anaemia in RA. Recovery from anaemia occurred more frequently in iron depleted anaemic patients than in those with anaemia of chronic disease. Anaemic patients, particularly those with anaemia of chronic disease, seemed to have a more serious course of their RA compared with non-anaemic patients.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer A. N., Dessypris E. N., Krantz S. B. The pathogenesis of anemia in rheumatoid arthritis: a clinical and laboratory analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Feb;19(4):209–223. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(90)90001-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgegård G., Hällgren R., Caro J. Serum erythropoietin in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory arthritides: relationship to anaemia and the effect of anti-inflammatory treatment. Br J Haematol. 1987 Apr;65(4):479–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb04154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake D. R., Waterworth R. F., Bacon P. A. Assessment of iron stores in inflammation by assay of serum ferritin concentrations. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Oct 31;283(6300):1147–1148. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6300.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. D. Clinical evaluation of iron deficiency. Semin Hematol. 1982 Jan;19(1):6–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. D., Skikne B. S., Lynch S. R., Reusser M. E. Estimates of iron sufficiency in the US population. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):726–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen N. E. The anaemia of chronic disorders. A bag of unsolved questions. Scand J Haematol. 1983 Nov;31(5):397–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1983.tb01532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. M., Hansen N. E. Serum ferritin as indicator of iron responsive anaemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Jul;45(7):596–602. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.7.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent S., Weinberg E. D., Stuart-Macadam P. The etiology of the anemia of chronic disease and infection. J Clin Epidemiol. 1994 Jan;47(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(94)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz S. B. Pathogenesis and treatment of the anemia of chronic disease. Am J Med Sci. 1994 May;307(5):353–359. doi: 10.1097/00000441-199405000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. R. The anemia of chronic disease. Semin Hematol. 1983 Apr;20(2):61–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means R. T., Jr, Krantz S. B. Progress in understanding the pathogenesis of the anemia of chronic disease. Blood. 1992 Oct 1;80(7):1639–1647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman N., Kirchhoff M. Iron stores in 1359, 30- to 60-year-old Danish women: evaluation by serum ferritin and hemoglobin. Ann Hematol. 1992 Jan;64(1):22–27. doi: 10.1007/BF01811467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen O. J., Andersen L. S., Ludwigsen E., Bouchelouche P., Hansen T. M., Birgens H., Hansen N. E. Anaemia of rheumatoid arthritis: serum erythropoietin concentrations and red cell distribution width in relation to iron status. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Jun;49(6):349–353. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.6.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. R., Sturrock R. D., Capell H. A. The use of serum ferritin estimation in the investigation of anaemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1994 Mar-Apr;12(2):179–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remacha A. F., Rodríguez-de la Serna A., García-Dié F., Geli C., Díaz C., Gimferrer E. Erythroid abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of erythropoietin. J Rheumatol. 1992 Nov;19(11):1687–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybo E., Bengtsson C., Hallberg L. Iron status of 38-year-old women in Gothenburg, Sweden. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1985;43:41–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1985.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Davis P., Thomson A. B., Wadsworth L. D., Fackre P. Serum ferritin levels in anemia of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1977 Winter;4(4):389–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibblin E., Bengtsson C., Hallberg L., Lennartsson J. Haemoglobin concentration and peripheral blood cell counts in women. The population study of women in Göteborg 1968-1969. Scand J Haematol. 1979 Jan;22(1):5–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1979.tb00394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreugdenhil G., Baltus C. A., van Eijk H. G., Swaak A. J. Anaemia of chronic disease: diagnostic significance of erythrocyte and serological parameters in iron deficient rheumatoid arthritis patients. Br J Rheumatol. 1990 Apr;29(2):105–110. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/29.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreugdenhil G., Baltus J. A., van Eijk H. G., Swaak A. J. Prediction and evaluation of the effect of iron treatment in anaemic RA patients. Clin Rheumatol. 1989 Sep;8(3):352–362. doi: 10.1007/BF02030348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreugdenhil G., Kroos M. J., van Eijk H. G., Löwenberg B., Swaak A. J. Impaired iron uptake and transferrin binding by erythroblasts in the anaemia of rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1990 Oct;29(5):335–339. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/29.5.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreugdenhil G., Löwenberg B., Van Eijk H. G., Swaak A. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha is associated with disease activity and the degree of anemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;22(7):488–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1992.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreugdenhil G., Wognum A. W., van Eijk H. G., Swaak A. J. Anaemia in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid deficiency, and erythropoietin responsiveness. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Feb;49(2):93–98. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.2.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Werre J. M., Julius H. W., Marx J. J. Decreased iron absorption in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis, with and without iron deficiency. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 May;47(5):404–409. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.5.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoli A., Altomonte L., Mirone L., Magaró M., Ricerca B. M., Storti S., Candido A., Bizzi M. Serum transferrin receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Oct;53(10):699–701. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.10.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


